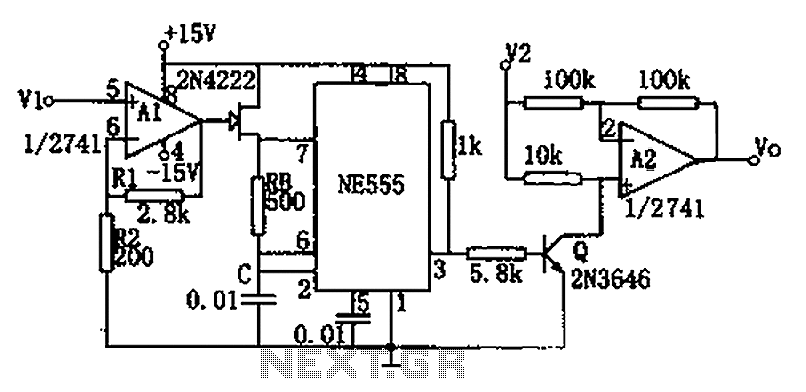
555 ultra-low frequency signal generator circuit diagram of a millivolt
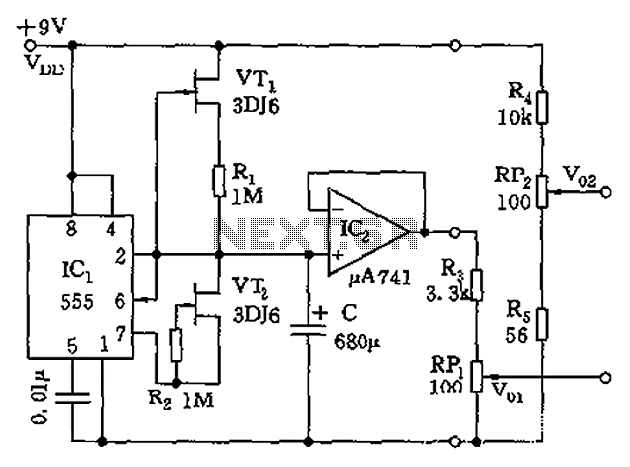
The circuit depicted in the figure is a generator that includes an oscillator, a voltage follower, a zero amplitude adjustment, and a zero shift circuit. It is utilized as a self-balancing recorder for testing signals. The output signal ranges from 0 to 50 mV, with a continuously adjustable output voltage of 25 mV for both positive and negative zero shifts. The duty cycle operates between 30 and 40 Hz. The circuit is constructed using IC1 (555), along with transistors VT1 and VT2, resistors R1 and R2, and capacitor C, forming an astable multivibrator. VT1, R1, and VT2, R2 create the charge and discharge current sources. IC2 functions as an operational amplifier configured as a voltage follower, primarily for impedance matching, providing a low impedance output. The output voltage V0 is determined by the difference V01 - V02, and can be adjusted to achieve the desired zero amplitude level and shift through the use of potentiometers RP1 and RP2.
The circuit functions as a versatile signal generator, primarily designed for applications in self-balancing recorders. The inclusion of an astable multivibrator, realized through the 555 timer IC, allows for the generation of a square wave signal. This signal can be finely tuned to operate within a specified frequency range, making it suitable for various testing scenarios.
The output stage, implemented with an operational amplifier configured as a voltage follower, serves to buffer the output signal. This configuration ensures that the output impedance is significantly lower than that of the input, allowing for better interfacing with subsequent stages of the circuit or external devices. The voltage follower also prevents loading effects that could distort the signal integrity.
The adjustable output voltage, with a range of 0 to 50 mV, is crucial for applications that require precise control over signal levels. The ability to continuously adjust the output voltage at 25 mV for both positive and negative shifts enhances the circuit's flexibility, enabling it to accommodate various testing conditions.
Overall, the circuit's design leverages standard components to create a reliable and adaptable generator that can meet the needs of self-balancing recorders and other related applications, ensuring accurate signal generation and manipulation. Circuit shown in Figure generator consists of an oscillator, voltage follower, the amplitude of zero, zero shift circuit. Used as a self-balancing recorder running test signal source, output signal 0 ~ 50mV, 25mV output voltage is continuously adjustable positive and negative zero shift, the Duty Cycle 30 ~ 40Hz. IC1 (555) and VT1, VT2, R1, R2, C composition astable multivibrator, VT1, R1 and VT2, R2 respectively composed of charge and discharge current source.
IC2 operational amplifier as a voltage follower used primarily for impedance matching, low impedance output. The output voltage V0 V01-V02, by adjusting the RP1, RP2, can achieve zero amplitude level and migration.
The circuit functions as a versatile signal generator, primarily designed for applications in self-balancing recorders. The inclusion of an astable multivibrator, realized through the 555 timer IC, allows for the generation of a square wave signal. This signal can be finely tuned to operate within a specified frequency range, making it suitable for various testing scenarios.
The output stage, implemented with an operational amplifier configured as a voltage follower, serves to buffer the output signal. This configuration ensures that the output impedance is significantly lower than that of the input, allowing for better interfacing with subsequent stages of the circuit or external devices. The voltage follower also prevents loading effects that could distort the signal integrity.
The adjustable output voltage, with a range of 0 to 50 mV, is crucial for applications that require precise control over signal levels. The ability to continuously adjust the output voltage at 25 mV for both positive and negative shifts enhances the circuit's flexibility, enabling it to accommodate various testing conditions.
Overall, the circuit's design leverages standard components to create a reliable and adaptable generator that can meet the needs of self-balancing recorders and other related applications, ensuring accurate signal generation and manipulation. Circuit shown in Figure generator consists of an oscillator, voltage follower, the amplitude of zero, zero shift circuit. Used as a self-balancing recorder running test signal source, output signal 0 ~ 50mV, 25mV output voltage is continuously adjustable positive and negative zero shift, the Duty Cycle 30 ~ 40Hz. IC1 (555) and VT1, VT2, R1, R2, C composition astable multivibrator, VT1, R1 and VT2, R2 respectively composed of charge and discharge current source.
IC2 operational amplifier as a voltage follower used primarily for impedance matching, low impedance output. The output voltage V0 V01-V02, by adjusting the RP1, RP2, can achieve zero amplitude level and migration.