Watermelon raw and cooked discriminating circuit
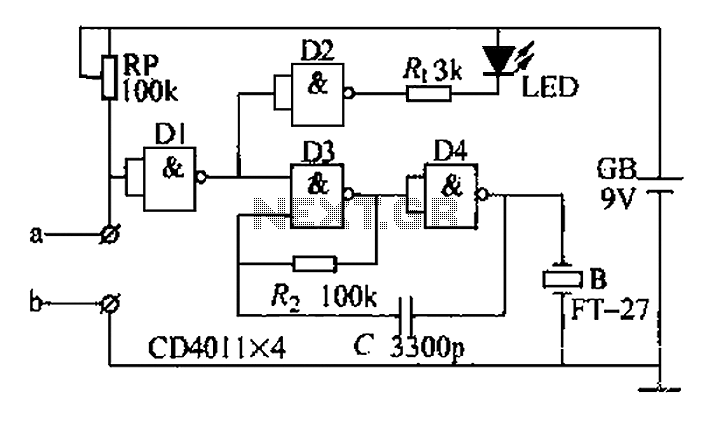
An annual listing of the watermelon season reveals that many individuals lack the intuitive judgment to differentiate between raw and cooked watermelon. This often leads to unnecessary disputes regarding the classification of the fruit. A proposed solution is the design of an electrical circuit that accurately determines the state of the watermelon (raw or cooked). The watermelon raw and cooked discriminator circuit, as illustrated in Figure 149, utilizes a 2-input NAND gate from an integrated circuit (IC). The circuit includes components D1, D2, and D4, which are connected to an inverter (NOT gate). The input level at D1 is determined by the resistance of the watermelon and probes that measure the partial pressure of the gas (GB) in question. Since raw and ripe watermelons have different ion concentrations, their conductivities vary; ripe watermelon exhibits lower resistance, while green watermelon has higher resistance. When probes A and B are inserted into ripe watermelon, the resistance is lower. Consequently, the input at D1 becomes low (less than V_swollen/2), resulting in a high output that activates the inputs D2 and D3. The output at D2, being inverted, results in a low power state, causing an LED to illuminate. Simultaneously, D3 and D4 trigger an audio multivibrator, producing sound through a piezoelectric ceramic element. In contrast, when probes A and B are inserted into raw watermelon, the resistance is higher, leading to a high input at D1 (greater than V_swollen/2), which results in a low output that silences D2 and D3, preventing the LED from lighting and the sound from emitting. Thus, the circuit can effectively determine the state of the watermelon by measuring its electrical properties.
The watermelon raw and cooked discriminator circuit operates based on the principles of electrical resistance and conductivity, which are influenced by the water content and ripeness of the fruit. The integrated circuit's NAND gate serves as the core processing unit, interpreting the varying resistance levels presented by the watermelon. The use of probes A and B is crucial, as they provide the necessary input to gauge the electrical characteristics of the watermelon.
The circuit design consists of the following components:
1. **Integrated Circuit (IC)**: The 2-input NAND gate is the primary logic element that processes the input signals from the probes.
2. **Probes (A and B)**: These are inserted into the watermelon to measure the resistance, which correlates with the fruit's ripeness.
3. **Resistors (RP)**: These resistors form part of the voltage divider that helps in determining the input level at D1 based on the resistance of the watermelon.
4. **Inverter (NOT Gate)**: This component is crucial for inverting the output from the NAND gate, allowing for the activation of the LED and audio output.
5. **LED (Light Emitting Diode)**: This visual indicator provides immediate feedback on the state of the watermelon, illuminating when ripe.
6. **Piezoelectric Ceramic Element**: This component generates sound signals, providing an auditory indication of the watermelon’s state.
The circuit's operation can be summarized as follows: when a ripe watermelon is probed, the lower resistance leads to a low input at D1, resulting in a high output that activates both the LED and the audio signal. Conversely, probing a raw watermelon results in a higher resistance, leading to a high input at D1 that silences the LED and audio output. This innovative approach not only enhances the understanding of watermelon ripeness but also provides a practical solution to the common disputes regarding the classification of the fruit.Annual listing of watermelon season, many people lack Yin Chi intuitive judgment raw and cooked watermelon Yun experience, often unnecessary disputes and saying this person has . If you design an electrical path, we can accurately determine the two melon raw and cooked, it is a very good way. Watermelon raw and cooked discriminator circuit 149 shown in FIG. Its core device is a 2-input NAND gate terminal 4 of the integrated circuit lC, where Dl, DZ and D4 are connected to an inverter (NOT gate) use.
Dl input level to the level of resistance of the battery by the RP watermelon and probes to measure the partial pressure of GB of the decision. Since raw ripe melon and water melon, ion concentration is not the same, sometimes they are not the same conductivity, low resistance ripe melon, green melon electrical resistance large.
When the probe a, b inserted ripe melon, melon smaller resistance. DJ input terminal is low (less than V swollen/2), Dl output high level are applied to the input terminal D2 and D3, D2 one hand inverted output: low power peace, light emitting diode (LED) two end get some electrical bits shame to emit light} on the other hand makes D3, D4 bonito into rhyme audio multivibrator work, piezoelectric ceramics guide is issued. Di - a ring of sound. Probe a, b inserted when raw melon, melon larger resistance, Dl input is high (greater than vJim/2), it is satisfied that the output of low points do not seal D2 and D3 input to make LEb silent k B does not emit light, sound and according to whether the light-emitting LED and 9B.
It can be determined by measuring the degree of raw and cooked watermelon..
The watermelon raw and cooked discriminator circuit operates based on the principles of electrical resistance and conductivity, which are influenced by the water content and ripeness of the fruit. The integrated circuit's NAND gate serves as the core processing unit, interpreting the varying resistance levels presented by the watermelon. The use of probes A and B is crucial, as they provide the necessary input to gauge the electrical characteristics of the watermelon.
The circuit design consists of the following components:
1. **Integrated Circuit (IC)**: The 2-input NAND gate is the primary logic element that processes the input signals from the probes.
2. **Probes (A and B)**: These are inserted into the watermelon to measure the resistance, which correlates with the fruit's ripeness.
3. **Resistors (RP)**: These resistors form part of the voltage divider that helps in determining the input level at D1 based on the resistance of the watermelon.
4. **Inverter (NOT Gate)**: This component is crucial for inverting the output from the NAND gate, allowing for the activation of the LED and audio output.
5. **LED (Light Emitting Diode)**: This visual indicator provides immediate feedback on the state of the watermelon, illuminating when ripe.
6. **Piezoelectric Ceramic Element**: This component generates sound signals, providing an auditory indication of the watermelon’s state.
The circuit's operation can be summarized as follows: when a ripe watermelon is probed, the lower resistance leads to a low input at D1, resulting in a high output that activates both the LED and the audio signal. Conversely, probing a raw watermelon results in a higher resistance, leading to a high input at D1 that silences the LED and audio output. This innovative approach not only enhances the understanding of watermelon ripeness but also provides a practical solution to the common disputes regarding the classification of the fruit.Annual listing of watermelon season, many people lack Yin Chi intuitive judgment raw and cooked watermelon Yun experience, often unnecessary disputes and saying this person has . If you design an electrical path, we can accurately determine the two melon raw and cooked, it is a very good way. Watermelon raw and cooked discriminator circuit 149 shown in FIG. Its core device is a 2-input NAND gate terminal 4 of the integrated circuit lC, where Dl, DZ and D4 are connected to an inverter (NOT gate) use.
Dl input level to the level of resistance of the battery by the RP watermelon and probes to measure the partial pressure of GB of the decision. Since raw ripe melon and water melon, ion concentration is not the same, sometimes they are not the same conductivity, low resistance ripe melon, green melon electrical resistance large.
When the probe a, b inserted ripe melon, melon smaller resistance. DJ input terminal is low (less than V swollen/2), Dl output high level are applied to the input terminal D2 and D3, D2 one hand inverted output: low power peace, light emitting diode (LED) two end get some electrical bits shame to emit light} on the other hand makes D3, D4 bonito into rhyme audio multivibrator work, piezoelectric ceramics guide is issued. Di - a ring of sound. Probe a, b inserted when raw melon, melon larger resistance, Dl input is high (greater than vJim/2), it is satisfied that the output of low points do not seal D2 and D3 input to make LEb silent k B does not emit light, sound and according to whether the light-emitting LED and 9B.
It can be determined by measuring the degree of raw and cooked watermelon..