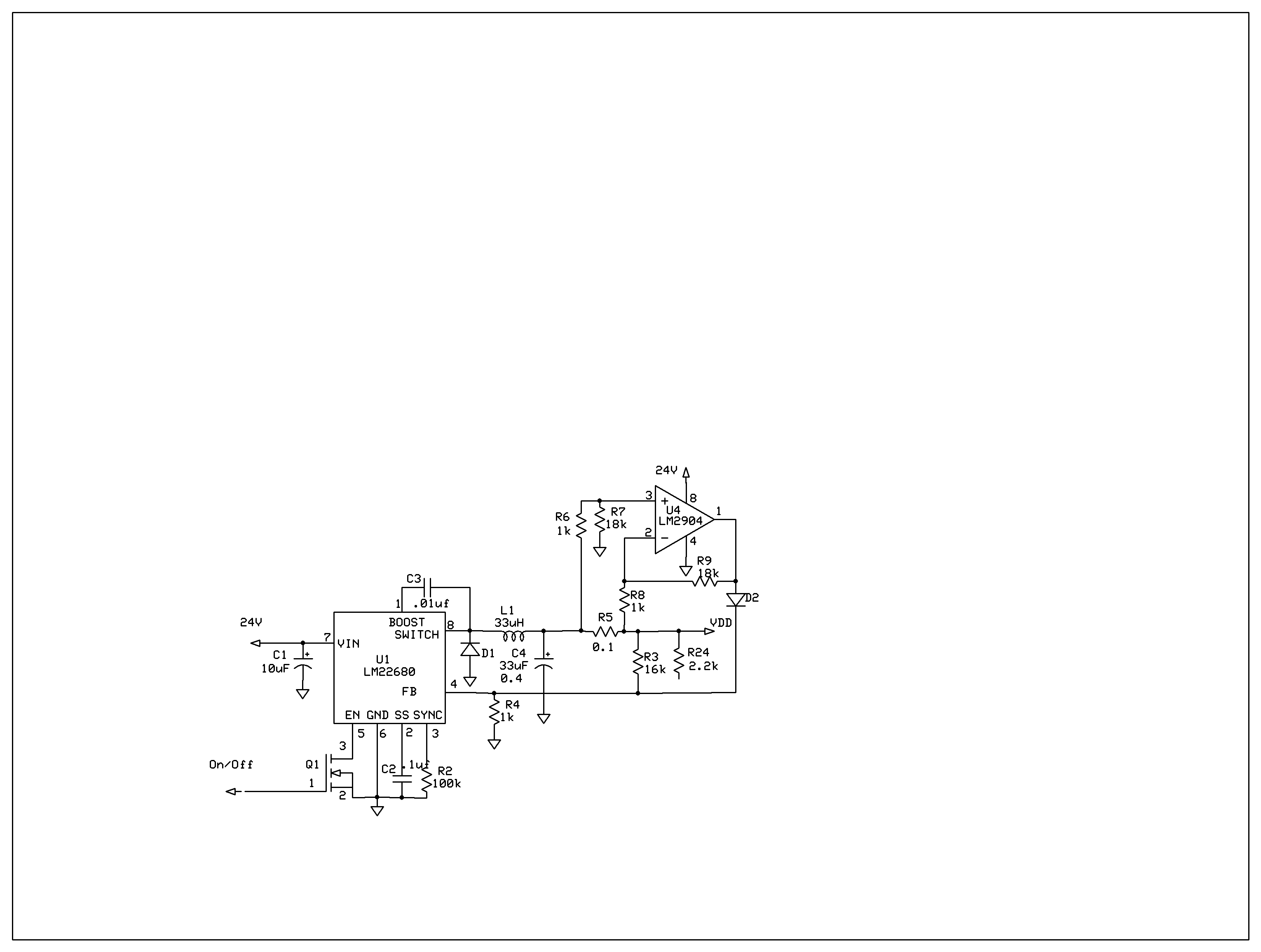
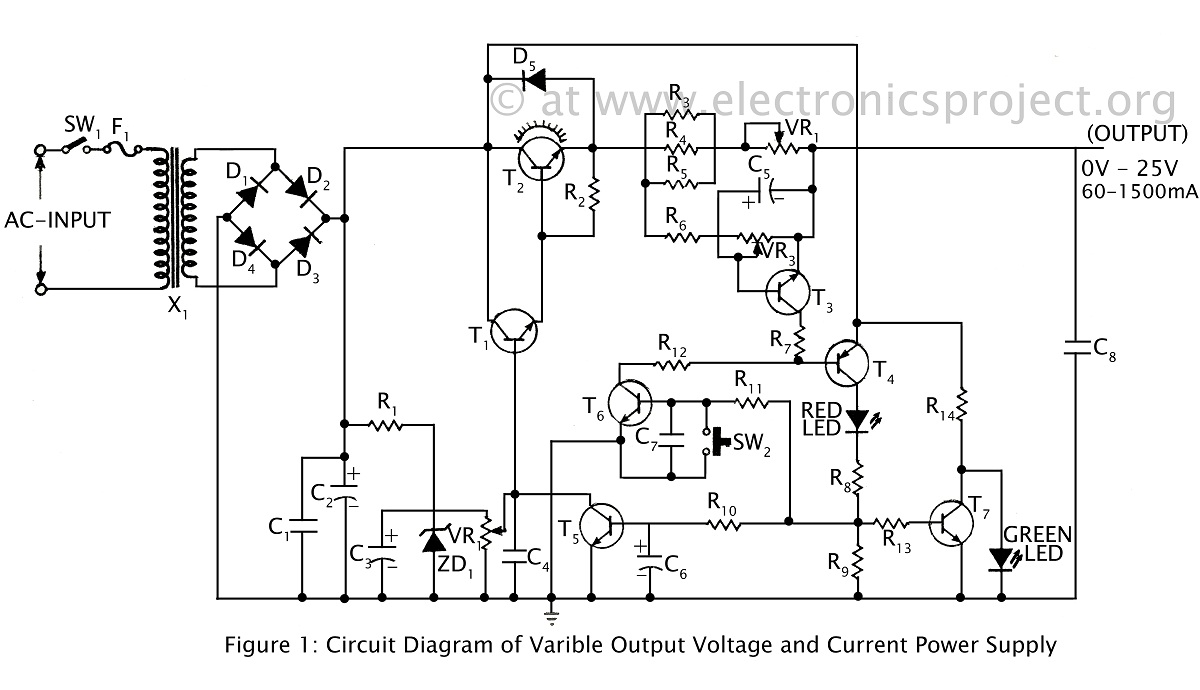
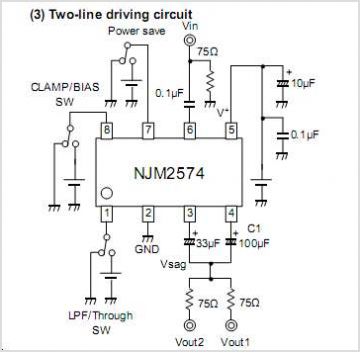
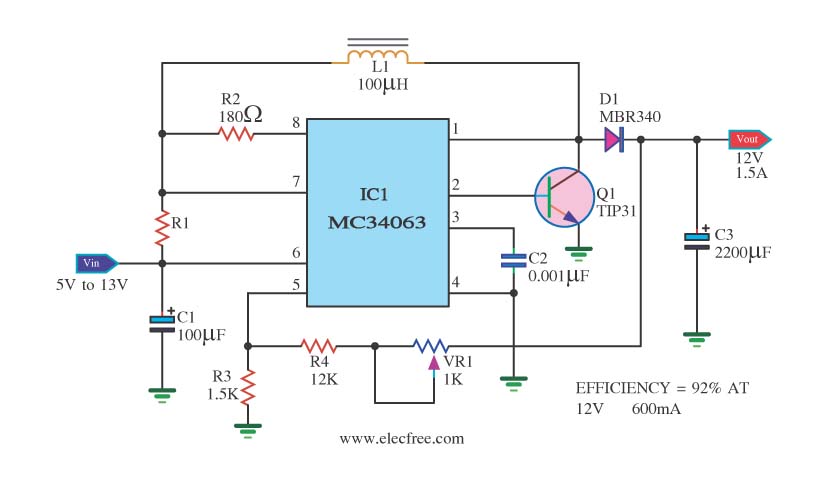
Voltage Multiplier
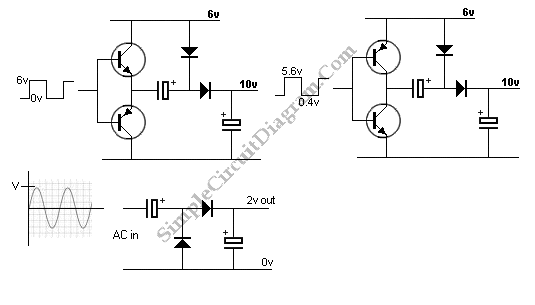
This is a voltage multiplier circuit. The first circuit is used to double a square wave (of any amplitude). However, there is a drawback of approximately 2V losses in the base-emitter.
A voltage multiplier circuit is designed to increase the voltage level of an input signal, typically a square wave, by utilizing capacitors and diodes to achieve the desired output. In this specific configuration, the circuit doubles the amplitude of the input square wave. The basic operation involves charging capacitors during one half of the waveform and discharging them to the load during the other half.
The circuit typically consists of a series of diodes and capacitors arranged in a specific topology. For instance, in a simple two-stage voltage doubler, the first diode allows current to flow into the capacitor during the positive half-cycle of the input waveform, charging it to the peak voltage minus the forward voltage drop of the diode. During the negative half-cycle, the charged capacitor discharges through the load, effectively doubling the output voltage.
It is important to note that there is a voltage drop associated with the base-emitter junction of transistors present in the circuit. This drop is typically around 2V, which must be accounted for in the design to ensure that the output voltage meets the required specifications. The overall efficiency of the circuit can be affected by these losses, and careful selection of components can help mitigate them.
Additional considerations for optimizing performance include selecting diodes with low forward voltage drops and capacitors with appropriate voltage ratings to handle the increased output voltage. The load connected to the output should also be considered, as it will influence the overall behavior of the circuit and its ability to maintain the desired output voltage under varying conditions. Proper thermal management may also be necessary to ensure reliability and longevity of the components used in the circuit.This is a voltage multiplier circuit. First circuit is used to double the a square wave (any amplitude). However there is minus about 2v losses in base-emitter.. 🔗 External reference
A voltage multiplier circuit is designed to increase the voltage level of an input signal, typically a square wave, by utilizing capacitors and diodes to achieve the desired output. In this specific configuration, the circuit doubles the amplitude of the input square wave. The basic operation involves charging capacitors during one half of the waveform and discharging them to the load during the other half.
The circuit typically consists of a series of diodes and capacitors arranged in a specific topology. For instance, in a simple two-stage voltage doubler, the first diode allows current to flow into the capacitor during the positive half-cycle of the input waveform, charging it to the peak voltage minus the forward voltage drop of the diode. During the negative half-cycle, the charged capacitor discharges through the load, effectively doubling the output voltage.
It is important to note that there is a voltage drop associated with the base-emitter junction of transistors present in the circuit. This drop is typically around 2V, which must be accounted for in the design to ensure that the output voltage meets the required specifications. The overall efficiency of the circuit can be affected by these losses, and careful selection of components can help mitigate them.
Additional considerations for optimizing performance include selecting diodes with low forward voltage drops and capacitors with appropriate voltage ratings to handle the increased output voltage. The load connected to the output should also be considered, as it will influence the overall behavior of the circuit and its ability to maintain the desired output voltage under varying conditions. Proper thermal management may also be necessary to ensure reliability and longevity of the components used in the circuit.This is a voltage multiplier circuit. First circuit is used to double the a square wave (any amplitude). However there is minus about 2v losses in base-emitter.. 🔗 External reference