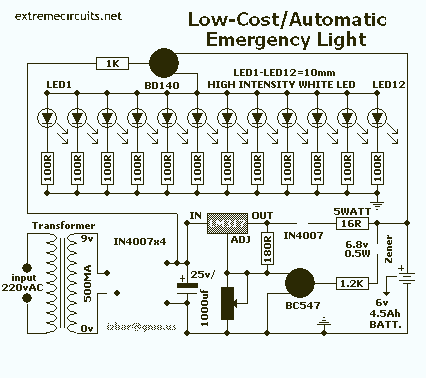
Series DC power supply

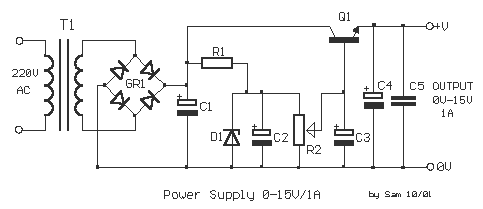
A power supply typically consists of a transformer, rectifier, filter, adjustment components, and reference power supply and sampling circuits. Additionally, it may include overload or short circuit protection devices. The circuit begins with a 220V step-down transformer (T) that converts the voltage to 10V, which is then rectified by diodes VD1 to VD4 into a pulsating DC. This pulsating DC is filtered by capacitor C1 and regulated to provide an output DC voltage (Uo) of 6V through an adjustment tube (VT2). By changing the value of the sampling resistor (RP), the output voltage (U) can be varied. The circuit is designed to provide an output current (Io) of 200mA. The regulation process involves sampling the output voltage through a resistor divider, comparing it with a reference voltage, and amplifying the error signal to adjust the base of the regulator, ensuring a stable output voltage. A larger amplification factor generally leads to higher stability. The reference voltage must be stable, as fluctuations can affect the output voltage stability. Silicon reference voltage regulators are commonly used for this purpose, with careful selection of current limiting resistors to ensure stable operation.
The power supply circuit described functions as a versatile voltage regulator with a defined output. The transformer (T) is essential for stepping down the mains voltage from 220V AC to a lower voltage suitable for the subsequent rectification stage. The bridge rectifier, formed by diodes VD1 to VD4, converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC. The capacitor (C1) serves as a filter to smooth out the pulsations, leading to a more stable DC voltage.
The adjustment tube (VT2) plays a crucial role in regulating the output voltage. The output voltage (Uo) is set to 6V, but can be adjusted by varying the resistance of the sampling resistor (RP). This provides flexibility in the output voltage, allowing it to cater to different load requirements. The circuit is designed to handle a maximum output current of 200mA, making it suitable for various electronic applications.
The regulation mechanism relies on feedback control. When the output voltage deviates from the desired level, the resistor divider samples the output voltage and compares it against a stable reference voltage. The resulting error signal is amplified and used to adjust the base of the regulator, which in turn modifies the voltage drop across the adjustment tube (VT2). This feedback loop ensures that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in load or input voltage.
Stability in the output voltage is paramount, and it is influenced by the choice of the reference voltage and the amplification factor in the circuit. A stable reference voltage is critical; if it fluctuates, it can lead to variations in the output voltage, compromising the overall stability of the power supply. Silicon-based voltage regulators are often utilized due to their reliability and stable performance. Proper selection of current limiting resistors is also essential to maintain the minimum current required for the regulator to function correctly, which is necessary for achieving stable output voltages under varying conditions.
In summary, this power supply circuit is an effective solution for providing a stable and adjustable DC output voltage, suitable for powering various electronic devices while incorporating necessary protection and stability features.As can be seen, a power supply is usually the transformer, rectifier filter, adjust the yuan pieces, more zoom, six partial reference power supply and sampling, etc., there are some power supply overload or short circuit protection device. Circuit from 220V step-down transformer T to 10V, VD1 ~ VD4 bridge rectifier into a pulsating the AC 10V DC, through the capacitor c1 filter, and then by the regulation, amplification, sampling aspects, the adjustment tube VT2, the output DC Uo to 6V. Adjust the sampling resistor RP large small, you can change the output voltage U. 6V changes within the circuit output current Io is 200mA. It regulators working process is: when the output voltage changes, through a resistor divider to sample, after comparison with the reference power, amplification will amplify the error signal, to the base of the pole to adjust their regulator pressure drop in order to achieve a stable output voltage.
Generally speaking, an enlarged part of the greater magnification, the higher the degree of stability. Let Control 12 - Stability turns 21a as shown in a block diagram of each power supply as follows: (1) the reference voltage of a reference voltage should be higher DC voltage stability, otherwise, since the reference voltage is changed, even if the U, not variable t It will cause the output voltage changes, affecting the stability of the output voltage.
Currently. Often using a silicon reference voltage regulator vs Phoenix and achieved, as shown in Figure 12-21b, the key is to choose the regulator circuit current limiting resistor, the resistance should be guaranteed when the input voltage [ minimum flow through the regulator Parker tube current nor less than the minimum current to maintain stable voltages
The power supply circuit described functions as a versatile voltage regulator with a defined output. The transformer (T) is essential for stepping down the mains voltage from 220V AC to a lower voltage suitable for the subsequent rectification stage. The bridge rectifier, formed by diodes VD1 to VD4, converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC. The capacitor (C1) serves as a filter to smooth out the pulsations, leading to a more stable DC voltage.
The adjustment tube (VT2) plays a crucial role in regulating the output voltage. The output voltage (Uo) is set to 6V, but can be adjusted by varying the resistance of the sampling resistor (RP). This provides flexibility in the output voltage, allowing it to cater to different load requirements. The circuit is designed to handle a maximum output current of 200mA, making it suitable for various electronic applications.
The regulation mechanism relies on feedback control. When the output voltage deviates from the desired level, the resistor divider samples the output voltage and compares it against a stable reference voltage. The resulting error signal is amplified and used to adjust the base of the regulator, which in turn modifies the voltage drop across the adjustment tube (VT2). This feedback loop ensures that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in load or input voltage.
Stability in the output voltage is paramount, and it is influenced by the choice of the reference voltage and the amplification factor in the circuit. A stable reference voltage is critical; if it fluctuates, it can lead to variations in the output voltage, compromising the overall stability of the power supply. Silicon-based voltage regulators are often utilized due to their reliability and stable performance. Proper selection of current limiting resistors is also essential to maintain the minimum current required for the regulator to function correctly, which is necessary for achieving stable output voltages under varying conditions.
In summary, this power supply circuit is an effective solution for providing a stable and adjustable DC output voltage, suitable for powering various electronic devices while incorporating necessary protection and stability features.As can be seen, a power supply is usually the transformer, rectifier filter, adjust the yuan pieces, more zoom, six partial reference power supply and sampling, etc., there are some power supply overload or short circuit protection device. Circuit from 220V step-down transformer T to 10V, VD1 ~ VD4 bridge rectifier into a pulsating the AC 10V DC, through the capacitor c1 filter, and then by the regulation, amplification, sampling aspects, the adjustment tube VT2, the output DC Uo to 6V. Adjust the sampling resistor RP large small, you can change the output voltage U. 6V changes within the circuit output current Io is 200mA. It regulators working process is: when the output voltage changes, through a resistor divider to sample, after comparison with the reference power, amplification will amplify the error signal, to the base of the pole to adjust their regulator pressure drop in order to achieve a stable output voltage.
Generally speaking, an enlarged part of the greater magnification, the higher the degree of stability. Let Control 12 - Stability turns 21a as shown in a block diagram of each power supply as follows: (1) the reference voltage of a reference voltage should be higher DC voltage stability, otherwise, since the reference voltage is changed, even if the U, not variable t It will cause the output voltage changes, affecting the stability of the output voltage.
Currently. Often using a silicon reference voltage regulator vs Phoenix and achieved, as shown in Figure 12-21b, the key is to choose the regulator circuit current limiting resistor, the resistance should be guaranteed when the input voltage [ minimum flow through the regulator Parker tube current nor less than the minimum current to maintain stable voltages
.jpg)