100W Guitar Amplifier
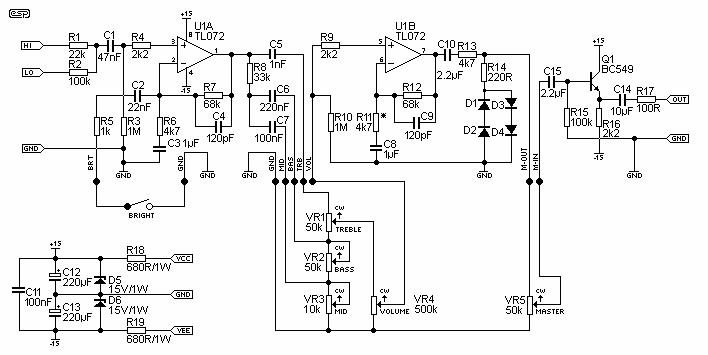
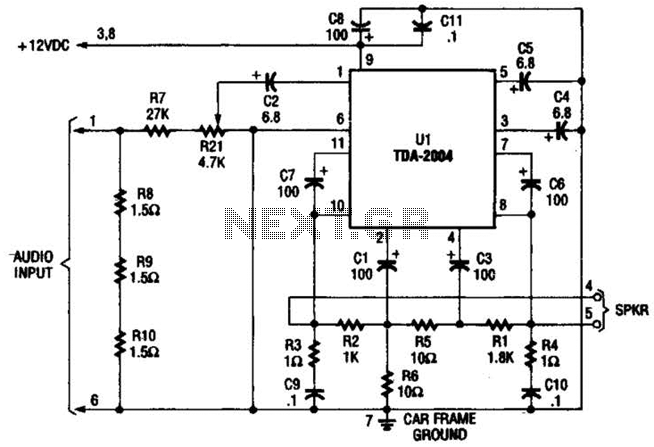
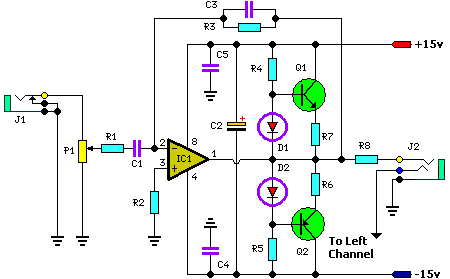
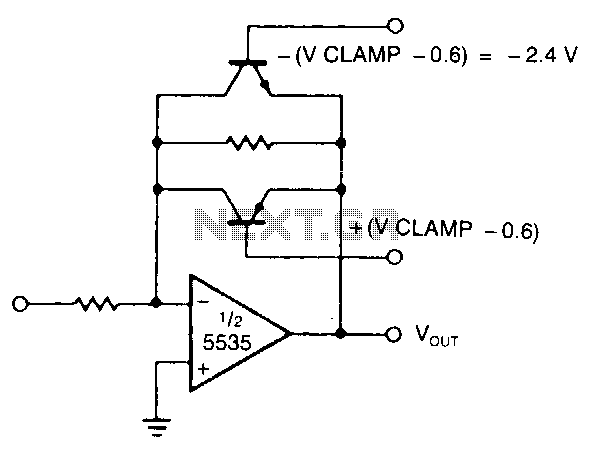
The amp is rated at 100W into a 4 Ohms load, as this is typical of a "combo" type amp with two 8 Ohm speakers in parallel. Alternatively, you can run the amp into a "quad" box (4 x 8 Ohm speakers in series parallel - see Figure 5 in Project 27b, the original article) and will get about 60 Watts. For the really adventurous, 2 quad boxes and the amp head will provide 100W, but will be much louder than the twin. More: The preamp circuit is shown in Figure 1, and has a few interesting characteristics that separate it from the "normal" - assuming that there is such a thing. This is simple but elegant design, that provides excellent tonal range. The gain structure.
The amplifier described operates at a rated output of 100W when connected to a 4 Ohm load, which is commonly seen in combo amplifiers utilizing two 8 Ohm speakers wired in parallel. This configuration allows the amplifier to deliver its full power efficiently while maintaining a manageable impedance. An alternative configuration involves connecting the amplifier to a quad box, which consists of four 8 Ohm speakers arranged in a series-parallel configuration. In this setup, the total load impedance is effectively reduced to 4 Ohms, allowing the amplifier to output approximately 60 Watts. For enhanced sound pressure levels, utilizing two quad boxes in conjunction with the amplifier head will enable the system to reach the full 100W output, significantly increasing the volume compared to the dual speaker setup.
The preamp circuit, as illustrated in Figure 1, exhibits unique characteristics that distinguish it from conventional designs. The simplicity of the design belies its sophistication, as it is engineered to provide a broad tonal range suitable for various musical styles. The gain structure within the preamp is optimized to allow for a versatile response, accommodating both clean and distorted signals without sacrificing audio fidelity. The thoughtful arrangement of components within the circuit ensures minimal noise and distortion, contributing to the overall performance of the amplifier. This preamp design offers musicians the ability to shape their sound effectively, making it a valuable feature in the amplifier's architecture.The amp is rated at 100W into a 4 Ohms load, as this is typical of a "combo" type amp with two 8 Ohm speakers in parallel. Alternatively, you can run the amp into a "quad" box (4 x 8 Ohm speakers in series parallel - see Figure 5 in Project 27b, the original article) and will get about 60 Watts.
For the really adventurous, 2 quad boxes and the amp head will provide 100W, but will be much louder than the twin. The preamp circuit is shown in Figure 1, and has a few interesting characteristics that separate it from the "normal" - assuming that there is such a thing. This is simple but elegant design, that provides excellent tonal range. The gain structu 🔗 External reference
The amplifier described operates at a rated output of 100W when connected to a 4 Ohm load, which is commonly seen in combo amplifiers utilizing two 8 Ohm speakers wired in parallel. This configuration allows the amplifier to deliver its full power efficiently while maintaining a manageable impedance. An alternative configuration involves connecting the amplifier to a quad box, which consists of four 8 Ohm speakers arranged in a series-parallel configuration. In this setup, the total load impedance is effectively reduced to 4 Ohms, allowing the amplifier to output approximately 60 Watts. For enhanced sound pressure levels, utilizing two quad boxes in conjunction with the amplifier head will enable the system to reach the full 100W output, significantly increasing the volume compared to the dual speaker setup.
The preamp circuit, as illustrated in Figure 1, exhibits unique characteristics that distinguish it from conventional designs. The simplicity of the design belies its sophistication, as it is engineered to provide a broad tonal range suitable for various musical styles. The gain structure within the preamp is optimized to allow for a versatile response, accommodating both clean and distorted signals without sacrificing audio fidelity. The thoughtful arrangement of components within the circuit ensures minimal noise and distortion, contributing to the overall performance of the amplifier. This preamp design offers musicians the ability to shape their sound effectively, making it a valuable feature in the amplifier's architecture.The amp is rated at 100W into a 4 Ohms load, as this is typical of a "combo" type amp with two 8 Ohm speakers in parallel. Alternatively, you can run the amp into a "quad" box (4 x 8 Ohm speakers in series parallel - see Figure 5 in Project 27b, the original article) and will get about 60 Watts.
For the really adventurous, 2 quad boxes and the amp head will provide 100W, but will be much louder than the twin. The preamp circuit is shown in Figure 1, and has a few interesting characteristics that separate it from the "normal" - assuming that there is such a thing. This is simple but elegant design, that provides excellent tonal range. The gain structu 🔗 External reference