1.5V LED Flasher Oscillator

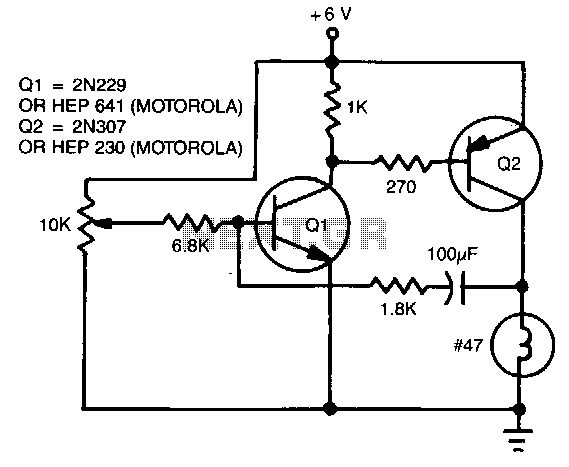
The 8-lead plastic mini-DIP LM3909 integrated circuit was developed by National Semiconductor in the mid-1970s. It is a monolithic oscillator specifically designed to flash Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). By utilizing the timing capacitor for voltage boosting, it can deliver pulses of 2 volts or more to the LED while operating on a supply voltage of 1.5 volts or less. The circuit is inherently self-starting and requires only the addition of a battery and capacitor to function as an LED flasher. However, the manufacturer discontinued production of this chip in 1998. Consequently, in response to requests from various correspondents, an attempt was made to emulate the operation of this IC using common discrete components, yielding unexpectedly satisfactory results.
The LM3909 integrated circuit operates as a simple yet effective LED flasher. Its design includes a monolithic oscillator that generates a square wave output, which is used to drive the LED. The oscillator's frequency and duty cycle can be adjusted by selecting appropriate values for the timing capacitor and resistor connected to the chip. The essential feature of the LM3909 is its ability to boost the voltage across the LED beyond the supply voltage, allowing for brighter illumination even at lower power supplies.
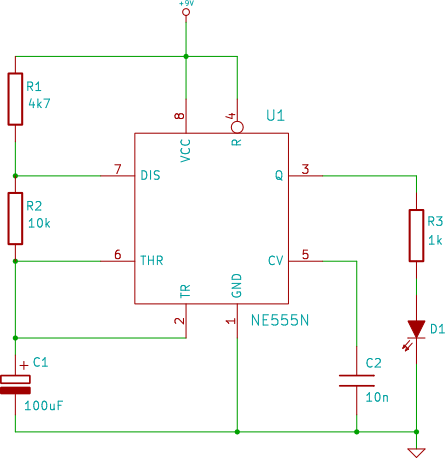
To replicate the functionality of the LM3909 using discrete components, a similar oscillator circuit can be constructed using a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. In this configuration, the timing capacitor and resistors can be chosen to set the desired flashing frequency. A transistor can be employed to drive the LED, providing the necessary current amplification to achieve the desired brightness. By incorporating a charge pump circuit or a boost converter, the output voltage can be increased to ensure that the LED receives sufficient forward voltage for optimal operation.
The resulting circuit can be compact and cost-effective, utilizing readily available components. The self-starting nature of the original LM3909 can be mimicked by ensuring that the circuit is designed to stabilize quickly after power is applied. Overall, this approach provides a viable alternative for applications requiring LED flashing without relying on the discontinued LM3909 IC.The 8-lead plastic mini-DIP LM3909 IC was developed by National Semiconductor in the mid `seventies of the past century. It was a monolithic oscillator specifically designed to flash Light Emitting Diodes. By using the timing capacitor for voltage boost, it delivered pulses of 2 or more volts to the LED while operating on a supply of 1.
5V or less. The circuit was inherently self-starting, and required addition of only a battery and capacitor to function as an LED flasher. Unfortunately, since 1998, the manufacturer discontinued the production of this chip. For this reason, and on request of some correspondents, I tried to emulate this IC operation using common discrete components, obtaining unexpected satisfactory results.
🔗 External reference
The LM3909 integrated circuit operates as a simple yet effective LED flasher. Its design includes a monolithic oscillator that generates a square wave output, which is used to drive the LED. The oscillator's frequency and duty cycle can be adjusted by selecting appropriate values for the timing capacitor and resistor connected to the chip. The essential feature of the LM3909 is its ability to boost the voltage across the LED beyond the supply voltage, allowing for brighter illumination even at lower power supplies.
To replicate the functionality of the LM3909 using discrete components, a similar oscillator circuit can be constructed using a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. In this configuration, the timing capacitor and resistors can be chosen to set the desired flashing frequency. A transistor can be employed to drive the LED, providing the necessary current amplification to achieve the desired brightness. By incorporating a charge pump circuit or a boost converter, the output voltage can be increased to ensure that the LED receives sufficient forward voltage for optimal operation.
The resulting circuit can be compact and cost-effective, utilizing readily available components. The self-starting nature of the original LM3909 can be mimicked by ensuring that the circuit is designed to stabilize quickly after power is applied. Overall, this approach provides a viable alternative for applications requiring LED flashing without relying on the discontinued LM3909 IC.The 8-lead plastic mini-DIP LM3909 IC was developed by National Semiconductor in the mid `seventies of the past century. It was a monolithic oscillator specifically designed to flash Light Emitting Diodes. By using the timing capacitor for voltage boost, it delivered pulses of 2 or more volts to the LED while operating on a supply of 1.
5V or less. The circuit was inherently self-starting, and required addition of only a battery and capacitor to function as an LED flasher. Unfortunately, since 1998, the manufacturer discontinued the production of this chip. For this reason, and on request of some correspondents, I tried to emulate this IC operation using common discrete components, obtaining unexpected satisfactory results.
🔗 External reference