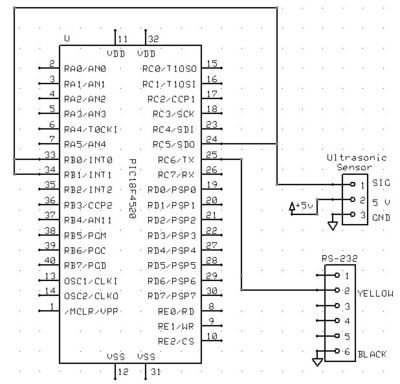
Ultrasonic Radar AlarmCircuit Project
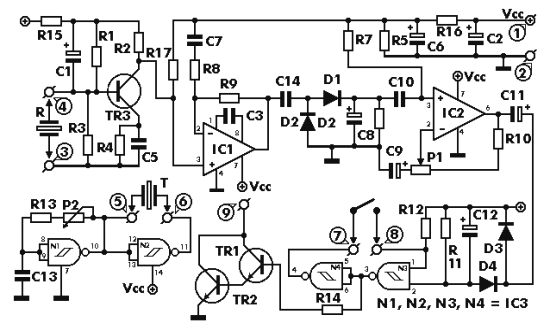
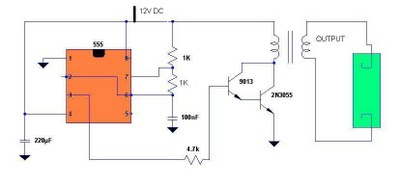
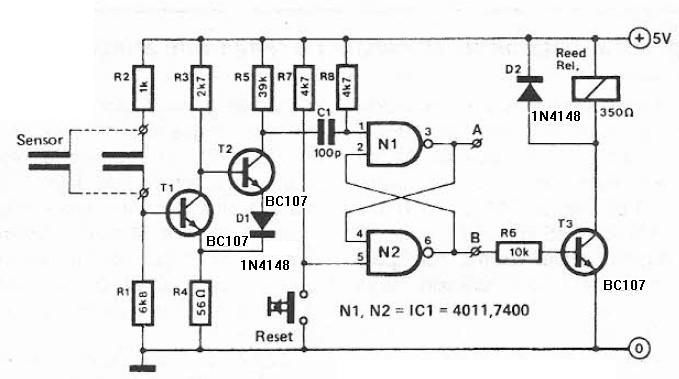
The circuit consists of an ultrasonic transmitter and a receiver that operate at the same frequency. Ultrasonic piezoelectric transducers serve as the output and input devices, respectively, with their frequency of operation determined by the specific devices used. The transmitter utilizes two NAND gates from IC3, configured as inverters, forming a multivibrator that drives the transducer. A trimmer, P2, adjusts the output frequency of the transmitter, which should match the resonance frequency of the transducers for optimal efficiency. The receiver employs a transducer to capture reflected signals, which are amplified by transistor TR3 and operational amplifier IC1 (741). The output from IC1 feeds into the non-inverting input of IC2, with the amplification factor adjustable via P1. The circuit remains balanced as long as the transmitter's output frequency remains unchanged. If movement occurs within the ultrasonic emission's coverage area, the reflected signal is distorted, causing the circuit to become unbalanced. This results in a sudden change in IC2's output, triggering the Schmitt trigger circuit built around the remaining two gates in IC3. This action activates output transistors TR1 and TR2, which can signal an alarm system or activate a relay connected in series with TR1's collector. The circuit operates on a voltage range of 9-12 VDC and can be powered by batteries or an external power supply.
When constructing electronic circuits on a printed circuit board (PCB), the board is typically made from a thin insulating material coated with a layer of conductive copper, which forms the necessary connections between components. A well-designed PCB is advantageous as it accelerates construction and minimizes errors. Smart Kit boards come pre-drilled with component outlines and identifications printed on the component side to facilitate assembly. To protect the PCB from oxidation during storage and ensure it arrives in optimal condition, the copper is tinned during manufacturing and coated with a special varnish that prevents oxidation and simplifies soldering.
Soldering components to the board is essential for circuit assembly, and the technique employed significantly impacts the success of the project. A lightweight soldering iron, with a maximum power of 25 Watts and a fine tip, is recommended. It is crucial to maintain a clean tip, which can be achieved using specially designed damp sponges to remove residue. Avoid filing or sanding a dirty or worn tip; if cleaning is ineffective, replace the tip. Selecting high-quality solder that contains the necessary flux in its core is important for creating reliable joints. Using additional soldering flux not included in the solder can lead to circuit malfunctions; if extra flux is necessary, it should be thoroughly cleaned after use.
To solder a component correctly, the following procedure should be followed: the hot iron's tip should be placed on the component lead while the end of the solder wire is held at the joint, allowing for proper melting and bonding of the materials.As it has already been stated the circuit consists of an ultrasonic transmitter and a receiver both of which work at the same frequency. They use ultrasonic piezoelectric transducers as output and input devices respectively and their frequency of operation is determined by the particular devices in use.
The transmitter is built around two NAND gat es of the four found in IC3 which are used here wired as inverters and in the particular circuit they form a multivibrator the output of which drives the transducer. The trimmer P2 adjusts the output frequency of the transmitter and for greater efficiency it should be made the same as the frequency of resonance of the transducers in use.
The receiver similarly uses a transducer to receive the signals that are reflected back to it the output of which is amplified by the transistor TR3, and IC1 which is a 741 op-amp. The output of IC1 is taken to the non inverting input of IC2 the amplification factor of which is adjusted by means of P1.
The circuit is adjusted in such a way as to stay in balance as long the same as the output frequency of the transmitter. If there is some movement in the area covered by the ultrasonic emission the signal that is reflected back to the receiver becomes distorted and the circuit is thrown out of balance.
The output of IC2 changes abruptly and the Schmitt trigger circuit which is built around the remaining two gates in IC3 is triggered. This drives the output transistors TR1, 2 which in turn give a signal to the alarm system or if there is a relay connected to the circuit, in series with the collector of TR1, it becomes activated.
The circuit works from 9-12 VDC and can be used with batteries or a power supply. First of all let us consider a few basics in building electronic circuits on a printed circuit board. The board is made of a thin insulating material clad with a thin layer of conductive copper that is shaped in such a way as to form the necessary conductors between the various components of the circuit.
The use of a properly designed printed circuit board is very desirable as it speeds construction up considerably and reduces the possibility of making errors. Smart Kit boards also come pre-drilled and with the outline of the components and their identification printed on the component side to make construction easier.
To protect the board during storage from oxidation and assure it gets to you in perfect condition the copper is tinned during manufacturing and covered with a special varnish that protects it from getting oxidised and also makes soldering easier. Soldering the components to the board is the only way to build your circuit and from the way you do it depends greatly your success or failure.
This work is not very difficult and if you stick to a few rules you should have no problems. The soldering iron that you use must be light and its power should not exceed the 25 Watts. The tip should be fine and must be kept clean at all times. For this purpose come very handy specially made sponges that are kept wet and from time to time you can wipe the hot tip on them to remove all the residues that tend to accumulate on it. DO NOT file or sandpaper a dirty or worn out tip. If the tip cannot be cleaned, replace it. There are many different types of solder in the market and you should choose a good quality one that contains the necessary flux in its core, to assure a perfect joint every time.
DO NOT use soldering flux apart from that which is already included in your solder. Too much flux can cause many problems and is one of the main causes of circuit malfunction. If nevertheless you have to use extra flux, as it is the case when you have to tin copper wires, clean it very thoroughly after you finish your work. In order to solder a component correctly you should do the following: @Take the hot iron and place its tip on the component lead while holding the end of the solder wire at the
🔗 External reference
When constructing electronic circuits on a printed circuit board (PCB), the board is typically made from a thin insulating material coated with a layer of conductive copper, which forms the necessary connections between components. A well-designed PCB is advantageous as it accelerates construction and minimizes errors. Smart Kit boards come pre-drilled with component outlines and identifications printed on the component side to facilitate assembly. To protect the PCB from oxidation during storage and ensure it arrives in optimal condition, the copper is tinned during manufacturing and coated with a special varnish that prevents oxidation and simplifies soldering.
Soldering components to the board is essential for circuit assembly, and the technique employed significantly impacts the success of the project. A lightweight soldering iron, with a maximum power of 25 Watts and a fine tip, is recommended. It is crucial to maintain a clean tip, which can be achieved using specially designed damp sponges to remove residue. Avoid filing or sanding a dirty or worn tip; if cleaning is ineffective, replace the tip. Selecting high-quality solder that contains the necessary flux in its core is important for creating reliable joints. Using additional soldering flux not included in the solder can lead to circuit malfunctions; if extra flux is necessary, it should be thoroughly cleaned after use.
To solder a component correctly, the following procedure should be followed: the hot iron's tip should be placed on the component lead while the end of the solder wire is held at the joint, allowing for proper melting and bonding of the materials.As it has already been stated the circuit consists of an ultrasonic transmitter and a receiver both of which work at the same frequency. They use ultrasonic piezoelectric transducers as output and input devices respectively and their frequency of operation is determined by the particular devices in use.
The transmitter is built around two NAND gat es of the four found in IC3 which are used here wired as inverters and in the particular circuit they form a multivibrator the output of which drives the transducer. The trimmer P2 adjusts the output frequency of the transmitter and for greater efficiency it should be made the same as the frequency of resonance of the transducers in use.
The receiver similarly uses a transducer to receive the signals that are reflected back to it the output of which is amplified by the transistor TR3, and IC1 which is a 741 op-amp. The output of IC1 is taken to the non inverting input of IC2 the amplification factor of which is adjusted by means of P1.
The circuit is adjusted in such a way as to stay in balance as long the same as the output frequency of the transmitter. If there is some movement in the area covered by the ultrasonic emission the signal that is reflected back to the receiver becomes distorted and the circuit is thrown out of balance.
The output of IC2 changes abruptly and the Schmitt trigger circuit which is built around the remaining two gates in IC3 is triggered. This drives the output transistors TR1, 2 which in turn give a signal to the alarm system or if there is a relay connected to the circuit, in series with the collector of TR1, it becomes activated.
The circuit works from 9-12 VDC and can be used with batteries or a power supply. First of all let us consider a few basics in building electronic circuits on a printed circuit board. The board is made of a thin insulating material clad with a thin layer of conductive copper that is shaped in such a way as to form the necessary conductors between the various components of the circuit.
The use of a properly designed printed circuit board is very desirable as it speeds construction up considerably and reduces the possibility of making errors. Smart Kit boards also come pre-drilled and with the outline of the components and their identification printed on the component side to make construction easier.
To protect the board during storage from oxidation and assure it gets to you in perfect condition the copper is tinned during manufacturing and covered with a special varnish that protects it from getting oxidised and also makes soldering easier. Soldering the components to the board is the only way to build your circuit and from the way you do it depends greatly your success or failure.
This work is not very difficult and if you stick to a few rules you should have no problems. The soldering iron that you use must be light and its power should not exceed the 25 Watts. The tip should be fine and must be kept clean at all times. For this purpose come very handy specially made sponges that are kept wet and from time to time you can wipe the hot tip on them to remove all the residues that tend to accumulate on it. DO NOT file or sandpaper a dirty or worn out tip. If the tip cannot be cleaned, replace it. There are many different types of solder in the market and you should choose a good quality one that contains the necessary flux in its core, to assure a perfect joint every time.
DO NOT use soldering flux apart from that which is already included in your solder. Too much flux can cause many problems and is one of the main causes of circuit malfunction. If nevertheless you have to use extra flux, as it is the case when you have to tin copper wires, clean it very thoroughly after you finish your work. In order to solder a component correctly you should do the following: @Take the hot iron and place its tip on the component lead while holding the end of the solder wire at the
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713