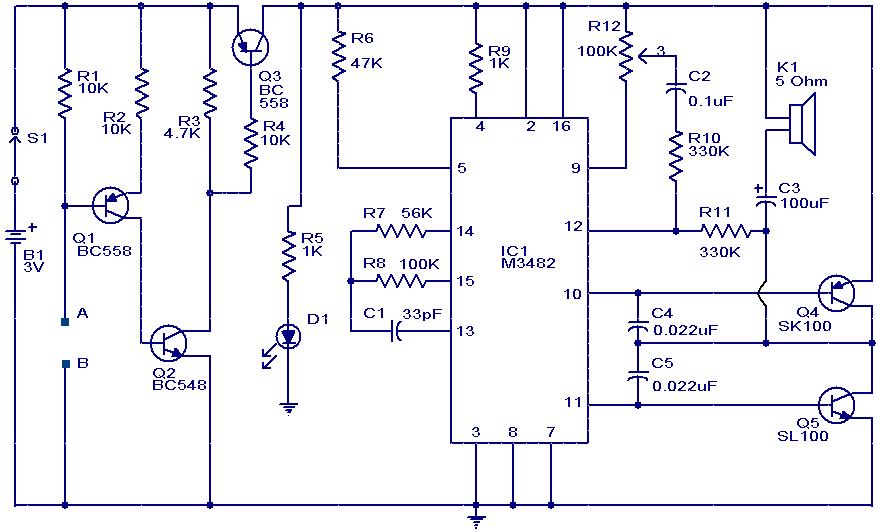
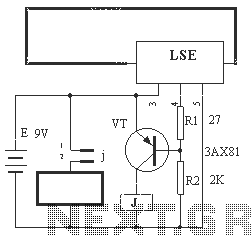
water activated alarm using ic 555
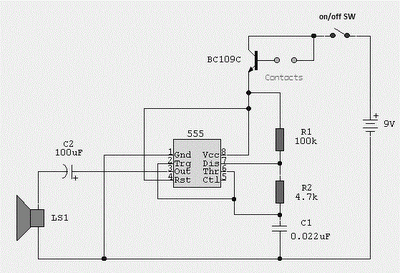
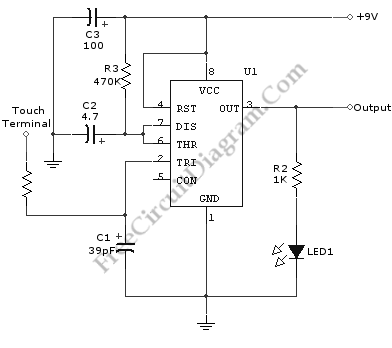
Probes or contacts may utilize a non-reactive metal. Gold or silver plated contacts from an old relay may be used; however, a cost-effective alternative is to wire alternate copper strips from a piece of veroboard. These will eventually oxidize, but since very little current flows in the base circuit, the increased impedance caused by oxidation is not significant. No base resistor is necessary as the transistor operates in an emitter follower configuration, with the current limited by the impedance at the emitter (the oscillator circuit).
The circuit described involves the use of non-reactive metal contacts for probes, which is essential for ensuring reliable electrical connections over time. Gold and silver plated contacts are preferred due to their excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion. In scenarios where cost is a concern, using copper strips from veroboard presents a viable alternative. While copper is prone to oxidation, the impact on circuit performance is minimal in this application because the current flowing through the base circuit is very low.
The configuration of the transistor as an emitter follower is crucial. In this setup, the transistor's emitter voltage closely follows the base voltage, which allows for a high input impedance and a low output impedance. This characteristic makes the emitter follower ideal for buffering signals, as it can drive loads without significantly affecting the input signal. The absence of a base resistor simplifies the design, as the transistor's operation is primarily governed by the impedance at the emitter. This aspect is particularly relevant in oscillator circuits, where maintaining signal integrity is essential while keeping the component count and complexity to a minimum.
In summary, this circuit design leverages the properties of various materials and the unique characteristics of the emitter follower configuration to achieve an efficient and effective solution for low-current applications.Probe/contacts may use a non-reactive metal. Gold or silver plated contacts from an old relay May be Used, however a cheap alternative is to wire alternate copper strips from a piece of veroboard. These will eventually oxidize over but as very little current is flowing in the base circuit, the higher impedance the caused by oxidization is not Impo
rtant. No base resistor is Necessary as the transistor is in emitter follower, current limit being the impedance at the emitter (the oscillator circuit). 🔗 External reference
The circuit described involves the use of non-reactive metal contacts for probes, which is essential for ensuring reliable electrical connections over time. Gold and silver plated contacts are preferred due to their excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion. In scenarios where cost is a concern, using copper strips from veroboard presents a viable alternative. While copper is prone to oxidation, the impact on circuit performance is minimal in this application because the current flowing through the base circuit is very low.
The configuration of the transistor as an emitter follower is crucial. In this setup, the transistor's emitter voltage closely follows the base voltage, which allows for a high input impedance and a low output impedance. This characteristic makes the emitter follower ideal for buffering signals, as it can drive loads without significantly affecting the input signal. The absence of a base resistor simplifies the design, as the transistor's operation is primarily governed by the impedance at the emitter. This aspect is particularly relevant in oscillator circuits, where maintaining signal integrity is essential while keeping the component count and complexity to a minimum.
In summary, this circuit design leverages the properties of various materials and the unique characteristics of the emitter follower configuration to achieve an efficient and effective solution for low-current applications.Probe/contacts may use a non-reactive metal. Gold or silver plated contacts from an old relay May be Used, however a cheap alternative is to wire alternate copper strips from a piece of veroboard. These will eventually oxidize over but as very little current is flowing in the base circuit, the higher impedance the caused by oxidization is not Impo
rtant. No base resistor is Necessary as the transistor is in emitter follower, current limit being the impedance at the emitter (the oscillator circuit). 🔗 External reference