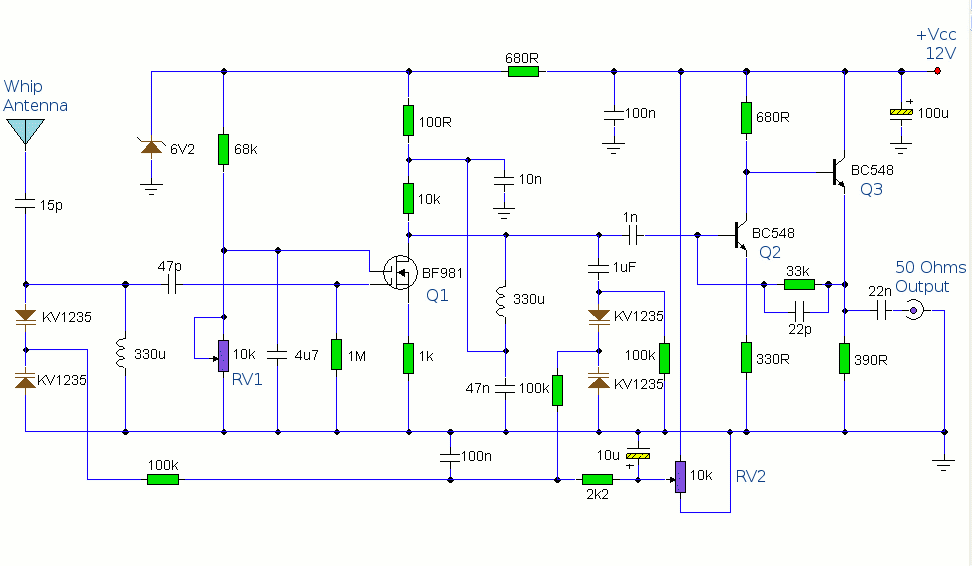
TV Preamplifier via UHF Band
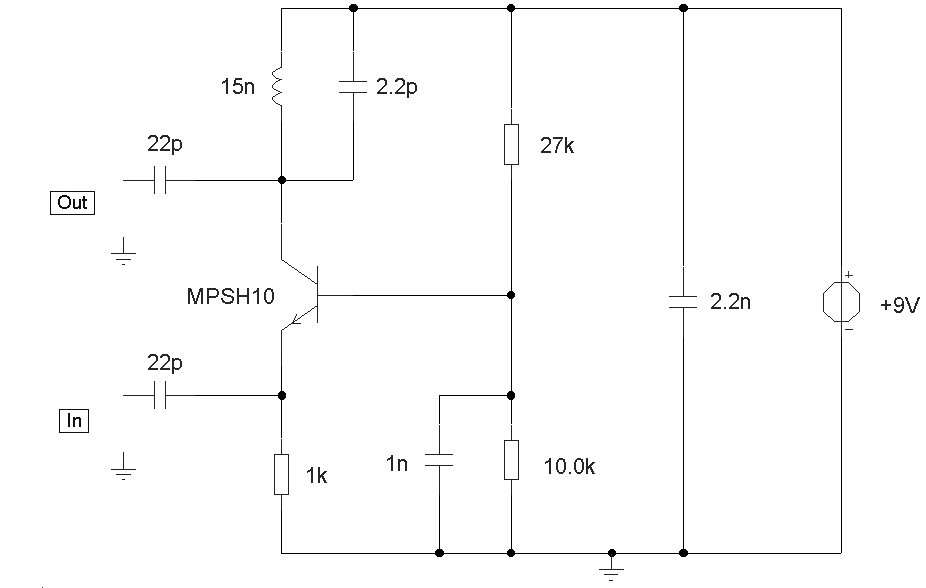
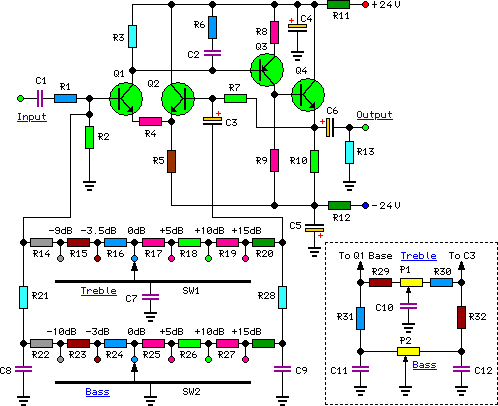
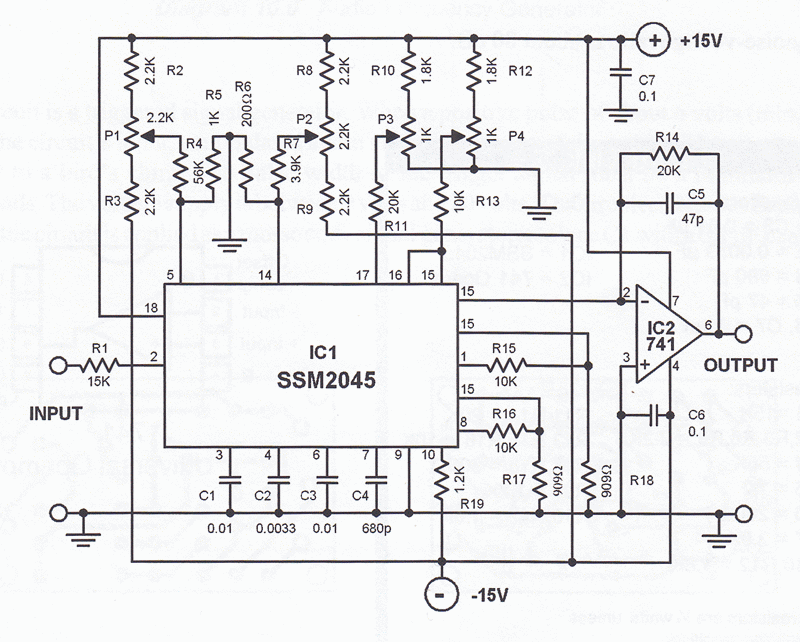
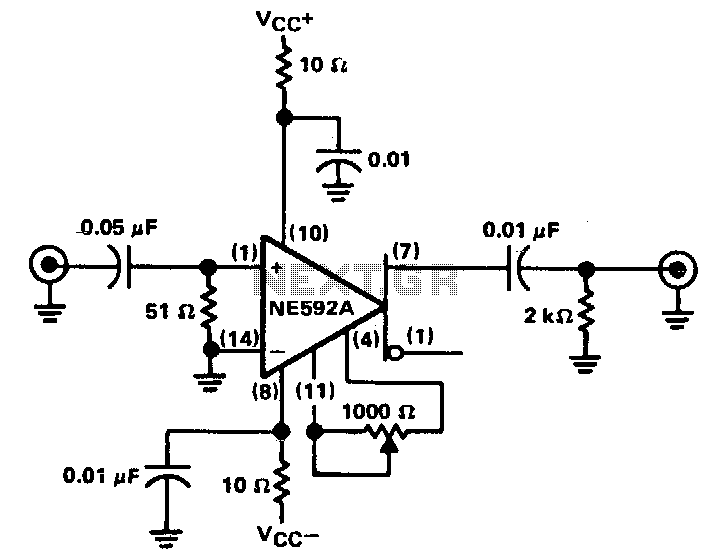
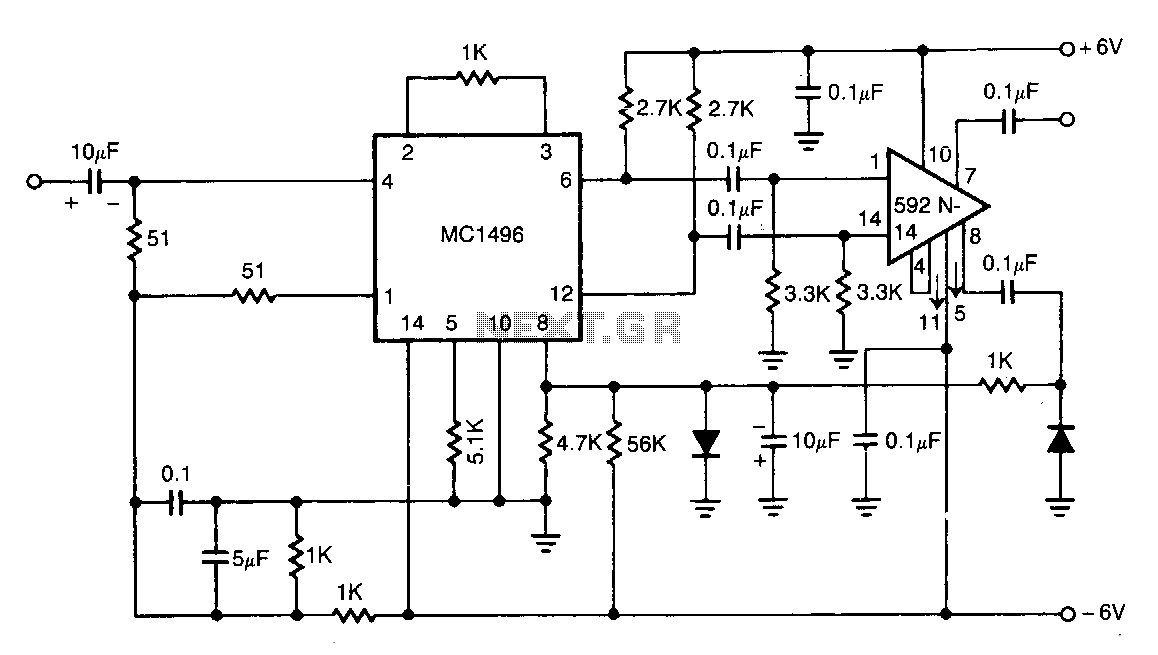
The circuit design aims to create a preamplifier for television systems that operates within the UHF frequency range of 450 MHz to 800 MHz.
The preamplifier circuit is essential for enhancing weak television signals before they are processed by the main receiver. In the UHF frequency range of 450 MHz to 800 MHz, signals can be significantly attenuated due to various factors such as distance from the transmission tower and environmental obstructions. Therefore, an effective preamplifier must be designed to amplify these signals while minimizing noise and distortion.
The preamplifier typically includes a low-noise amplifier (LNA) stage, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity. The choice of components, such as transistors or operational amplifiers, is vital for achieving the desired gain and noise figure. For UHF applications, RF transistors like the BFP420 or low-noise operational amplifiers such as the AD8000 can be utilized.
The circuit should also incorporate impedance matching networks to ensure maximum power transfer from the antenna to the preamplifier. This can be achieved using LC networks or transformers designed for the specific frequency range. Proper filtering must be included to eliminate unwanted signals and harmonics, which can interfere with the desired UHF signals.
Power supply considerations are also crucial, as the preamplifier must operate efficiently across the specified frequency range. A regulated power supply circuit can be integrated to provide stable voltage levels, ensuring consistent performance.
In summary, the design of a UHF preamplifier circuit involves careful selection of components, consideration of impedance matching, filtering, and power supply management to effectively amplify weak television signals within the frequency range of 450 MHz to 800 MHz.The design of the circuit is aimed to create a preamplifier for television systems that would operate in the UHF frequency range of 450 MHz to 800 MHz and.. 🔗 External reference
The preamplifier circuit is essential for enhancing weak television signals before they are processed by the main receiver. In the UHF frequency range of 450 MHz to 800 MHz, signals can be significantly attenuated due to various factors such as distance from the transmission tower and environmental obstructions. Therefore, an effective preamplifier must be designed to amplify these signals while minimizing noise and distortion.
The preamplifier typically includes a low-noise amplifier (LNA) stage, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity. The choice of components, such as transistors or operational amplifiers, is vital for achieving the desired gain and noise figure. For UHF applications, RF transistors like the BFP420 or low-noise operational amplifiers such as the AD8000 can be utilized.
The circuit should also incorporate impedance matching networks to ensure maximum power transfer from the antenna to the preamplifier. This can be achieved using LC networks or transformers designed for the specific frequency range. Proper filtering must be included to eliminate unwanted signals and harmonics, which can interfere with the desired UHF signals.
Power supply considerations are also crucial, as the preamplifier must operate efficiently across the specified frequency range. A regulated power supply circuit can be integrated to provide stable voltage levels, ensuring consistent performance.
In summary, the design of a UHF preamplifier circuit involves careful selection of components, consideration of impedance matching, filtering, and power supply management to effectively amplify weak television signals within the frequency range of 450 MHz to 800 MHz.The design of the circuit is aimed to create a preamplifier for television systems that would operate in the UHF frequency range of 450 MHz to 800 MHz and.. 🔗 External reference