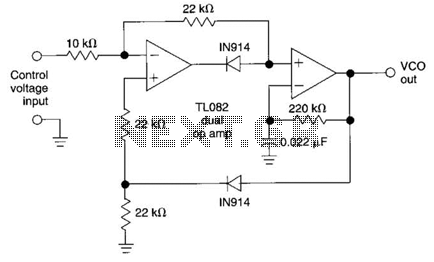
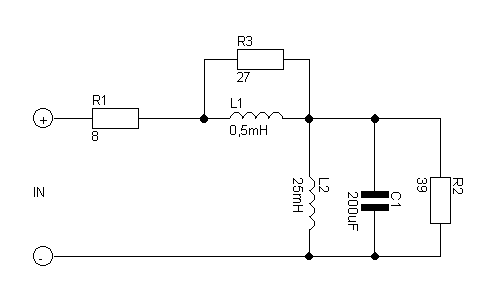
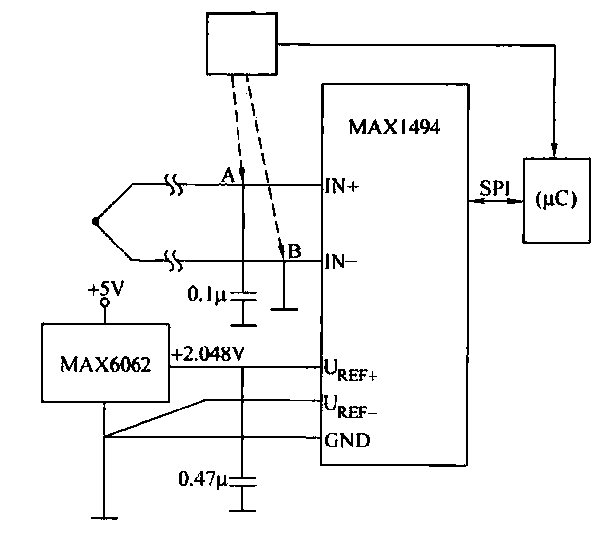
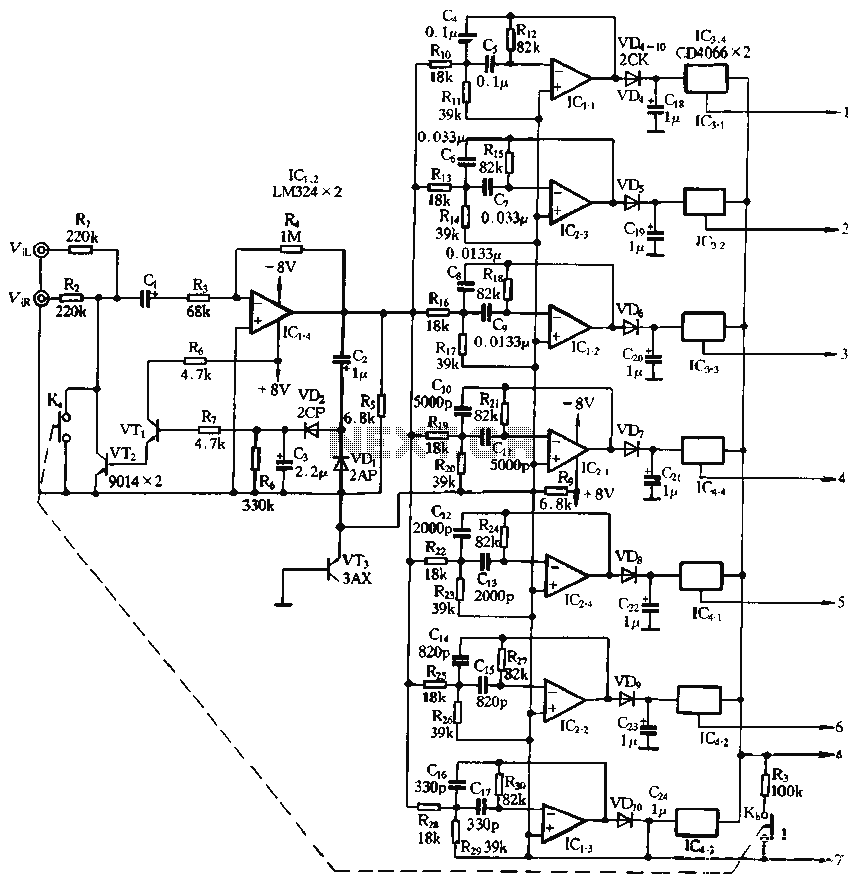
Stereo Headphone Amplifier Circuit Schematic
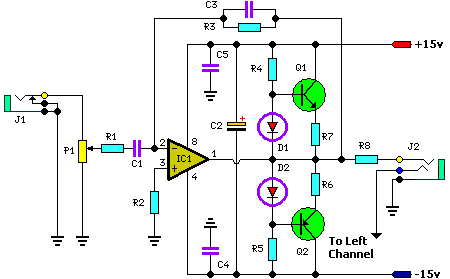
In addition to its primary function as a headphone amplifier, this circuit is applicable in various scenarios requiring a wide bandwidth low power amplifier. It utilizes an operational amplifier (op-amp) with its output current enhanced by a pair of transistors.
This circuit is designed to provide amplification across a broad frequency range while maintaining low power consumption, making it suitable for portable and battery-operated devices. The operational amplifier serves as the core component, responsible for signal processing and initial amplification. The inclusion of transistors at the output stage is crucial, as it allows for increased current drive capability, enabling the circuit to drive low-impedance loads such as headphones or speakers effectively.
The configuration typically involves a feedback loop connected to the op-amp, which stabilizes the gain and improves linearity. The choice of transistors is essential; they should be selected based on their current handling capacity and frequency response to ensure optimal performance. The circuit may also include passive components such as resistors and capacitors to set the gain, filter unwanted frequencies, and stabilize the power supply.
For applications beyond headphone amplification, this circuit can be adapted for use in audio processing equipment, signal conditioning for sensors, or as part of a larger system requiring low power amplification. The versatility of the design allows for modifications to accommodate various input and output requirements, making it a valuable addition to any electronic engineer's toolkit.Apart from the obvious usage as a headphone amplifier, the circuit can be used for a range of applications where a wide bandwidth low power amplifier is needed. The circuit is based on an opamp, with its output current boosted by a pair of transistors 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to provide amplification across a broad frequency range while maintaining low power consumption, making it suitable for portable and battery-operated devices. The operational amplifier serves as the core component, responsible for signal processing and initial amplification. The inclusion of transistors at the output stage is crucial, as it allows for increased current drive capability, enabling the circuit to drive low-impedance loads such as headphones or speakers effectively.
The configuration typically involves a feedback loop connected to the op-amp, which stabilizes the gain and improves linearity. The choice of transistors is essential; they should be selected based on their current handling capacity and frequency response to ensure optimal performance. The circuit may also include passive components such as resistors and capacitors to set the gain, filter unwanted frequencies, and stabilize the power supply.
For applications beyond headphone amplification, this circuit can be adapted for use in audio processing equipment, signal conditioning for sensors, or as part of a larger system requiring low power amplification. The versatility of the design allows for modifications to accommodate various input and output requirements, making it a valuable addition to any electronic engineer's toolkit.Apart from the obvious usage as a headphone amplifier, the circuit can be used for a range of applications where a wide bandwidth low power amplifier is needed. The circuit is based on an opamp, with its output current boosted by a pair of transistors 🔗 External reference