140W amateur radio linear amplifier 2-30Mhz
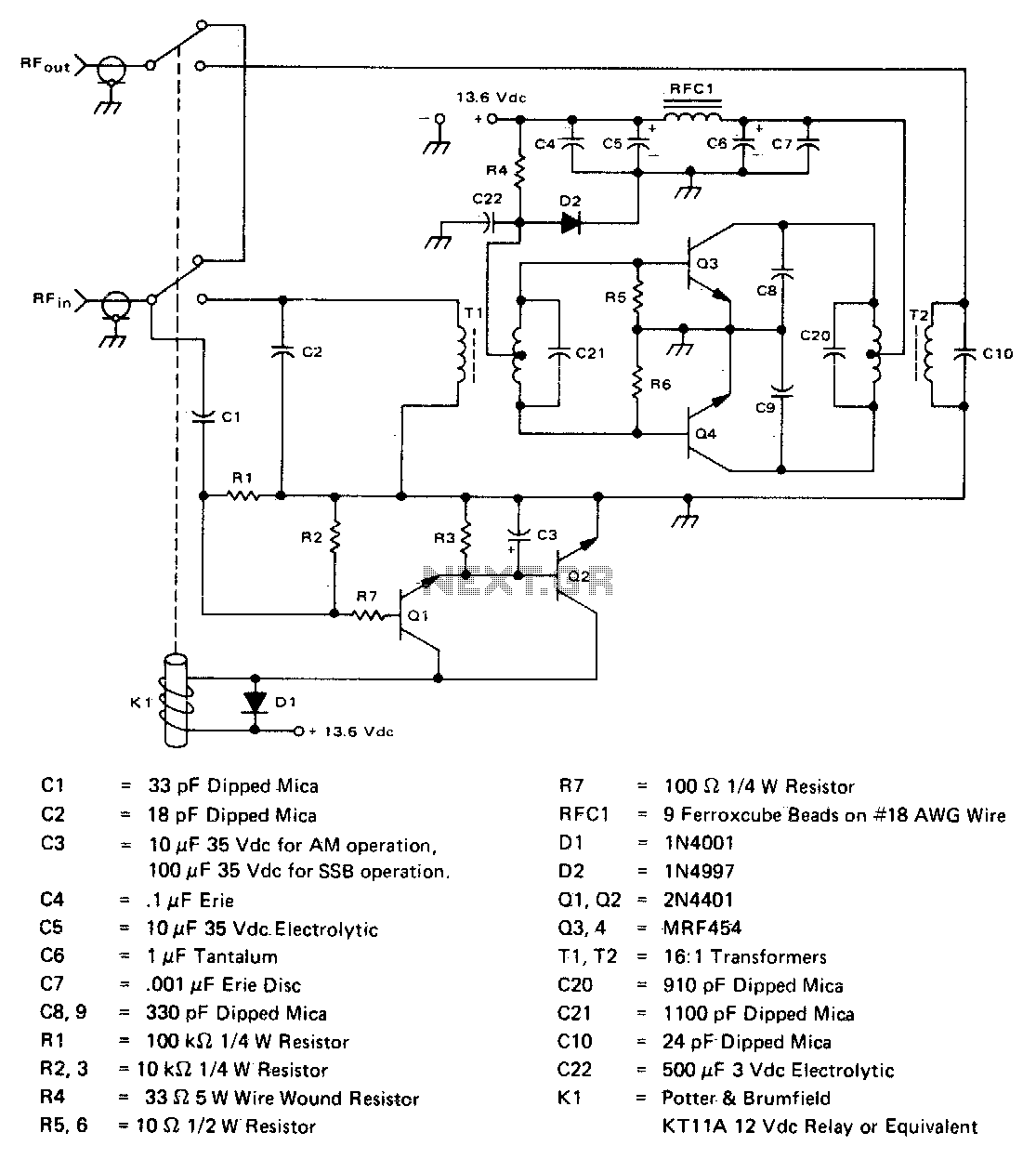
This inexpensive, easy-to-construct amplifier utilizes two MRF454 devices. It is specified for an 80 W power output with a 5 W input drive at a frequency of 30 MHz and operates on a 12 V DC supply.
The amplifier circuit is designed to efficiently amplify RF signals, making it suitable for various applications, including communication systems and signal processing. The MRF454 devices are known for their high efficiency and reliability, which contributes to the overall performance of the amplifier.
The design typically includes a few critical components: the two MRF454 transistors, biasing resistors, coupling capacitors, and a power supply decoupling network. The transistors are arranged in a push-pull configuration to maximize power output and improve linearity. The input drive of 5 W is fed into the base of the transistors through coupling capacitors, which block DC voltage while allowing AC signals to pass.
The output stage of the amplifier is designed to deliver 80 W of power, ensuring that the amplified signal maintains fidelity and strength. The circuit should also incorporate adequate heat sinking for the MRF454 devices to manage thermal dissipation effectively during operation.
Power supply considerations are crucial; a stable 12 V DC source is necessary to ensure consistent performance. Additional bypass capacitors may be included near the power supply connections to filter out any noise and provide a stable voltage to the amplifier during operation.
Overall, this amplifier circuit is a practical solution for those needing a cost-effective and efficient amplification system, leveraging the capabilities of the MRF454 transistors to achieve the desired performance specifications.This inexpensive, easy to construct amplifier uses two MRF454 devices Specified at 80 W power output with 5 W of input drive, 30 MHz, ana 12 Vdc.
The amplifier circuit is designed to efficiently amplify RF signals, making it suitable for various applications, including communication systems and signal processing. The MRF454 devices are known for their high efficiency and reliability, which contributes to the overall performance of the amplifier.
The design typically includes a few critical components: the two MRF454 transistors, biasing resistors, coupling capacitors, and a power supply decoupling network. The transistors are arranged in a push-pull configuration to maximize power output and improve linearity. The input drive of 5 W is fed into the base of the transistors through coupling capacitors, which block DC voltage while allowing AC signals to pass.
The output stage of the amplifier is designed to deliver 80 W of power, ensuring that the amplified signal maintains fidelity and strength. The circuit should also incorporate adequate heat sinking for the MRF454 devices to manage thermal dissipation effectively during operation.
Power supply considerations are crucial; a stable 12 V DC source is necessary to ensure consistent performance. Additional bypass capacitors may be included near the power supply connections to filter out any noise and provide a stable voltage to the amplifier during operation.
Overall, this amplifier circuit is a practical solution for those needing a cost-effective and efficient amplification system, leveraging the capabilities of the MRF454 transistors to achieve the desired performance specifications.This inexpensive, easy to construct amplifier uses two MRF454 devices Specified at 80 W power output with 5 W of input drive, 30 MHz, ana 12 Vdc.