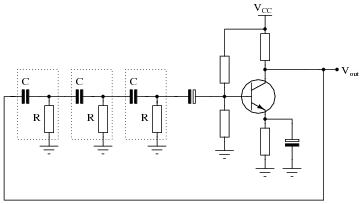
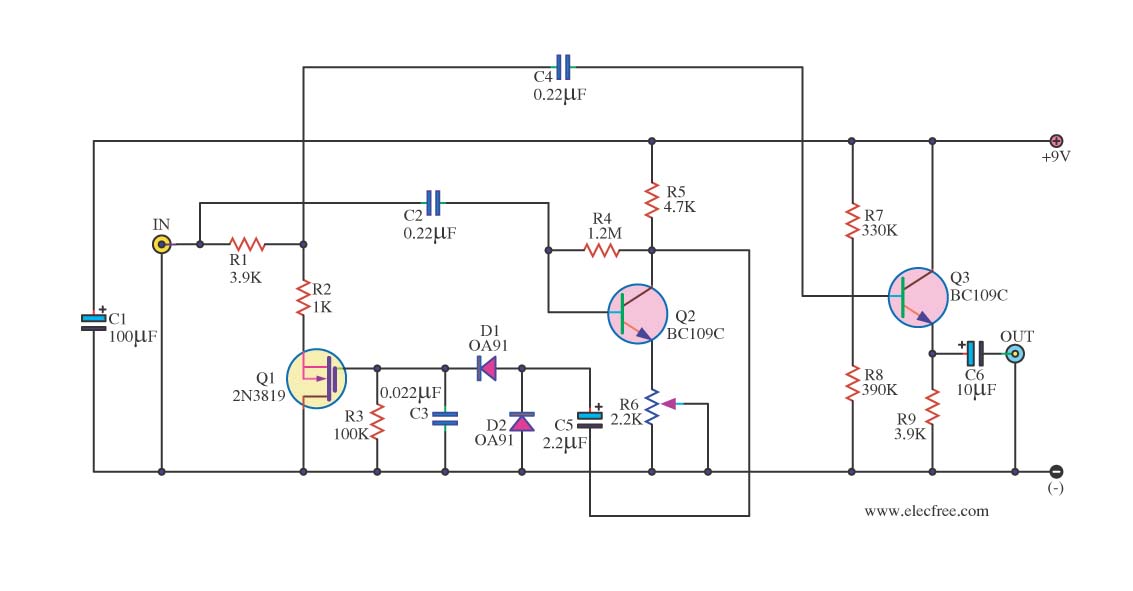
Thyristor-controlled three-level withdrawable circuits
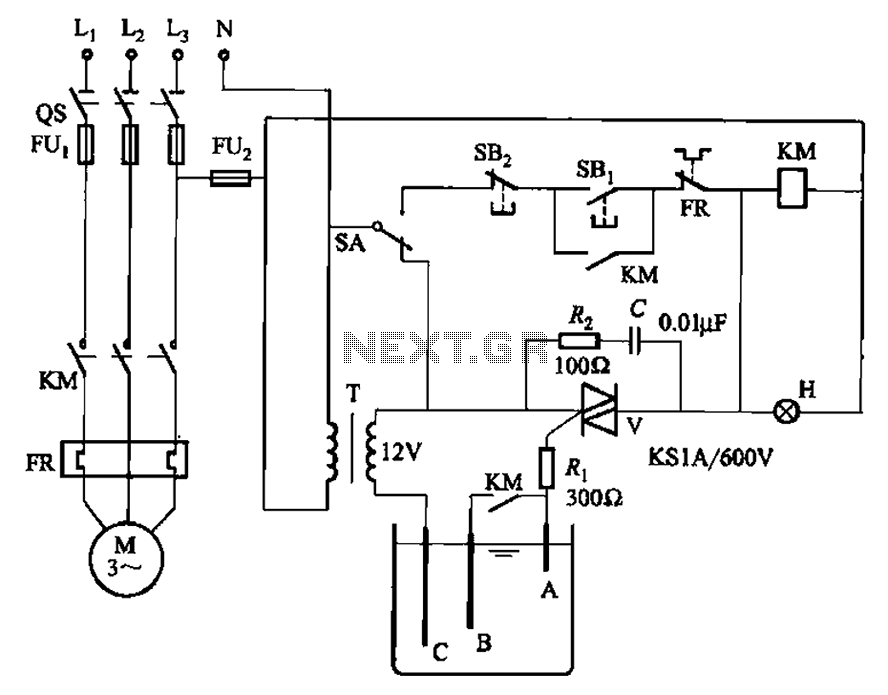
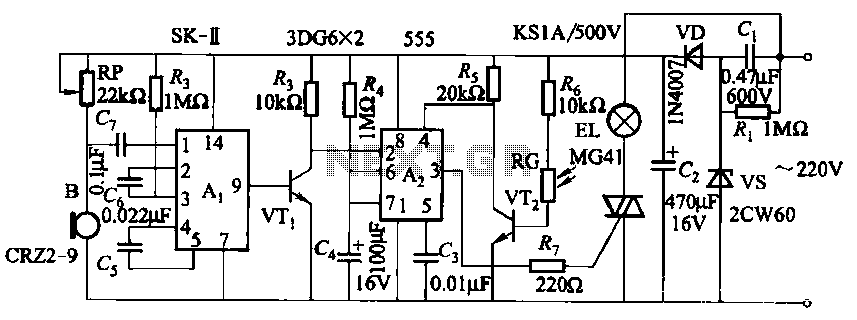
Bidirectional thyristor control manages the trigger voltage output from the step-down transformer at 12V when the water activates the electrodes. It is part of a drawable circuit that regulates the level. The circuit includes a current-limiting resistor (Ri) to prevent damage to the tubes, and a capacitance-resistance protection circuit (Rz, C) to safeguard the TRIAC from overvoltage damage.
The described circuit employs a bidirectional thyristor, commonly known as a TRIAC, which is suitable for controlling AC loads. The control mechanism is initiated by the output from a step-down transformer, which provides a reduced voltage of 12V. This voltage is crucial for activating the electrodes that facilitate the water flow, thus allowing for an efficient control system.
The current-limiting resistor (Ri) plays a vital role in protecting the circuit components. It is strategically placed in series with the load to limit the amount of current flowing through the system. This prevents excessive current that could lead to overheating or burning of the tubes, which are essential for the operation of the electrodes.
Additionally, the circuit incorporates a capacitance-resistance (RC) protection scheme (Rz, C) to shield the TRIAC from potential overvoltage conditions. The resistor (Rz) and capacitor (C) work together to absorb transient voltage spikes that may occur during operation. This protection is crucial, as TRIACs are sensitive to overvoltage, which can lead to failure or erratic behavior.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines a bidirectional thyristor control with protective components to ensure reliable operation in applications where water level control is necessary. The thoughtful integration of a current-limiting resistor and an RC protection circuit enhances the durability and functionality of the system, making it suitable for various electronic applications. Bidirectional thyristor control, control the very trigger voltage output from the step-down transformer T 12V (when the water is turned on electrodes). It belongs to the withdr awable circuit controlled level. Figure, Ri current limiting resistor, so as not to burn the tubes; Rz, C is capacitance-resistance protection circuit to protect TRIAC from overvoltage damage.
The described circuit employs a bidirectional thyristor, commonly known as a TRIAC, which is suitable for controlling AC loads. The control mechanism is initiated by the output from a step-down transformer, which provides a reduced voltage of 12V. This voltage is crucial for activating the electrodes that facilitate the water flow, thus allowing for an efficient control system.
The current-limiting resistor (Ri) plays a vital role in protecting the circuit components. It is strategically placed in series with the load to limit the amount of current flowing through the system. This prevents excessive current that could lead to overheating or burning of the tubes, which are essential for the operation of the electrodes.
Additionally, the circuit incorporates a capacitance-resistance (RC) protection scheme (Rz, C) to shield the TRIAC from potential overvoltage conditions. The resistor (Rz) and capacitor (C) work together to absorb transient voltage spikes that may occur during operation. This protection is crucial, as TRIACs are sensitive to overvoltage, which can lead to failure or erratic behavior.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines a bidirectional thyristor control with protective components to ensure reliable operation in applications where water level control is necessary. The thoughtful integration of a current-limiting resistor and an RC protection circuit enhances the durability and functionality of the system, making it suitable for various electronic applications. Bidirectional thyristor control, control the very trigger voltage output from the step-down transformer T 12V (when the water is turned on electrodes). It belongs to the withdr awable circuit controlled level. Figure, Ri current limiting resistor, so as not to burn the tubes; Rz, C is capacitance-resistance protection circuit to protect TRIAC from overvoltage damage.