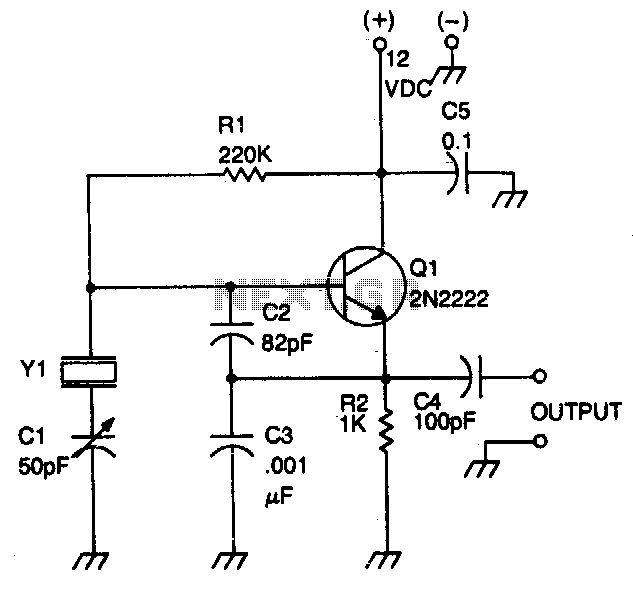
Two-Transistor Sine-Wave Oscillator
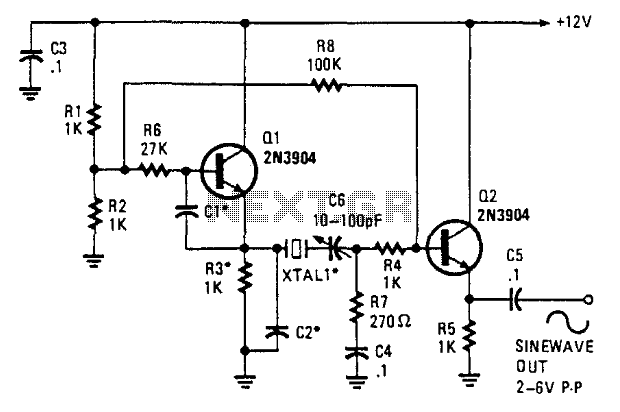
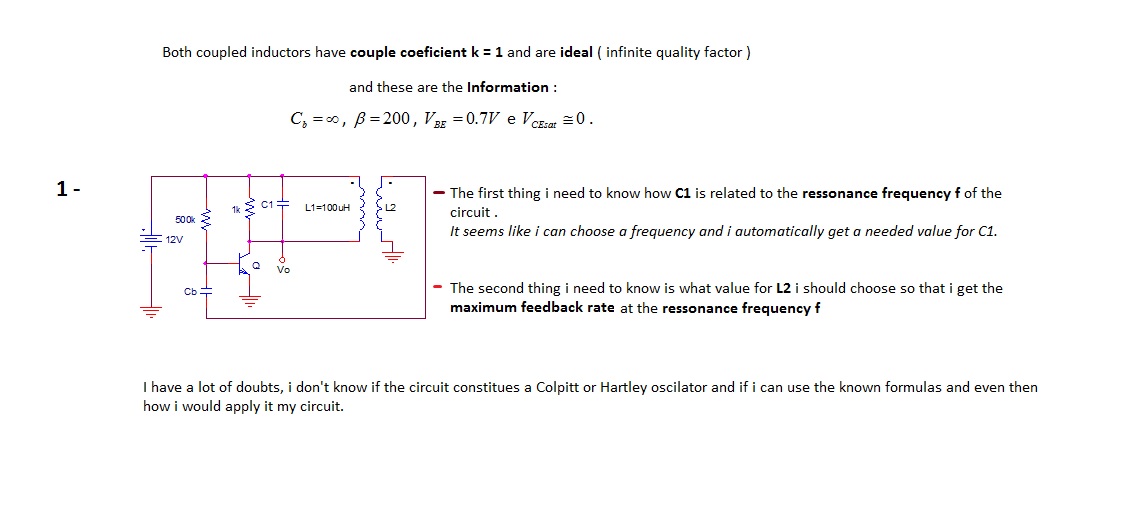
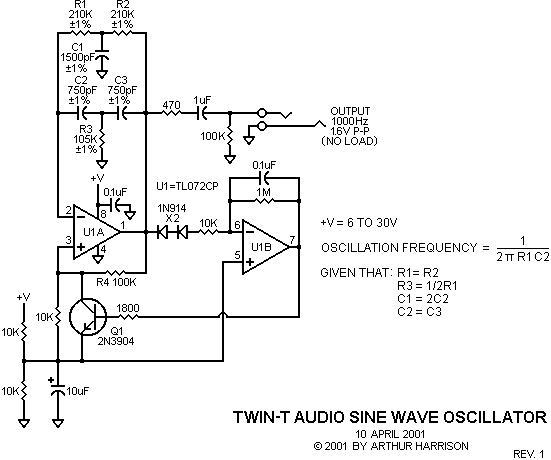
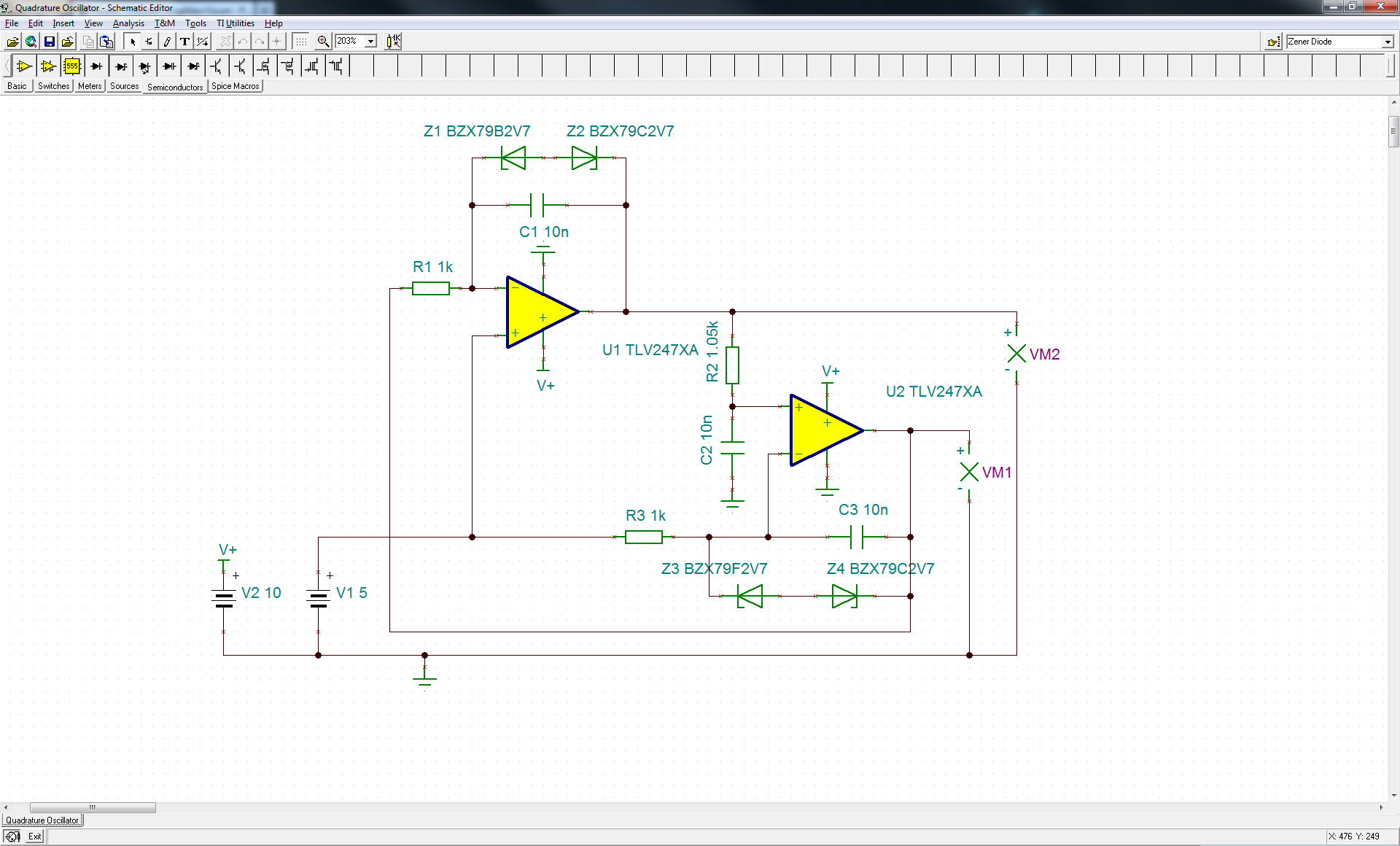
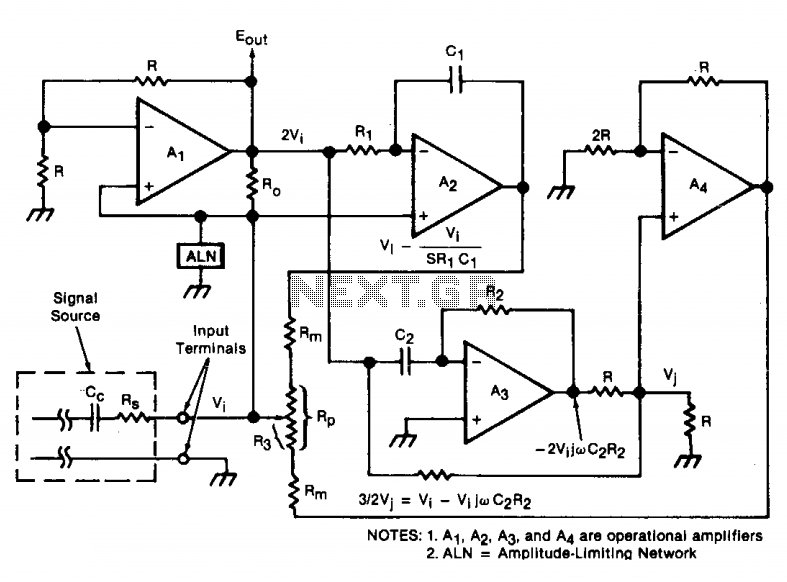
This oscillator employs two transistors and operates the crystal in its fundamental mode. Capacitors CT and C2 should be approximately 2,700 pF for 1 MHz, 680 pF for 5 MHz, and 330 pF for 10 MHz. A capacitance of 150 pF can be utilized for frequencies up to 20 MHz. The output produced is a near-perfect sine wave. It is recommended to vary Ci and C2 to achieve the best waveform. An output voltage of approximately 2 to 6 Vpp is available.
The described oscillator circuit is designed to generate stable sine wave signals using a two-transistor configuration. The fundamental mode operation of the crystal ensures that the oscillator is tuned to the desired frequency with high precision. The choice of capacitors CT and C2 is critical for frequency selection and stability; their values must be adjusted according to the target frequency as outlined.
For a frequency of 1 MHz, a capacitance of 2,700 pF is recommended, which helps to set the oscillation frequency by creating a resonant circuit with the crystal. At 5 MHz, the capacitance should be reduced to 680 pF, and for 10 MHz, 330 pF is appropriate. For applications requiring frequencies up to 20 MHz, a minimum capacitance of 150 pF is suggested. This systematic adjustment of the capacitors allows for fine-tuning of the oscillator frequency and ensures optimal performance.
The output of the oscillator is characterized by a near-perfect sine wave, making it suitable for various applications where signal purity is essential, such as in audio or RF applications. The output voltage range of 2 to 6 Vpp indicates that the circuit can provide sufficient signal level for driving subsequent stages in a circuit.
To achieve the best waveform quality, it is advisable to experiment with the values of capacitors Ci and C2. By carefully varying these capacitances, one can minimize distortion and improve the overall signal integrity. This adaptability is crucial in practical applications where different load conditions or circuit configurations may affect the oscillator's performance.
In summary, this oscillator circuit provides a versatile solution for generating sine wave signals across a range of frequencies, with specific attention to component values that dictate its operational characteristics. The careful selection of capacitors and the ability to adjust them for optimal performance are key aspects of this design. This oscillator uses two transistors and operates the crystal in the fundamental mode. CT and C2 should be about 2 700 pF for 1 MHz, 680 pF for 5 MHz, and 330 pF for 10 MHz. 150 pF can be used for up to 20 MHz. The output is a near perfect sine wave. Try varying Ci and C2 for best waveform. About 2 to 6 Vpp is available.
The described oscillator circuit is designed to generate stable sine wave signals using a two-transistor configuration. The fundamental mode operation of the crystal ensures that the oscillator is tuned to the desired frequency with high precision. The choice of capacitors CT and C2 is critical for frequency selection and stability; their values must be adjusted according to the target frequency as outlined.
For a frequency of 1 MHz, a capacitance of 2,700 pF is recommended, which helps to set the oscillation frequency by creating a resonant circuit with the crystal. At 5 MHz, the capacitance should be reduced to 680 pF, and for 10 MHz, 330 pF is appropriate. For applications requiring frequencies up to 20 MHz, a minimum capacitance of 150 pF is suggested. This systematic adjustment of the capacitors allows for fine-tuning of the oscillator frequency and ensures optimal performance.
The output of the oscillator is characterized by a near-perfect sine wave, making it suitable for various applications where signal purity is essential, such as in audio or RF applications. The output voltage range of 2 to 6 Vpp indicates that the circuit can provide sufficient signal level for driving subsequent stages in a circuit.
To achieve the best waveform quality, it is advisable to experiment with the values of capacitors Ci and C2. By carefully varying these capacitances, one can minimize distortion and improve the overall signal integrity. This adaptability is crucial in practical applications where different load conditions or circuit configurations may affect the oscillator's performance.
In summary, this oscillator circuit provides a versatile solution for generating sine wave signals across a range of frequencies, with specific attention to component values that dictate its operational characteristics. The careful selection of capacitors and the ability to adjust them for optimal performance are key aspects of this design. This oscillator uses two transistors and operates the crystal in the fundamental mode. CT and C2 should be about 2 700 pF for 1 MHz, 680 pF for 5 MHz, and 330 pF for 10 MHz. 150 pF can be used for up to 20 MHz. The output is a near perfect sine wave. Try varying Ci and C2 for best waveform. About 2 to 6 Vpp is available.