555 audio oscillator circuit diagram of a radio-frequency drive
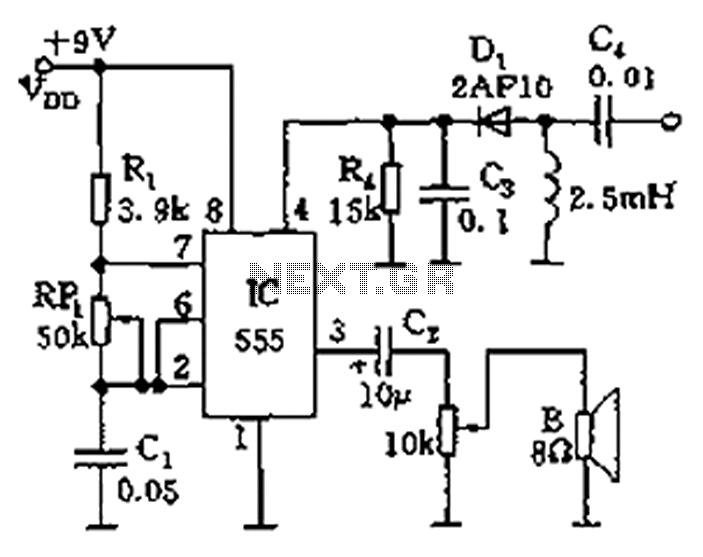
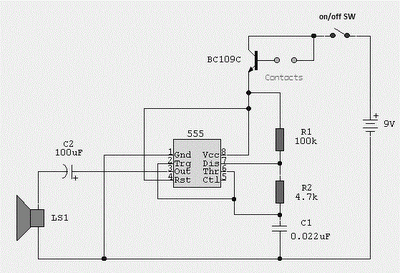
The circuit features a 555 timer integrated circuit along with components R1, RP1, C1, and others, which together form an audio oscillator. The frequency of the oscillator is determined by the formula f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * RP1) * C1), allowing for frequency adjustments within the range of 600 Hz to 20 kHz by varying RP1. The operation of the oscillator is controlled by the reset terminal (pin 4). When no radio frequency (RF) signal is present, the voltage at pin 4 is low, causing the 555 timer to cease oscillation. Conversely, when a designated RF signal is detected by the diode (D1), the voltage at pin 4 increases above 1V, triggering the oscillator to produce an audio signal through the connected speaker.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate audio frequencies. The resistors R1 and RP1, along with capacitor C1, set the timing intervals that define the output frequency. The frequency of oscillation can be fine-tuned by adjusting the variable resistor RP1, allowing for a broad range of audio outputs suitable for various applications, such as tone generation or sound signaling.
The reset functionality of the 555 timer is crucial for controlling the oscillator's operation. When pin 4 receives a low signal, the timer is reset, halting any oscillation. This feature is particularly useful in scenarios where the circuit must remain inactive in the absence of an RF signal. The presence of an RF signal is detected by diode D1, which rectifies the incoming signal and applies a voltage to pin 4. If this voltage exceeds the threshold of 1V, it enables the oscillator, producing a continuous audio tone through the speaker.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective method for generating audio signals based on external RF input, leveraging the versatile capabilities of the 555 timer IC. The design can be employed in various applications, including alarms, sound effects, and communication devices where audio signaling is required.As illustrated, 555 and R1, RP1, C1 and other components controlled audio oscillator, f frequency of 1.44/(R1 + 2RP1) C1, illustrated parameters between 600Hz ~ 20kHz, can be s elected by adjusting the RP1. The oscillator or not, depending on the reset terminal 4 foot level. When no RF signal, 4 feet was low, 555 state to stop vibration; when a designated radio frequency signal, the detector diode detector D1, the video signal is applied to pin 4, when the signal level is higher than 1V, the start-up, the speaker will be issued tone given audio signal
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate audio frequencies. The resistors R1 and RP1, along with capacitor C1, set the timing intervals that define the output frequency. The frequency of oscillation can be fine-tuned by adjusting the variable resistor RP1, allowing for a broad range of audio outputs suitable for various applications, such as tone generation or sound signaling.
The reset functionality of the 555 timer is crucial for controlling the oscillator's operation. When pin 4 receives a low signal, the timer is reset, halting any oscillation. This feature is particularly useful in scenarios where the circuit must remain inactive in the absence of an RF signal. The presence of an RF signal is detected by diode D1, which rectifies the incoming signal and applies a voltage to pin 4. If this voltage exceeds the threshold of 1V, it enables the oscillator, producing a continuous audio tone through the speaker.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective method for generating audio signals based on external RF input, leveraging the versatile capabilities of the 555 timer IC. The design can be employed in various applications, including alarms, sound effects, and communication devices where audio signaling is required.As illustrated, 555 and R1, RP1, C1 and other components controlled audio oscillator, f frequency of 1.44/(R1 + 2RP1) C1, illustrated parameters between 600Hz ~ 20kHz, can be s elected by adjusting the RP1. The oscillator or not, depending on the reset terminal 4 foot level. When no RF signal, 4 feet was low, 555 state to stop vibration; when a designated radio frequency signal, the detector diode detector D1, the video signal is applied to pin 4, when the signal level is higher than 1V, the start-up, the speaker will be issued tone given audio signal