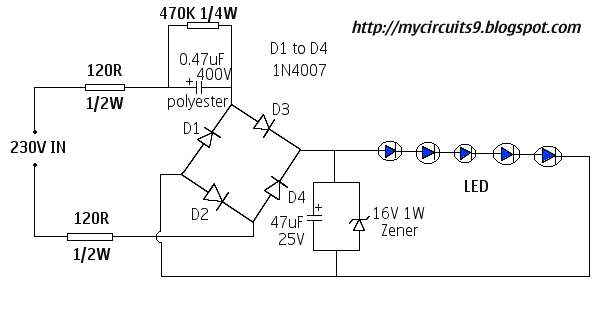
Video Line Driver
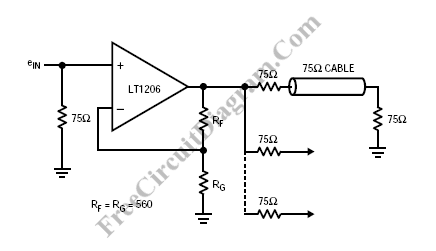
The LT1206 is designed to drive multiple video cables, featuring a bandwidth of 60 MHz, an output current capability of 250 mA, and low output impedance.
The LT1206 operational amplifier is optimized for video signal applications, making it an excellent choice for driving multiple video cables in various electronic systems. Its 60 MHz bandwidth allows it to effectively handle high-frequency signals, ensuring minimal signal degradation over long cable runs. The capability to provide up to 250 mA of output current makes the LT1206 suitable for driving loads with varying impedance, which is particularly important in video applications where signal integrity is critical.
The low output impedance of the LT1206 contributes to its ability to drive multiple cables while maintaining signal quality. This characteristic reduces the voltage drop across the output stage when connected to capacitive loads, thus preserving the integrity of the transmitted video signal. Furthermore, the LT1206's design incorporates features that minimize distortion and noise, which are essential for high-fidelity video transmission.
In practical applications, the LT1206 can be configured in various circuit topologies, including inverting and non-inverting amplifier configurations, as well as voltage follower setups. These configurations allow for flexibility in circuit design, enabling engineers to tailor the amplifier's response to specific system requirements. The device can be integrated into video distribution amplifiers, signal processing units, and other video-related electronic equipment, providing robust performance in demanding environments.
Overall, the LT1206's combination of high bandwidth, substantial output current capability, and low output impedance makes it a highly effective solution for driving multiple video cables in a wide range of electronic applications.LT1206 is suitable for driving multiple video cables since it has 60MHz bandwidth, 250mA output current capability, and low output impedance. Please keep in. 🔗 External reference
The LT1206 operational amplifier is optimized for video signal applications, making it an excellent choice for driving multiple video cables in various electronic systems. Its 60 MHz bandwidth allows it to effectively handle high-frequency signals, ensuring minimal signal degradation over long cable runs. The capability to provide up to 250 mA of output current makes the LT1206 suitable for driving loads with varying impedance, which is particularly important in video applications where signal integrity is critical.
The low output impedance of the LT1206 contributes to its ability to drive multiple cables while maintaining signal quality. This characteristic reduces the voltage drop across the output stage when connected to capacitive loads, thus preserving the integrity of the transmitted video signal. Furthermore, the LT1206's design incorporates features that minimize distortion and noise, which are essential for high-fidelity video transmission.
In practical applications, the LT1206 can be configured in various circuit topologies, including inverting and non-inverting amplifier configurations, as well as voltage follower setups. These configurations allow for flexibility in circuit design, enabling engineers to tailor the amplifier's response to specific system requirements. The device can be integrated into video distribution amplifiers, signal processing units, and other video-related electronic equipment, providing robust performance in demanding environments.
Overall, the LT1206's combination of high bandwidth, substantial output current capability, and low output impedance makes it a highly effective solution for driving multiple video cables in a wide range of electronic applications.LT1206 is suitable for driving multiple video cables since it has 60MHz bandwidth, 250mA output current capability, and low output impedance. Please keep in. 🔗 External reference