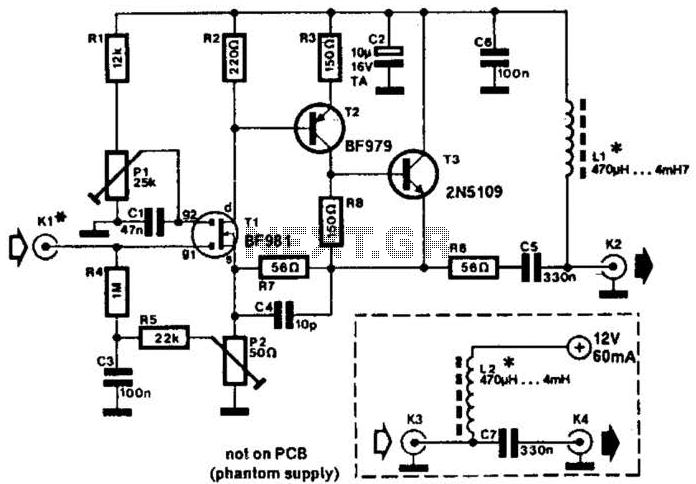
High-quality low-noise preamplifier
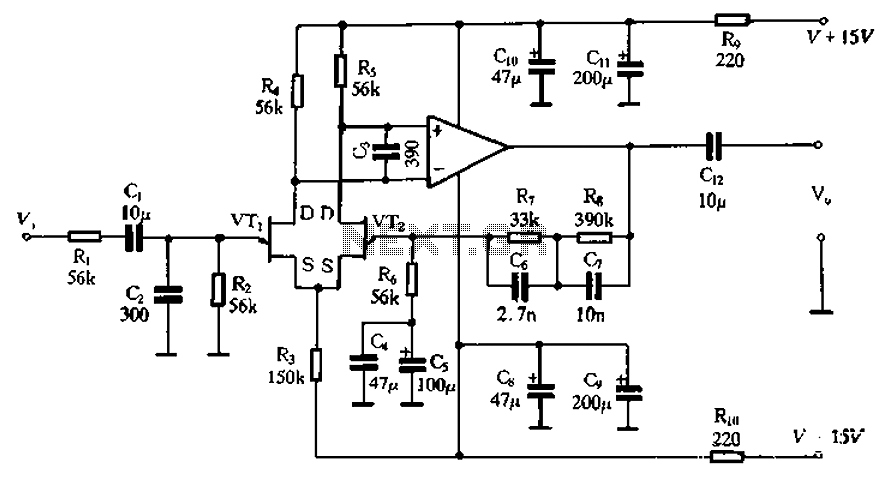
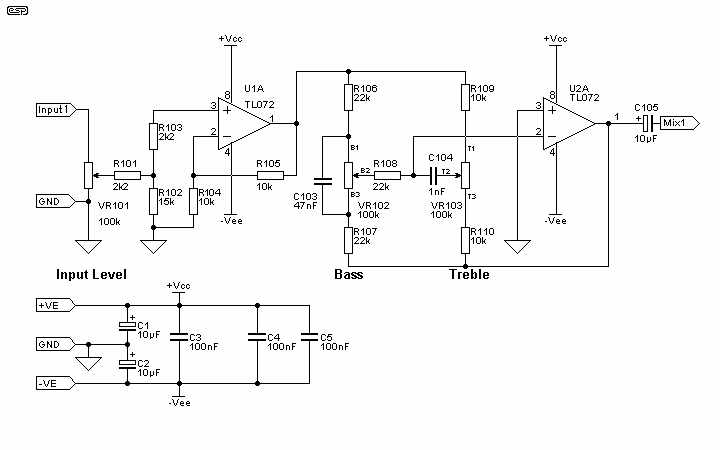
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-8 involves an input signal that passes through a low-pass filter before entering the differential amplifier. The composition of the FET (Field Effect Transistor) is evaluated at the preamplifier output. The differential amplifier connects to the non-inverting input and the inverting input of an operational amplifier. Given that the operational amplifier operates as a differential circuit, the signal output from the differential circuit's FET is processed by the operational amplifier after being amplified by the differential amplifier. The circuit includes an RIAA phono equalization circuit with components such as R7, C6, and C7. The differential input FET can be a 3DJ4F or another low-noise, high-quality FET with an IDSS of 2mA and a matching error of 3%. The operational amplifier can be a TL072, TU082, or another high-performance option like the NE5532. Metal film resistors with Class I accuracy are recommended for the resistive components, while polyester capacitors are suggested for the capacitive coupling. The power supply should be a positive-negative symmetrical configuration.
The described circuit is designed to process audio signals, particularly for applications such as phono preamplifiers. The low-pass filter at the input serves to eliminate high-frequency noise, ensuring that only the desired audio frequencies are amplified. The differential amplifier stage allows for the rejection of common-mode noise, enhancing the signal integrity before it reaches the operational amplifier.
The choice of FET, such as the 3DJ4F, is critical as it provides low noise and high gain characteristics essential for audio applications. The specified IDSS of 2mA ensures that the FET operates within its optimal range, while the 3% matching error is acceptable for maintaining signal fidelity. The operational amplifiers recommended, including the TL072 and NE5532, are known for their low distortion and high bandwidth, making them suitable for high-quality audio processing.
The RIAA equalization circuit is crucial for restoring the frequency response of vinyl records, which is typically modified during the cutting process. Components R7, C6, and C7 are configured to achieve the required frequency response curve as per RIAA standards.
For the resistive components, the use of metal film resistors ensures minimal thermal noise and high accuracy, which is vital for maintaining the integrity of the audio signal. The polyester capacitors used for coupling are chosen for their stability and low leakage, further enhancing the circuit's performance.
Finally, the symmetrical power supply is essential for providing the operational amplifier and FET with the necessary voltage levels to operate efficiently, ensuring that the circuit can handle dynamic audio signals without distortion. This well-designed circuit configuration is suitable for high-fidelity audio applications, ensuring optimal performance in signal amplification and processing. Circuit shown in Figure 3-8. Input signal through a low pass filter to the input of the differential amplifier FET former composition are evaluated once preamplifier output of the differential amplifier are input operational amplifier din-inverting input and an inverting input terminal. Since the input terminal of the operational amplifier is a differential circuit, the signal output from the differential circuit field effect transistor, the op amp input after at least has had a differential amplifier.
RIAA phono equalization circuit o the R7, people and C6, C7, etc differential input FET can be used 3DJ4F or other low-noise high-quality FET, IDSS 2mA, press IDSS paired t error 3%. Op amp can be used TL0 72, TU082 or other high-performance op amp NE5532. Selected resistance metal film resistors, Class I accuracy. The amount of capacitance with highly capacitive coupling capacitors should be polyester capacitors. Power supply with positive negative symmetrical power supply.
The described circuit is designed to process audio signals, particularly for applications such as phono preamplifiers. The low-pass filter at the input serves to eliminate high-frequency noise, ensuring that only the desired audio frequencies are amplified. The differential amplifier stage allows for the rejection of common-mode noise, enhancing the signal integrity before it reaches the operational amplifier.
The choice of FET, such as the 3DJ4F, is critical as it provides low noise and high gain characteristics essential for audio applications. The specified IDSS of 2mA ensures that the FET operates within its optimal range, while the 3% matching error is acceptable for maintaining signal fidelity. The operational amplifiers recommended, including the TL072 and NE5532, are known for their low distortion and high bandwidth, making them suitable for high-quality audio processing.
The RIAA equalization circuit is crucial for restoring the frequency response of vinyl records, which is typically modified during the cutting process. Components R7, C6, and C7 are configured to achieve the required frequency response curve as per RIAA standards.
For the resistive components, the use of metal film resistors ensures minimal thermal noise and high accuracy, which is vital for maintaining the integrity of the audio signal. The polyester capacitors used for coupling are chosen for their stability and low leakage, further enhancing the circuit's performance.
Finally, the symmetrical power supply is essential for providing the operational amplifier and FET with the necessary voltage levels to operate efficiently, ensuring that the circuit can handle dynamic audio signals without distortion. This well-designed circuit configuration is suitable for high-fidelity audio applications, ensuring optimal performance in signal amplification and processing. Circuit shown in Figure 3-8. Input signal through a low pass filter to the input of the differential amplifier FET former composition are evaluated once preamplifier output of the differential amplifier are input operational amplifier din-inverting input and an inverting input terminal. Since the input terminal of the operational amplifier is a differential circuit, the signal output from the differential circuit field effect transistor, the op amp input after at least has had a differential amplifier.
RIAA phono equalization circuit o the R7, people and C6, C7, etc differential input FET can be used 3DJ4F or other low-noise high-quality FET, IDSS 2mA, press IDSS paired t error 3%. Op amp can be used TL0 72, TU082 or other high-performance op amp NE5532. Selected resistance metal film resistors, Class I accuracy. The amount of capacitance with highly capacitive coupling capacitors should be polyester capacitors. Power supply with positive negative symmetrical power supply.