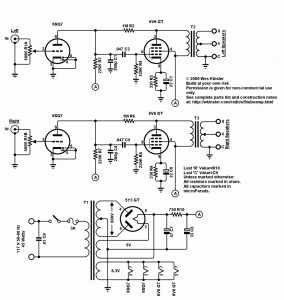
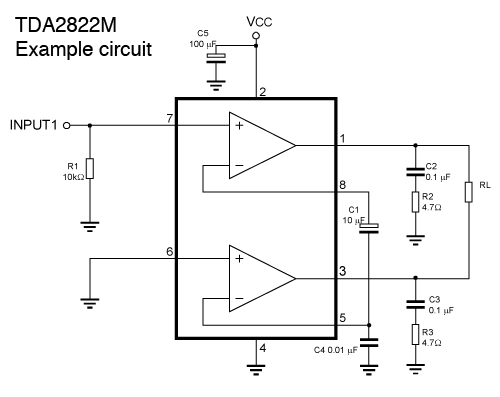
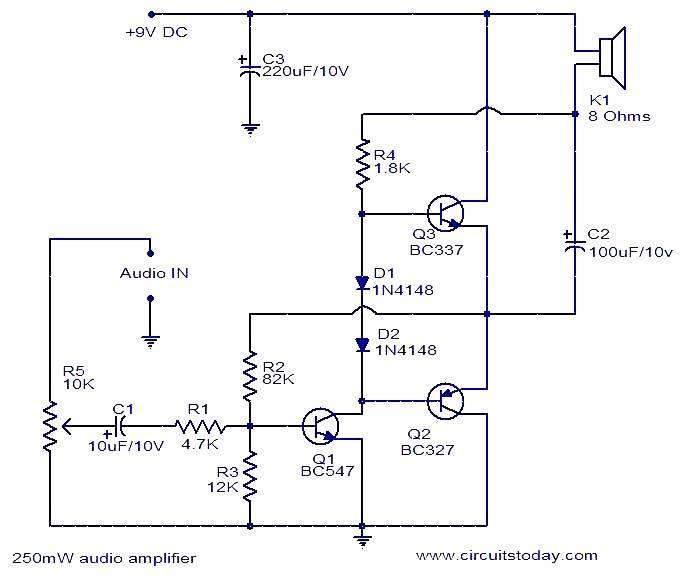
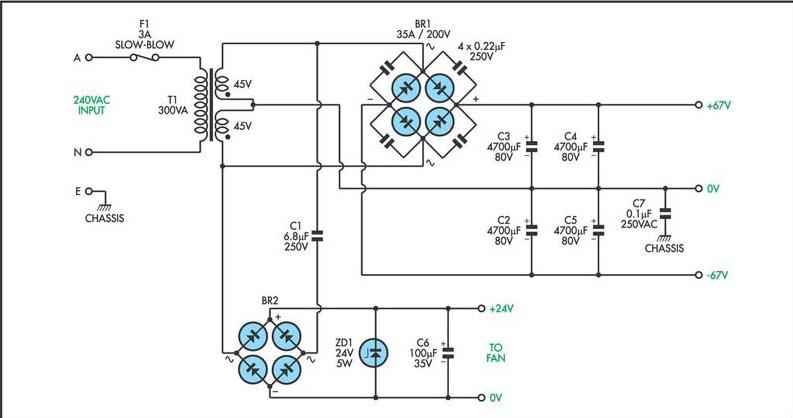
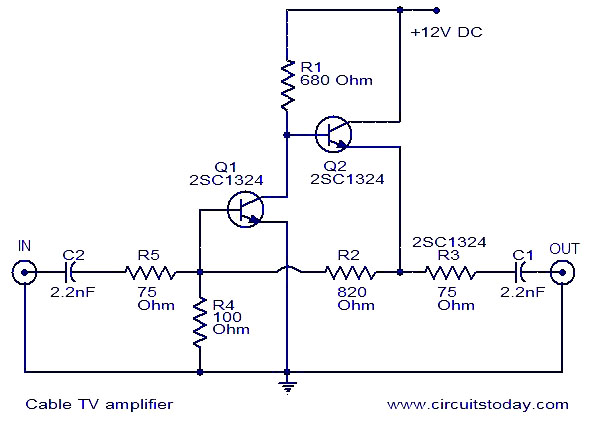
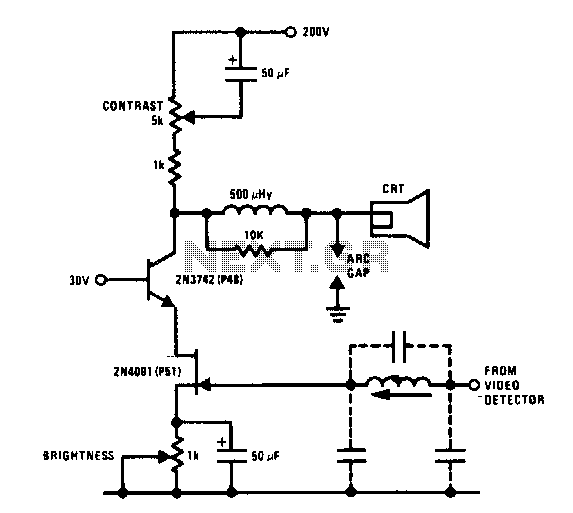
Wideband high-frequency amplifier
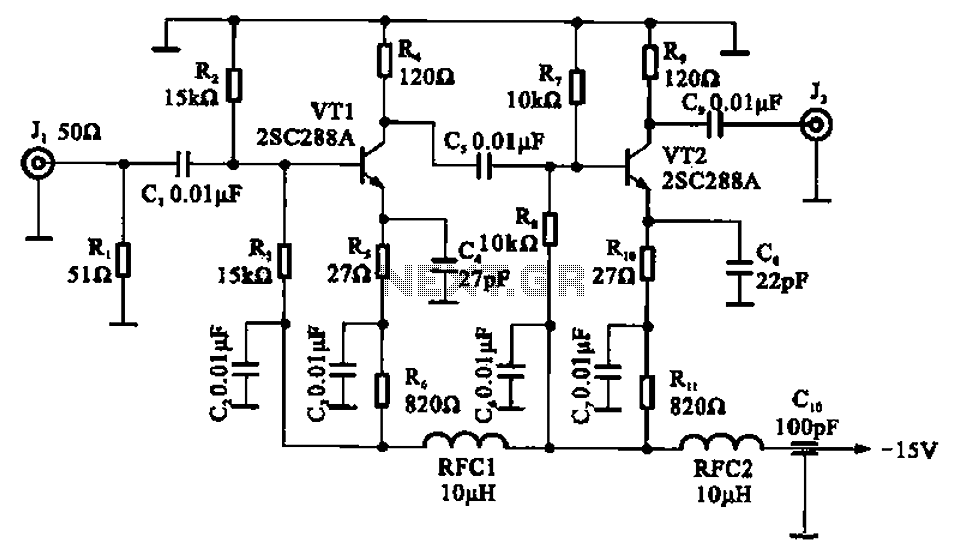
A wideband high-frequency amplifier circuit is presented, utilizing resistance and capacitance coupling in a common emitter configuration to amplify high-frequency signals. When a high-frequency signal with an input impedance of 50 ohms is applied to the amplifier through a coupling capacitor (C1) at the base of transistor VT1, it is subsequently amplified and fed to the base of transistor VT2 via capacitor C5. The amplified signal is then output from the collector. The bandwidth can be adjusted by selecting appropriate capacitors, ensuring that the frequency characteristic maintains a 1 dB variation, aided by high-frequency compensation capacitors.
The wideband high-frequency amplifier circuit is designed to operate effectively across a broad frequency range, making it suitable for applications in communications and signal processing. The common emitter configuration is particularly advantageous in this design due to its inherent ability to provide significant voltage gain while maintaining a relatively simple topology.
The circuit includes two transistors, VT1 and VT2, which are configured to work in tandem. The input signal is introduced through a coupling capacitor (C1), which serves to block any DC component while allowing the AC signal to pass. This is crucial for ensuring that the transistors operate within their linear region, thereby avoiding distortion of the amplified signal.
Capacitor C5 plays a vital role in coupling the output of the first transistor (VT1) to the base of the second transistor (VT2). This coupling is essential for cascading the amplification stages and achieving the desired output gain. The choice of capacitors in the circuit, particularly for frequency compensation, is critical. These capacitors help stabilize the amplifier's performance and prevent unwanted oscillations, which can occur at high frequencies.
The output is taken from the collector of the second transistor (VT2), where the amplified signal can be further processed or transmitted. The design allows for tuning the bandwidth by adjusting the values of the capacitors involved, ensuring that the amplifier can maintain a consistent gain across the desired frequency range. The use of high-frequency compensation capacitors is also important in maintaining the integrity of the signal and minimizing phase shifts that could lead to instability.
Overall, this wideband high-frequency amplifier circuit exemplifies the principles of RF amplification, combining careful selection of components and configuration to achieve optimal performance in high-frequency applications.A wideband high-frequency amplifier is shown, the circuit resistance and capacitance coupling of common emitter amplifier can be used to amplify high frequency signals. When th e high-frequency signal Jl end to (input impedance 50 n), applied to the amplifier via a coupling capacitor cl VTI base and amplified by the c5 coupled together to VT2 base, the amplified signal from the collector output. Adjust the band No. capacitor band frequency characteristic can reach l dB, with number of high-frequency capacitor compensation capacitor.
The wideband high-frequency amplifier circuit is designed to operate effectively across a broad frequency range, making it suitable for applications in communications and signal processing. The common emitter configuration is particularly advantageous in this design due to its inherent ability to provide significant voltage gain while maintaining a relatively simple topology.
The circuit includes two transistors, VT1 and VT2, which are configured to work in tandem. The input signal is introduced through a coupling capacitor (C1), which serves to block any DC component while allowing the AC signal to pass. This is crucial for ensuring that the transistors operate within their linear region, thereby avoiding distortion of the amplified signal.
Capacitor C5 plays a vital role in coupling the output of the first transistor (VT1) to the base of the second transistor (VT2). This coupling is essential for cascading the amplification stages and achieving the desired output gain. The choice of capacitors in the circuit, particularly for frequency compensation, is critical. These capacitors help stabilize the amplifier's performance and prevent unwanted oscillations, which can occur at high frequencies.
The output is taken from the collector of the second transistor (VT2), where the amplified signal can be further processed or transmitted. The design allows for tuning the bandwidth by adjusting the values of the capacitors involved, ensuring that the amplifier can maintain a consistent gain across the desired frequency range. The use of high-frequency compensation capacitors is also important in maintaining the integrity of the signal and minimizing phase shifts that could lead to instability.
Overall, this wideband high-frequency amplifier circuit exemplifies the principles of RF amplification, combining careful selection of components and configuration to achieve optimal performance in high-frequency applications.A wideband high-frequency amplifier is shown, the circuit resistance and capacitance coupling of common emitter amplifier can be used to amplify high frequency signals. When th e high-frequency signal Jl end to (input impedance 50 n), applied to the amplifier via a coupling capacitor cl VTI base and amplified by the c5 coupled together to VT2 base, the amplified signal from the collector output. Adjust the band No. capacitor band frequency characteristic can reach l dB, with number of high-frequency capacitor compensation capacitor.