DC motor armature resistance in series to start debugging circuit 2
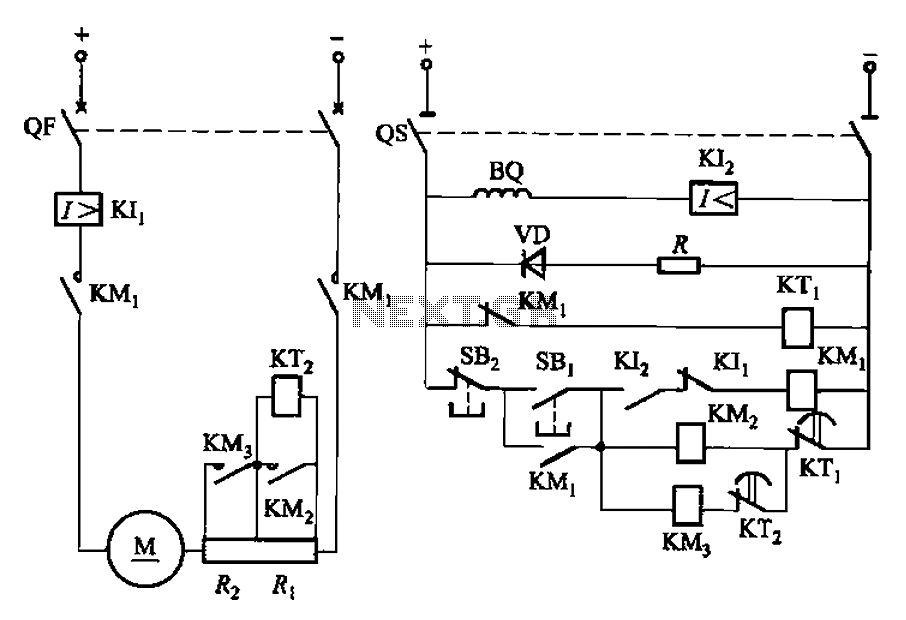
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-191 features a DC motor armature circuit that includes two series startup resistors, Ri and Rz. The operation of the motor is controlled using buttons for starting and stopping. During the startup phase, two relays, KTi and KTz, are automatically activated to engage the startup resistors.
The described circuit operates a DC motor with a two-stage startup mechanism to manage inrush current and ensure smooth operation. The resistors Ri and Rz are strategically placed in series with the motor's armature to limit the initial current when the motor is powered on. This is essential for preventing damage to the motor and associated components due to high starting currents.
The control of the motor is facilitated by push-button switches, which allow the user to initiate or halt the motor's operation. When the start button is pressed, it energizes the relays KTi and KTz, which subsequently engage the startup resistors. This configuration allows the motor to ramp up to its operational speed gradually, reducing mechanical stress and electrical strain.
Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the relays automatically disengage the startup resistors, allowing the motor to operate at full efficiency. This automatic cut-in feature is crucial for optimizing performance and extending the lifespan of the motor. The use of relays in this circuit not only provides a reliable means of control but also allows for the incorporation of additional safety features, such as overload protection, depending on the specific application requirements.
Overall, the design of this DC motor control circuit exemplifies a practical approach to managing motor startup conditions, ensuring both operational efficiency and component protection. Circuit shown in Figure 3-191. The line in the DC motor armature circuit in series two-stage startup resistor Ri, Rz, Lee realized using the buttons to start and stop the motor control. During startup time by two relays KTi, KTz automatic cut in addition to two start-up resistor.
The described circuit operates a DC motor with a two-stage startup mechanism to manage inrush current and ensure smooth operation. The resistors Ri and Rz are strategically placed in series with the motor's armature to limit the initial current when the motor is powered on. This is essential for preventing damage to the motor and associated components due to high starting currents.
The control of the motor is facilitated by push-button switches, which allow the user to initiate or halt the motor's operation. When the start button is pressed, it energizes the relays KTi and KTz, which subsequently engage the startup resistors. This configuration allows the motor to ramp up to its operational speed gradually, reducing mechanical stress and electrical strain.
Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the relays automatically disengage the startup resistors, allowing the motor to operate at full efficiency. This automatic cut-in feature is crucial for optimizing performance and extending the lifespan of the motor. The use of relays in this circuit not only provides a reliable means of control but also allows for the incorporation of additional safety features, such as overload protection, depending on the specific application requirements.
Overall, the design of this DC motor control circuit exemplifies a practical approach to managing motor startup conditions, ensuring both operational efficiency and component protection. Circuit shown in Figure 3-191. The line in the DC motor armature circuit in series two-stage startup resistor Ri, Rz, Lee realized using the buttons to start and stop the motor control. During startup time by two relays KTi, KTz automatic cut in addition to two start-up resistor.