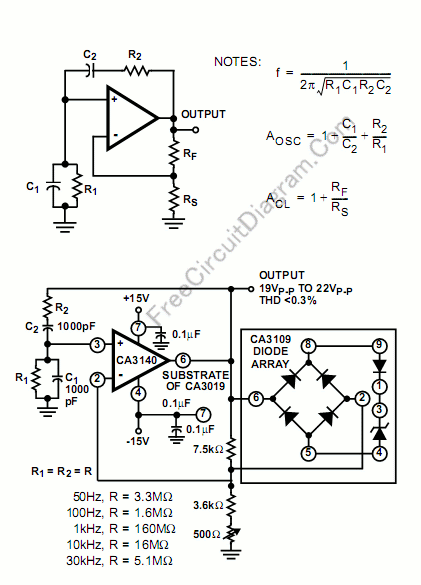
Single-phase torque motor speed control circuit 2
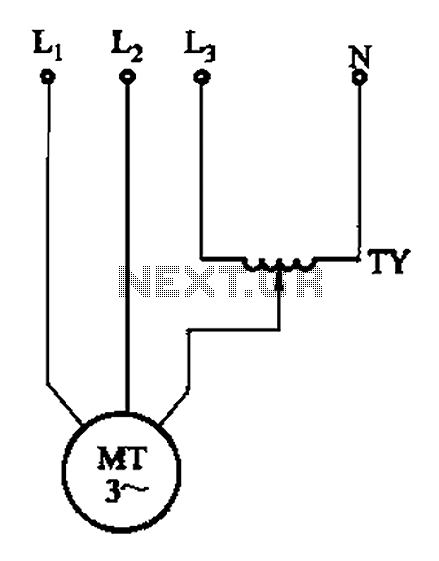
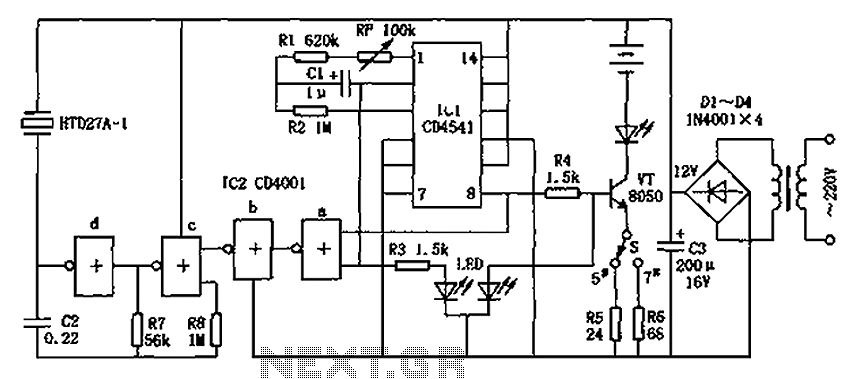
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-175 features a regulator connected between one phase and neutral. It is designed for use with a 380V torque motor. This method offers advantages over the serious line imbalance approach, resulting in improved operating conditions for the motor. Under these conditions, the motor can function effectively for extended periods at moderate speeds without producing negative torque; however, the range for torque adjustment is limited.
The circuit utilizes a phase control regulator, which modulates the voltage supplied to the motor by varying the phase angle of the input waveform. This allows for a more stable operation by reducing the impact of line imbalances that can occur in three-phase systems. By connecting the regulator between one phase and neutral, it effectively provides a controlled voltage to the motor, enabling it to operate smoothly under varying load conditions.
The 380V torque motor is specifically designed to handle high torque applications, making it suitable for industrial environments. The regulator ensures that the motor receives the appropriate voltage to maintain optimal performance without exceeding its rated specifications. The limitation in torque adjustment range is a trade-off for the enhanced stability and efficiency provided by this configuration.
To implement this circuit, attention must be given to the selection of components, such as the regulator type, which should be capable of handling the motor's current and voltage requirements. Proper heat dissipation mechanisms should also be integrated to prevent overheating during prolonged operation. Additionally, protective devices such as fuses or circuit breakers should be included to safeguard against overload conditions.
Overall, this circuit design is effective for applications where maintaining a consistent torque output is critical, while also reducing the risks associated with phase imbalances in the electrical supply. Circuit shown in Figure 3-175. Regulator connected between one phase and neutral. It applies to the rated voltage of 380V torque motor. This method than the degree of the imbal ance serious line method, so the motor is better working conditions, long working for speed is not too high, basically no negative torque, but the torque adjustment range is narrow.
The circuit utilizes a phase control regulator, which modulates the voltage supplied to the motor by varying the phase angle of the input waveform. This allows for a more stable operation by reducing the impact of line imbalances that can occur in three-phase systems. By connecting the regulator between one phase and neutral, it effectively provides a controlled voltage to the motor, enabling it to operate smoothly under varying load conditions.
The 380V torque motor is specifically designed to handle high torque applications, making it suitable for industrial environments. The regulator ensures that the motor receives the appropriate voltage to maintain optimal performance without exceeding its rated specifications. The limitation in torque adjustment range is a trade-off for the enhanced stability and efficiency provided by this configuration.
To implement this circuit, attention must be given to the selection of components, such as the regulator type, which should be capable of handling the motor's current and voltage requirements. Proper heat dissipation mechanisms should also be integrated to prevent overheating during prolonged operation. Additionally, protective devices such as fuses or circuit breakers should be included to safeguard against overload conditions.
Overall, this circuit design is effective for applications where maintaining a consistent torque output is critical, while also reducing the risks associated with phase imbalances in the electrical supply. Circuit shown in Figure 3-175. Regulator connected between one phase and neutral. It applies to the rated voltage of 380V torque motor. This method than the degree of the imbal ance serious line method, so the motor is better working conditions, long working for speed is not too high, basically no negative torque, but the torque adjustment range is narrow.