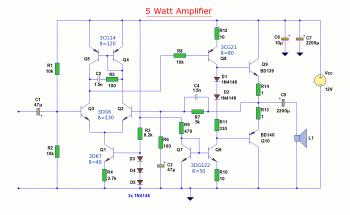
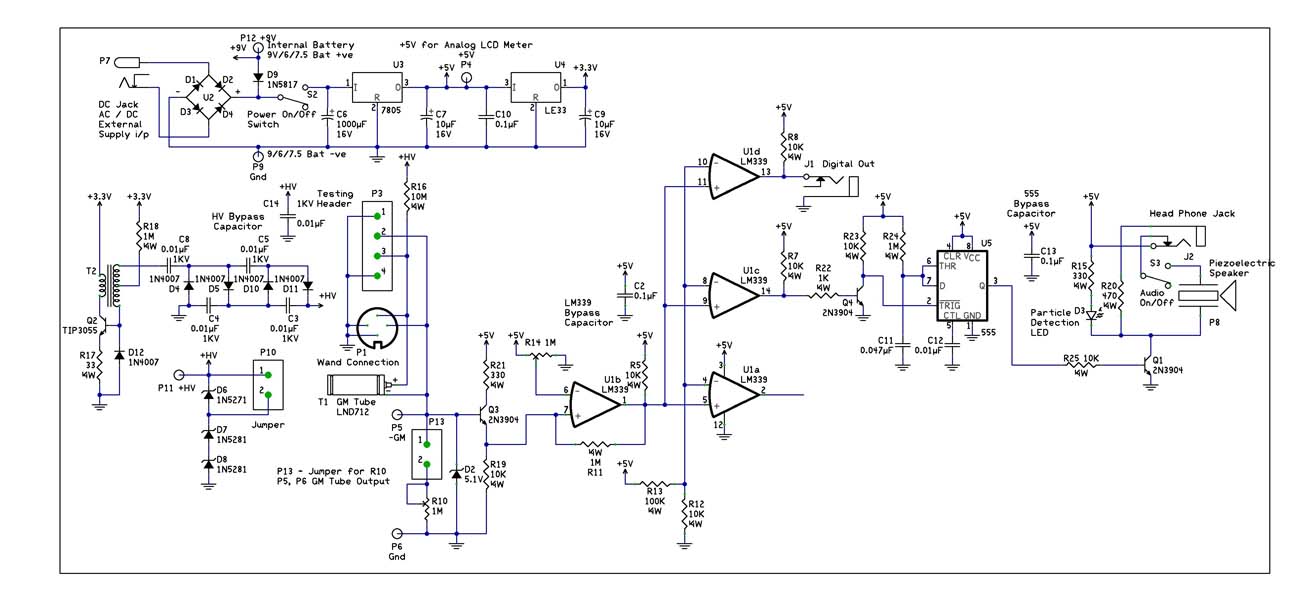
015Watt amplifier schematic
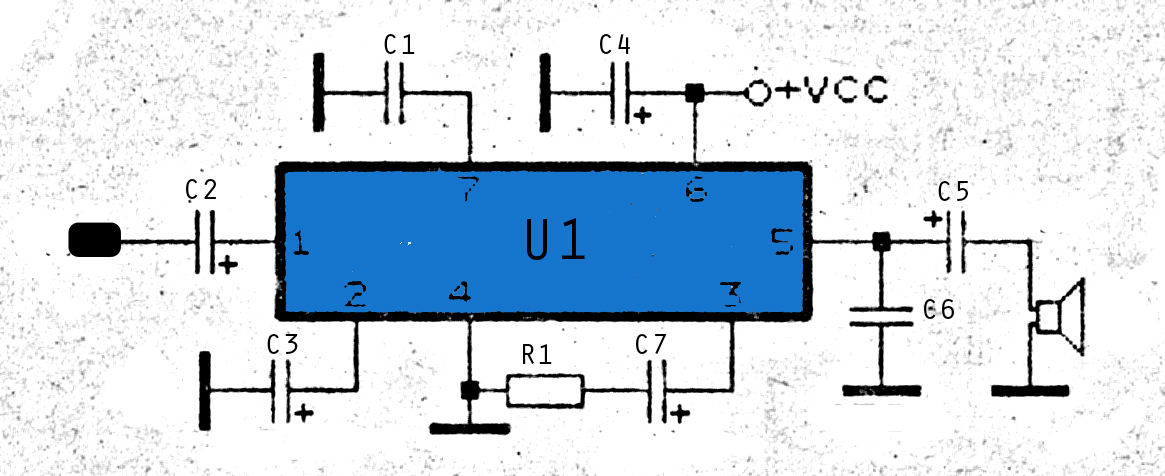
The amplifier circuit is highly suitable for use in FM radio receivers. It requires a supply voltage of 8 to 25 Volt DC and can deliver a maximum output power of 0.15W. Refer to the schematic below.
The described amplifier circuit is designed to enhance signal strength in FM radio receivers, which is crucial for maintaining audio clarity and reducing noise. The operational voltage range of 8 to 25 Volts DC allows for versatility in various applications, accommodating different power supply configurations commonly found in consumer electronics.
The circuit typically includes a transistor or operational amplifier configured to amplify weak RF signals received by the antenna. Key components may include resistors to set the gain, capacitors for coupling and decoupling, and possibly inductors for tuning purposes. The output stage is designed to deliver up to 0.15W, making it suitable for driving small speakers or headphones directly.
In terms of performance, the circuit should be optimized for low distortion and a wide frequency response to ensure that the audio output remains faithful to the original broadcast. Proper layout considerations, such as minimizing ground loops and shielding sensitive components, are essential to maintain signal integrity.
The schematic would illustrate the interconnections between these components, providing clear guidance on component values and configurations necessary for achieving the desired performance. This amplifier circuit can be an essential building block for hobbyists and engineers working on FM radio projects, enhancing the overall listening experience.Amplifier circuit is also very suitable when used in fm radio receiver. Supply voltage required 8 - 25 Volt DC with a maximum output power 0. 15W. See Schematic below. 🔗 External reference
The described amplifier circuit is designed to enhance signal strength in FM radio receivers, which is crucial for maintaining audio clarity and reducing noise. The operational voltage range of 8 to 25 Volts DC allows for versatility in various applications, accommodating different power supply configurations commonly found in consumer electronics.
The circuit typically includes a transistor or operational amplifier configured to amplify weak RF signals received by the antenna. Key components may include resistors to set the gain, capacitors for coupling and decoupling, and possibly inductors for tuning purposes. The output stage is designed to deliver up to 0.15W, making it suitable for driving small speakers or headphones directly.
In terms of performance, the circuit should be optimized for low distortion and a wide frequency response to ensure that the audio output remains faithful to the original broadcast. Proper layout considerations, such as minimizing ground loops and shielding sensitive components, are essential to maintain signal integrity.
The schematic would illustrate the interconnections between these components, providing clear guidance on component values and configurations necessary for achieving the desired performance. This amplifier circuit can be an essential building block for hobbyists and engineers working on FM radio projects, enhancing the overall listening experience.Amplifier circuit is also very suitable when used in fm radio receiver. Supply voltage required 8 - 25 Volt DC with a maximum output power 0. 15W. See Schematic below. 🔗 External reference