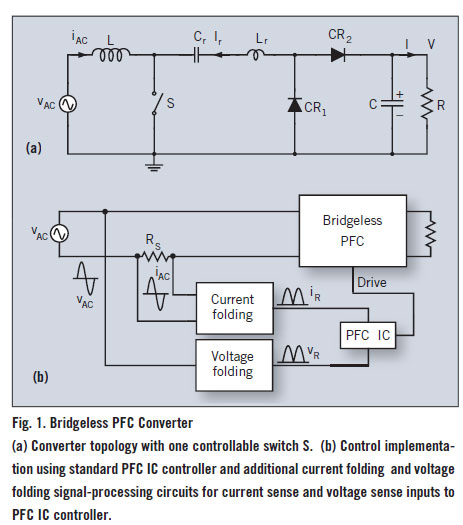
wien bridge oscillator
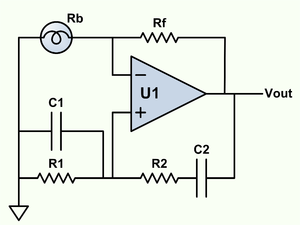
Wien bridge oscillator. A phase-shift feedback oscillator that uses a Wien bridge as the basis for its operation.
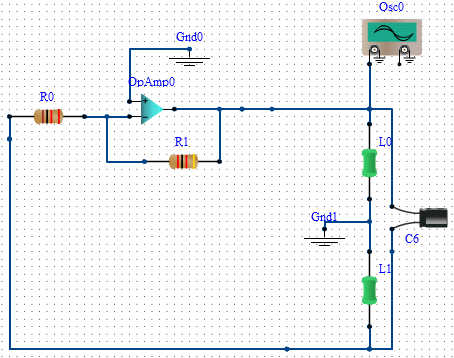
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It operates based on the principle of phase shift feedback, utilizing a Wien bridge circuit, which consists of resistors and capacitors arranged to create a specific frequency response. The circuit typically includes a combination of resistive and capacitive elements that determine the frequency of oscillation, allowing for precise control over the output frequency.
In a typical Wien bridge oscillator, the configuration includes two resistors and two capacitors forming a bridge circuit. The bridge is balanced at a certain frequency, which is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors. The feedback loop is crucial for sustaining oscillations; it provides the necessary phase shift and gain to maintain continuous output.
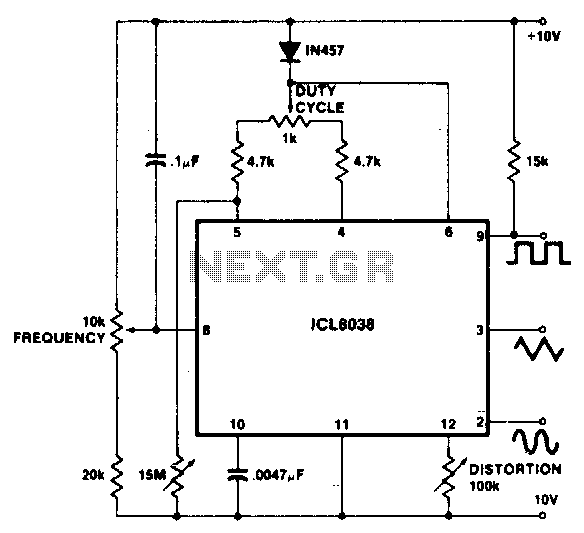
An essential feature of the Wien bridge oscillator is its automatic gain control mechanism, which stabilizes the amplitude of the output signal. This is often achieved using a thermistor or a light-dependent resistor (LDR) that adjusts the resistance in the feedback path based on the output signal's amplitude. This self-regulating aspect allows the oscillator to produce a stable sine wave without requiring manual adjustments.
The output frequency of the Wien bridge oscillator can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2 \pi R C} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance and \( C \) is the capacitance in the bridge. This relationship highlights the importance of selecting appropriate component values to achieve the desired frequency of oscillation.
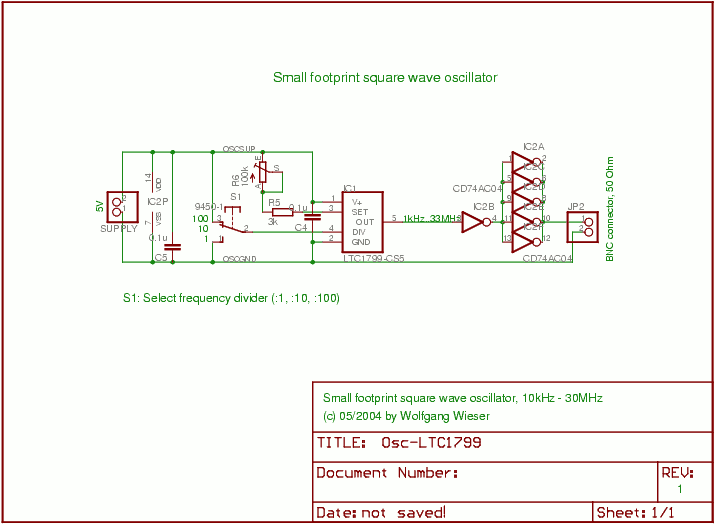
Applications of the Wien bridge oscillator include audio signal generation, function generators, and as a reference signal in various electronic devices. Its simplicity and reliability make it a popular choice in both educational and professional electronics projects.Wien bridge oscillator. A phase-shift feedback oscillator that uses a Wien bridge as the.. 🔗 External reference
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It operates based on the principle of phase shift feedback, utilizing a Wien bridge circuit, which consists of resistors and capacitors arranged to create a specific frequency response. The circuit typically includes a combination of resistive and capacitive elements that determine the frequency of oscillation, allowing for precise control over the output frequency.
In a typical Wien bridge oscillator, the configuration includes two resistors and two capacitors forming a bridge circuit. The bridge is balanced at a certain frequency, which is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors. The feedback loop is crucial for sustaining oscillations; it provides the necessary phase shift and gain to maintain continuous output.
An essential feature of the Wien bridge oscillator is its automatic gain control mechanism, which stabilizes the amplitude of the output signal. This is often achieved using a thermistor or a light-dependent resistor (LDR) that adjusts the resistance in the feedback path based on the output signal's amplitude. This self-regulating aspect allows the oscillator to produce a stable sine wave without requiring manual adjustments.
The output frequency of the Wien bridge oscillator can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2 \pi R C} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance and \( C \) is the capacitance in the bridge. This relationship highlights the importance of selecting appropriate component values to achieve the desired frequency of oscillation.
Applications of the Wien bridge oscillator include audio signal generation, function generators, and as a reference signal in various electronic devices. Its simplicity and reliability make it a popular choice in both educational and professional electronics projects.Wien bridge oscillator. A phase-shift feedback oscillator that uses a Wien bridge as the.. 🔗 External reference