Variable Frequency Sinewave Generator
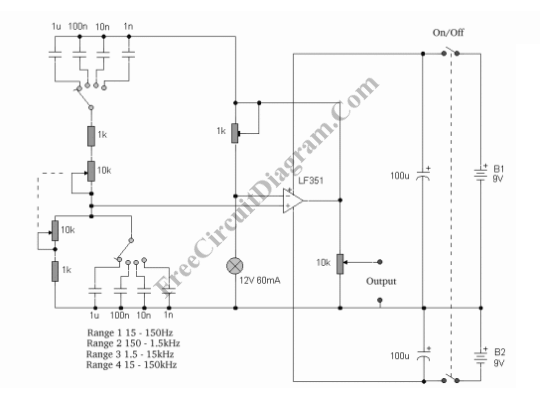
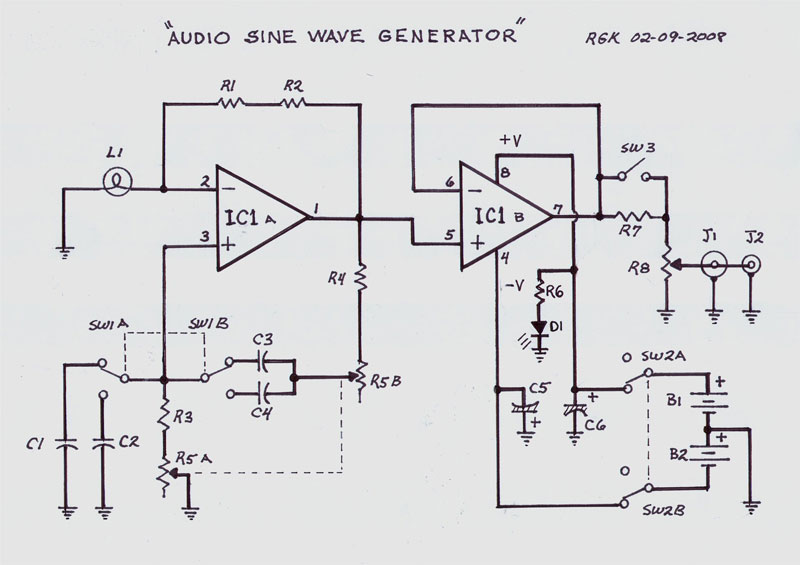
This sine wave generator is adjustable between 15 Hz and 150 kHz. The circuit is essentially a Wien-bridge oscillator, featuring multiple capacitor selections.
The sine wave generator operates on the principle of the Wien-bridge oscillator, which is known for producing low-distortion sine waves. The frequency range of 15 Hz to 150 kHz allows for versatile applications, including audio signal generation and testing of audio equipment.
The circuit design incorporates resistors and capacitors that form a bridge configuration, allowing for frequency adjustments by selecting different capacitors. The Wien-bridge oscillator typically includes a variable resistor that aids in stabilizing the amplitude of the output signal, ensuring consistent waveform characteristics.
In this particular design, the oscillator can be fine-tuned to achieve the desired frequency by adjusting the capacitor selection. The multiple capacitor options provide flexibility, enabling the user to select the appropriate value for the application at hand. The output can be taken from the oscillator's output node, which provides a clean sine wave signal suitable for various uses.
Power supply considerations should also be addressed, as the circuit typically requires a dual power supply to maintain proper operation across the frequency range. Additionally, incorporating a buffer amplifier at the output can improve the drive capability of the sine wave signal, allowing it to interface effectively with other circuit components or systems.
Overall, this sine wave generator circuit is an essential tool in electronic testing and signal processing, offering adjustable frequency output with low distortion characteristics, thanks to its Wien-bridge oscillator configuration.This sine wave generator is adjustable between 15 Hz to 150 kHz. The circuit is basically a Wien-bridge oscillator, with multiple capacitor selection. Here is. 🔗 External reference
The sine wave generator operates on the principle of the Wien-bridge oscillator, which is known for producing low-distortion sine waves. The frequency range of 15 Hz to 150 kHz allows for versatile applications, including audio signal generation and testing of audio equipment.
The circuit design incorporates resistors and capacitors that form a bridge configuration, allowing for frequency adjustments by selecting different capacitors. The Wien-bridge oscillator typically includes a variable resistor that aids in stabilizing the amplitude of the output signal, ensuring consistent waveform characteristics.
In this particular design, the oscillator can be fine-tuned to achieve the desired frequency by adjusting the capacitor selection. The multiple capacitor options provide flexibility, enabling the user to select the appropriate value for the application at hand. The output can be taken from the oscillator's output node, which provides a clean sine wave signal suitable for various uses.
Power supply considerations should also be addressed, as the circuit typically requires a dual power supply to maintain proper operation across the frequency range. Additionally, incorporating a buffer amplifier at the output can improve the drive capability of the sine wave signal, allowing it to interface effectively with other circuit components or systems.
Overall, this sine wave generator circuit is an essential tool in electronic testing and signal processing, offering adjustable frequency output with low distortion characteristics, thanks to its Wien-bridge oscillator configuration.This sine wave generator is adjustable between 15 Hz to 150 kHz. The circuit is basically a Wien-bridge oscillator, with multiple capacitor selection. Here is. 🔗 External reference