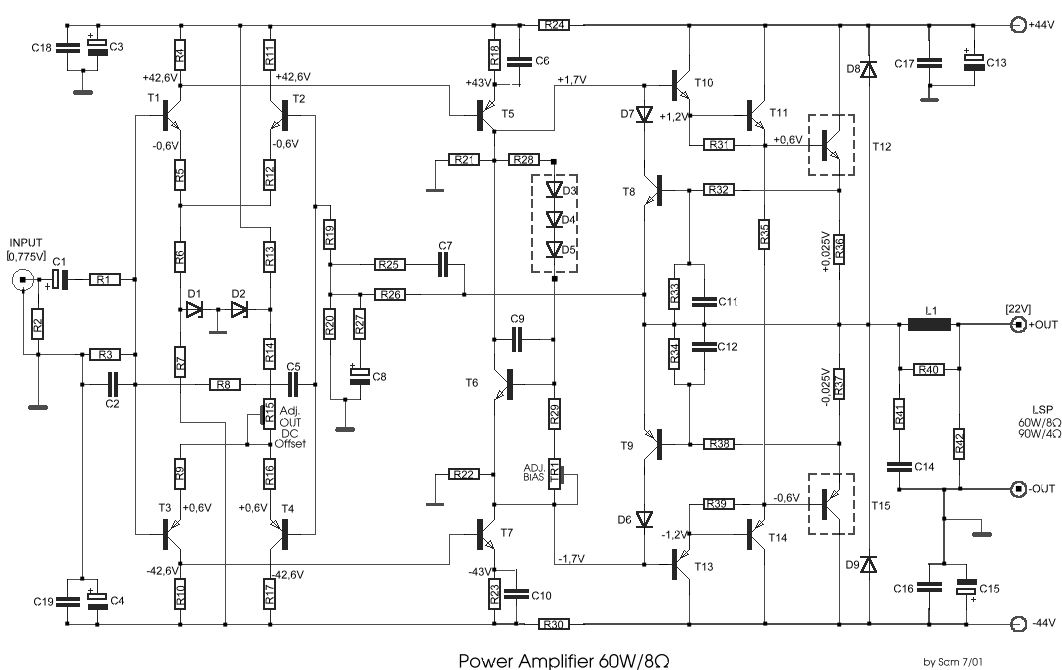
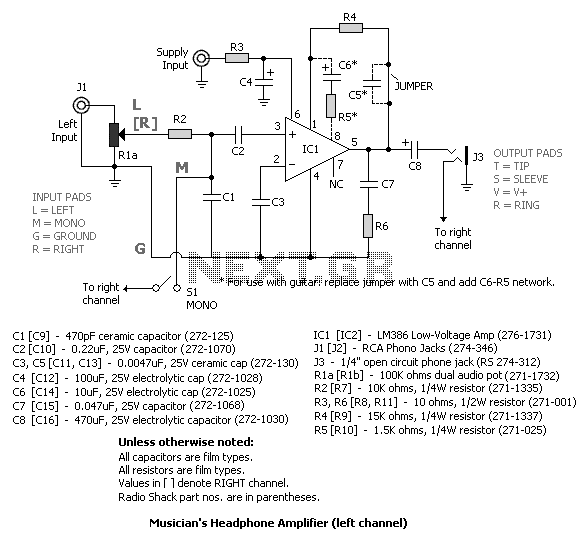
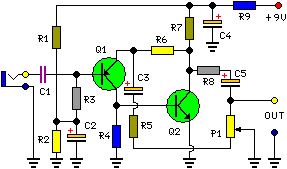
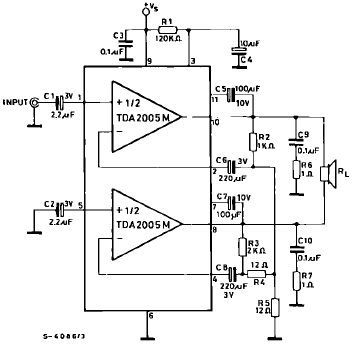
Wideband RF Amplifier
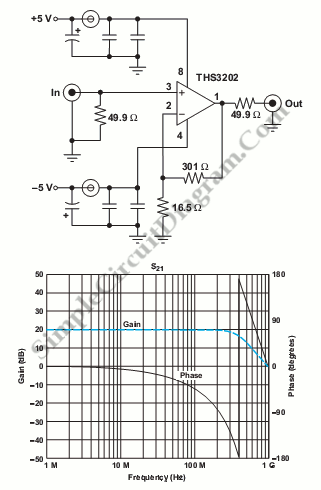
This circuit consists of wideband RF amplifiers that utilize current-feedback components such as the THS3202. The THS3202 was selected for its fast slew rate and wide bandwidth. The amplifier voltage gain of this circuit is 20, while the stage voltage gain is 10. The circuit requires only two resistors, an operational amplifier, decoupling components, and termination. The stage gain is determined by the values of Rf (RF) and Rg (RG). Additionally, the basis of an audio mixer is an inverting summing circuit. In practical applications, audio mixers rarely utilize a single-supply voltage due to the need for increased dynamic range, which often leads to operational amplifiers being pushed to or beyond their limits. There are also subtracting circuits, which are commonly employed to eliminate vocal tracks recorded at equal levels in both channels from stereo recordings. Furthermore, a Single Op-Amp Twin-T Band-Pass and Notch Filter circuit is described, using the twin-T topology that requires one or two operational amplifiers along with three resistors and three capacitors, indicating its reliance on a passive (RC) topology. The generation of a virtual ground is necessary for single-supply operation, typically at a voltage equal to Vcc/2. A simple voltage divider can be used to produce this Vcc/2, although its performance may deteriorate at low frequencies. The operational amplifier circuit shown below has a closed-loop gain defined by the ratio R2/R1 when this ratio is small in comparison to the amplifier's open-loop gain, classifying it as an inverting circuit. The input impedance is equal to...
The wideband RF amplifier circuit is an essential component in modern communication systems, enabling the amplification of high-frequency signals with minimal distortion. The use of the THS3202 operational amplifier is particularly advantageous due to its high slew rate, which allows for rapid changes in input signal levels without introducing significant phase shifts or distortion. The specified voltage gains of 20 for the amplifier and 10 for the stage are critical parameters that define the overall amplification characteristics of the circuit.
In terms of component selection, the resistors (Rf and Rg) are pivotal in setting the gain of the amplifier stages. The values of these resistors must be carefully calculated to achieve the desired performance while maintaining stability across varying frequencies. The inclusion of decoupling components is also vital to ensure that power supply variations do not affect the amplifier's performance, which is particularly important in RF applications where signal integrity is paramount.
The inverting summing circuit's role in audio mixing highlights its versatility in signal processing. By allowing multiple audio signals to be combined into a single output, it facilitates complex audio manipulations necessary for professional sound production. The use of a single-supply voltage in audio mixers, while less common, can simplify power supply requirements and reduce overall circuit complexity, although it necessitates careful design to maintain dynamic range.
The twin-T band-pass and notch filter circuit exemplifies the application of passive components in signal processing. This topology is effective for selecting specific frequency ranges while attenuating unwanted frequencies, which is crucial in various audio applications. The design considerations for achieving a virtual ground through a voltage divider emphasize the importance of stability and performance, particularly in low-frequency scenarios where the impedance characteristics of the circuit can significantly impact functionality.
In conclusion, the operational amplifier circuits described serve essential roles in both RF amplification and audio processing, illustrating the versatility and importance of these components in various electronic applications. The careful selection of components and design methodologies ensures optimal performance, stability, and reliability in the intended applications.This is a circuit of Wideband RF amplifiers. This circuit use current-feedback components like the THS3202. The THS3202 was chosen because it has fast slew rate and wide bandwidth. The amplifier voltage gain of this circuit is 20 and stage voltage gain of this circuit is 10. Here is the circuit: Compared to traditional RF circuitry, this circuit i s simpler. This circuit just require two resistors, op amp, decoupling components and the termination. the stage gain is set by The 301-O (RF) and 16. 5-O (RG). [Source: Texas Instruments Application Note] The basis of an audio mixer is an inverting summing circuit below. For real audio mixers, a single-supply voltage is seldom used. To increase dynamic range, the designer will often push an op amp up to, and sometimes beyond it`s Continue reading †’.
Not only a summing circuits, but there are also subtracting circuits. Here`s the circuit diagram: Subtracting circuit is a common application which is used to eliminate the vocal track (recorded at equal levels in both channels) from stereo recordings. R1 Continue reading †’. This is a Single Op-Amp Twin-T Band-Pass and Notch Filter circuit. This circuit uses the twin-T topology which requires one or two op amps and three resistors and three capacitors.
That`s mean this topology based on a passive (RC) topology. Continue reading †’. Generation of a virtual ground is required by single-supply operation. It`s usually required at a voltage equal to Vcc/2. We can use a simple voltage divider produce Vcc/2, but it`s performance deteriorates at low frequency. The values of R1 and Continue reading †’. The figure below show an operational amplifier circuit. Closed-loop gain given by this circuit is R2/R1 when this ratio is small compared with the amplifier open-loop gain, and it`s called as inverting circuit.
The value of input impedance is equal Continue reading †’. 🔗 External reference
The wideband RF amplifier circuit is an essential component in modern communication systems, enabling the amplification of high-frequency signals with minimal distortion. The use of the THS3202 operational amplifier is particularly advantageous due to its high slew rate, which allows for rapid changes in input signal levels without introducing significant phase shifts or distortion. The specified voltage gains of 20 for the amplifier and 10 for the stage are critical parameters that define the overall amplification characteristics of the circuit.
In terms of component selection, the resistors (Rf and Rg) are pivotal in setting the gain of the amplifier stages. The values of these resistors must be carefully calculated to achieve the desired performance while maintaining stability across varying frequencies. The inclusion of decoupling components is also vital to ensure that power supply variations do not affect the amplifier's performance, which is particularly important in RF applications where signal integrity is paramount.
The inverting summing circuit's role in audio mixing highlights its versatility in signal processing. By allowing multiple audio signals to be combined into a single output, it facilitates complex audio manipulations necessary for professional sound production. The use of a single-supply voltage in audio mixers, while less common, can simplify power supply requirements and reduce overall circuit complexity, although it necessitates careful design to maintain dynamic range.
The twin-T band-pass and notch filter circuit exemplifies the application of passive components in signal processing. This topology is effective for selecting specific frequency ranges while attenuating unwanted frequencies, which is crucial in various audio applications. The design considerations for achieving a virtual ground through a voltage divider emphasize the importance of stability and performance, particularly in low-frequency scenarios where the impedance characteristics of the circuit can significantly impact functionality.
In conclusion, the operational amplifier circuits described serve essential roles in both RF amplification and audio processing, illustrating the versatility and importance of these components in various electronic applications. The careful selection of components and design methodologies ensures optimal performance, stability, and reliability in the intended applications.This is a circuit of Wideband RF amplifiers. This circuit use current-feedback components like the THS3202. The THS3202 was chosen because it has fast slew rate and wide bandwidth. The amplifier voltage gain of this circuit is 20 and stage voltage gain of this circuit is 10. Here is the circuit: Compared to traditional RF circuitry, this circuit i s simpler. This circuit just require two resistors, op amp, decoupling components and the termination. the stage gain is set by The 301-O (RF) and 16. 5-O (RG). [Source: Texas Instruments Application Note] The basis of an audio mixer is an inverting summing circuit below. For real audio mixers, a single-supply voltage is seldom used. To increase dynamic range, the designer will often push an op amp up to, and sometimes beyond it`s Continue reading †’.
Not only a summing circuits, but there are also subtracting circuits. Here`s the circuit diagram: Subtracting circuit is a common application which is used to eliminate the vocal track (recorded at equal levels in both channels) from stereo recordings. R1 Continue reading †’. This is a Single Op-Amp Twin-T Band-Pass and Notch Filter circuit. This circuit uses the twin-T topology which requires one or two op amps and three resistors and three capacitors.
That`s mean this topology based on a passive (RC) topology. Continue reading †’. Generation of a virtual ground is required by single-supply operation. It`s usually required at a voltage equal to Vcc/2. We can use a simple voltage divider produce Vcc/2, but it`s performance deteriorates at low frequency. The values of R1 and Continue reading †’. The figure below show an operational amplifier circuit. Closed-loop gain given by this circuit is R2/R1 when this ratio is small compared with the amplifier open-loop gain, and it`s called as inverting circuit.
The value of input impedance is equal Continue reading †’. 🔗 External reference