1996 GL1500 modulators interfering with audio
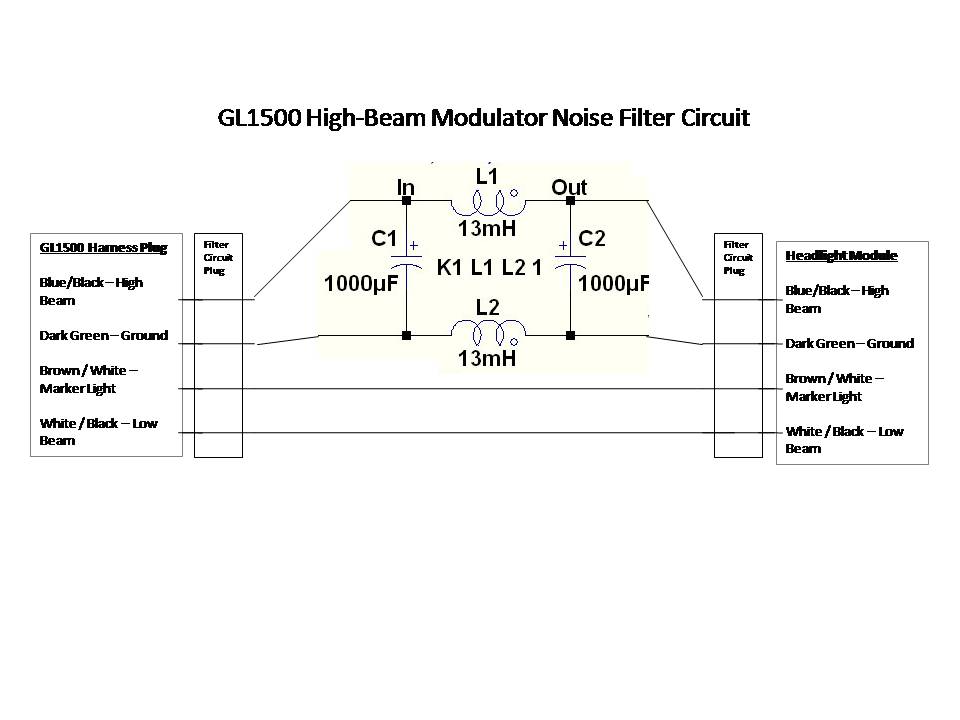
A power filter is a device that is placed before devices such as GPS, MP3 players, or radar detectors connected to the auxiliary circuit. When properly used and installed, these filters can eliminate modulator noise from any system. Observing the waveform with an oscilloscope can provide significant insights into the operation of these systems. For instance, connecting the oscilloscope test lead to the headlight circuit will reveal a substantial waveform resembling a nearly vertical square wave. This can be likened to a toggle switch rapidly turning headlights on and off, averaging about 70% of the DC voltage during the "modulated" cycle.
Experiences with headlight modulators have highlighted issues with audio interference in intercom systems, particularly in motorcycles. After upgrading to a headlight modulator on a Gold Wing motorcycle, significant clicking noises were encountered in the audio system when the modulator was active. The manufacturer of the audio system was unhelpful, attributing the issue to a perceived fault in the audio design and recommending the addition of a large capacitor to the power source. However, this suggestion did not resolve the issue satisfactorily.
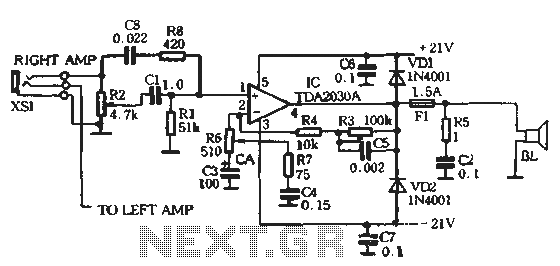
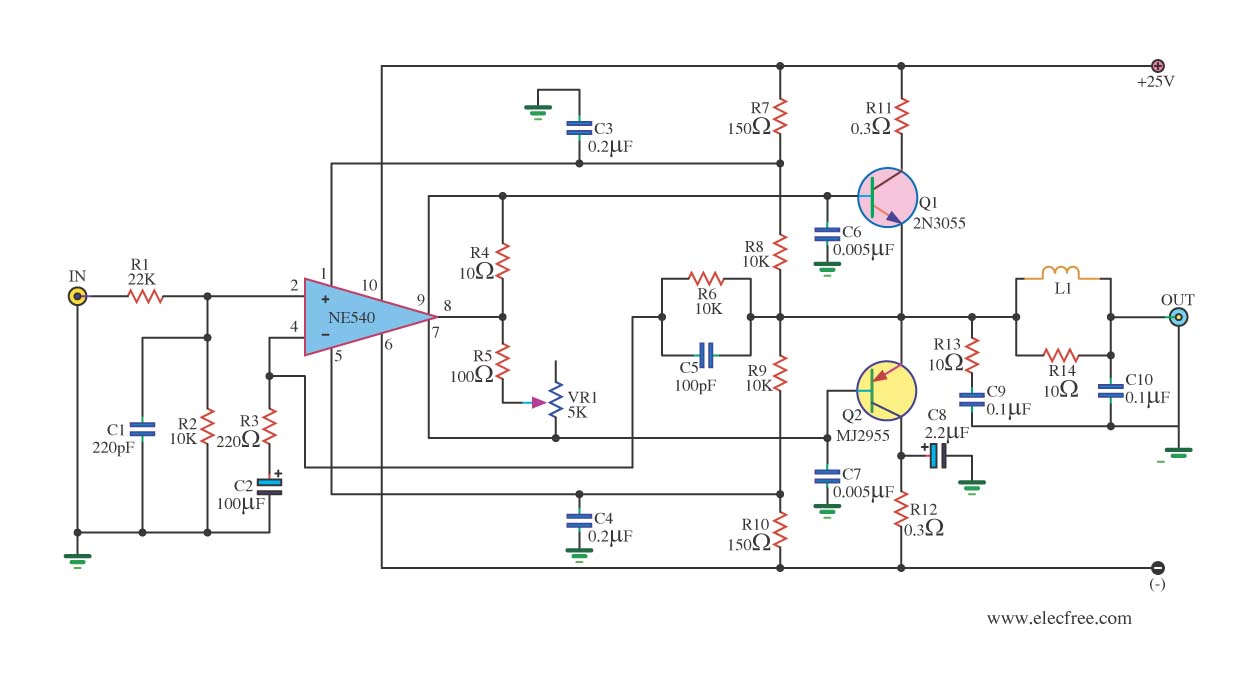
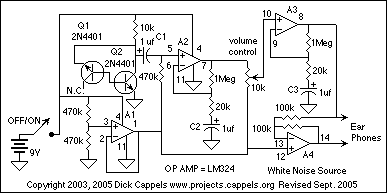
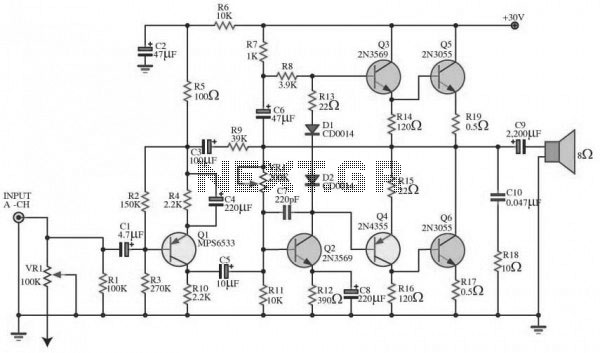
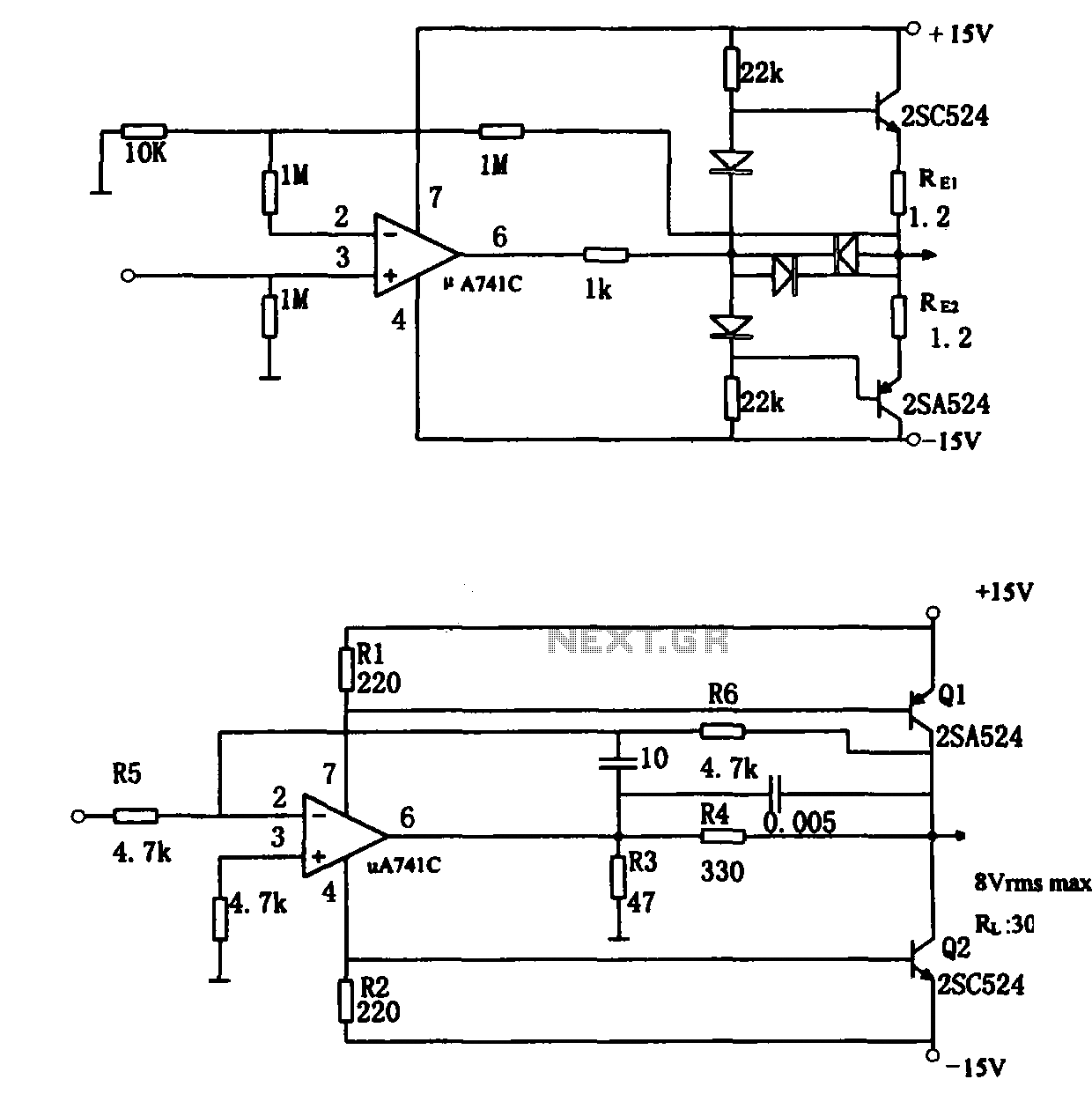
Further discussions with other manufacturers and community members revealed that modulator-induced noise is a common problem. A consensus emerged that isolating the voltage disruption caused by the modulator as close to the source as possible is crucial. The goal was to create a "filter" that could be easily integrated into the factory wiring for straightforward removal if necessary. A custom "filter" circuit was designed by a moderator from the AllAboutCircuits forum to address this issue.
The power filter circuit typically consists of capacitors, inductors, and resistors configured to attenuate high-frequency noise while allowing the desired DC voltage to pass through. The capacitors serve to shunt high-frequency noise to ground, while inductors can block high-frequency signals and allow low-frequency signals to pass. This combination can effectively reduce the interference experienced in audio systems when a headlight modulator is in operation.
The design of the filter should ensure compatibility with the existing wiring and components of the motorcycle, maintaining ease of installation and removal. Proper grounding and placement of the filter within the circuit are critical to achieving optimal performance. Testing the circuit with an oscilloscope before and after installation can provide valuable feedback on the effectiveness of the filter, helping to confirm that the modulator noise has been adequately suppressed.
In summary, the implementation of a power filter can significantly enhance the performance of auxiliary systems in motorcycles, particularly in mitigating the adverse effects of modulator-induced noise.A power filter is a device you put ahead of something like a GPS and MP3 player and or radar detector that you have run into the Aux Circuit. But these things used properly and properly installed will take the modulator noise out of any system.
If you were to observe what is happening with an oscilloscope, it would have a lot more meaning to you. Put the o`scope test lead on the headlight circuit and observe the waveform. It will be huge! Nearly a vertical square wave. Think of a toggle switch rapidly turn your headlights on/off at a rate so as to average about 70% of the DC voltage to the lights in the "modulated" cycle. IG ™ve been a motorcycle participant in several collisions with cars in my past. All of them shared the element that the driver of the car claimed, G I did not see youG . When I bought my Gold Wing, my first upgrade was a headlight modulator. I next upgraded my helmets with audio to allow rider to co-rider communication and immediately found that when the modulator was operating, there was a terribly annoying clicking noise on the intercom.
The manufacturer was totally uninterested in exploring a solution and claimed that my experience was the first theyG ™d ever heard of audio problems associated with modulator use. The manufacturerG ™s only guidance was that the Gold Wing must have a faulty audio/intercom design, and the best way to overcome this weakness would be to put a really big capacitor on the power source to the audio system.
They made it clear that any follow up on my problem would be under the condition of G fee for serviceG . If I ever buy another headlight modulator, I will consider other manufacturers first! I explored the situation with folks at J&M where I purchased my helmet audio. I spoke with manufacturers of other modulator systems and I spoke with folks at Electrical Connection.
It seems that I am not the first to have modulator induced noise in my audio system. I got some guidance from members on this forum who have had similar experiences and had considered various ways to resolve the audio noise. Finally I did extensive research using a variety of web resources, My summary of the resolution is NOT offered to provide an exactly repeatable solution that will be a fit to other modulator use scenarios, but as an educational perspective on the solvability of this type of problem.
Upon review of the symptoms by many of the folks I talked to ( except the manufacturer ), the consensus was that isolating the voltage disruption caused by the modulator induced current changes to the headlight, should be done as close to the source of the problem as possible. A primary design objective was to build a G filterG that could be plugged into the factory wiring to make removal simple, if needed.
The G filterG circuit, and build description below it, were custom designed by a very generous moderator of the AllAboutCircuits forum. As a disclaimer, I readily acknowledge that I donG ™t understand any o 🔗 External reference
Experiences with headlight modulators have highlighted issues with audio interference in intercom systems, particularly in motorcycles. After upgrading to a headlight modulator on a Gold Wing motorcycle, significant clicking noises were encountered in the audio system when the modulator was active. The manufacturer of the audio system was unhelpful, attributing the issue to a perceived fault in the audio design and recommending the addition of a large capacitor to the power source. However, this suggestion did not resolve the issue satisfactorily.
Further discussions with other manufacturers and community members revealed that modulator-induced noise is a common problem. A consensus emerged that isolating the voltage disruption caused by the modulator as close to the source as possible is crucial. The goal was to create a "filter" that could be easily integrated into the factory wiring for straightforward removal if necessary. A custom "filter" circuit was designed by a moderator from the AllAboutCircuits forum to address this issue.
The power filter circuit typically consists of capacitors, inductors, and resistors configured to attenuate high-frequency noise while allowing the desired DC voltage to pass through. The capacitors serve to shunt high-frequency noise to ground, while inductors can block high-frequency signals and allow low-frequency signals to pass. This combination can effectively reduce the interference experienced in audio systems when a headlight modulator is in operation.
The design of the filter should ensure compatibility with the existing wiring and components of the motorcycle, maintaining ease of installation and removal. Proper grounding and placement of the filter within the circuit are critical to achieving optimal performance. Testing the circuit with an oscilloscope before and after installation can provide valuable feedback on the effectiveness of the filter, helping to confirm that the modulator noise has been adequately suppressed.
In summary, the implementation of a power filter can significantly enhance the performance of auxiliary systems in motorcycles, particularly in mitigating the adverse effects of modulator-induced noise.A power filter is a device you put ahead of something like a GPS and MP3 player and or radar detector that you have run into the Aux Circuit. But these things used properly and properly installed will take the modulator noise out of any system.
If you were to observe what is happening with an oscilloscope, it would have a lot more meaning to you. Put the o`scope test lead on the headlight circuit and observe the waveform. It will be huge! Nearly a vertical square wave. Think of a toggle switch rapidly turn your headlights on/off at a rate so as to average about 70% of the DC voltage to the lights in the "modulated" cycle. IG ™ve been a motorcycle participant in several collisions with cars in my past. All of them shared the element that the driver of the car claimed, G I did not see youG . When I bought my Gold Wing, my first upgrade was a headlight modulator. I next upgraded my helmets with audio to allow rider to co-rider communication and immediately found that when the modulator was operating, there was a terribly annoying clicking noise on the intercom.
The manufacturer was totally uninterested in exploring a solution and claimed that my experience was the first theyG ™d ever heard of audio problems associated with modulator use. The manufacturerG ™s only guidance was that the Gold Wing must have a faulty audio/intercom design, and the best way to overcome this weakness would be to put a really big capacitor on the power source to the audio system.
They made it clear that any follow up on my problem would be under the condition of G fee for serviceG . If I ever buy another headlight modulator, I will consider other manufacturers first! I explored the situation with folks at J&M where I purchased my helmet audio. I spoke with manufacturers of other modulator systems and I spoke with folks at Electrical Connection.
It seems that I am not the first to have modulator induced noise in my audio system. I got some guidance from members on this forum who have had similar experiences and had considered various ways to resolve the audio noise. Finally I did extensive research using a variety of web resources, My summary of the resolution is NOT offered to provide an exactly repeatable solution that will be a fit to other modulator use scenarios, but as an educational perspective on the solvability of this type of problem.
Upon review of the symptoms by many of the folks I talked to ( except the manufacturer ), the consensus was that isolating the voltage disruption caused by the modulator induced current changes to the headlight, should be done as close to the source of the problem as possible. A primary design objective was to build a G filterG that could be plugged into the factory wiring to make removal simple, if needed.
The G filterG circuit, and build description below it, were custom designed by a very generous moderator of the AllAboutCircuits forum. As a disclaimer, I readily acknowledge that I donG ™t understand any o 🔗 External reference