Direct coupling audio power amplifier configuration A741 circuit
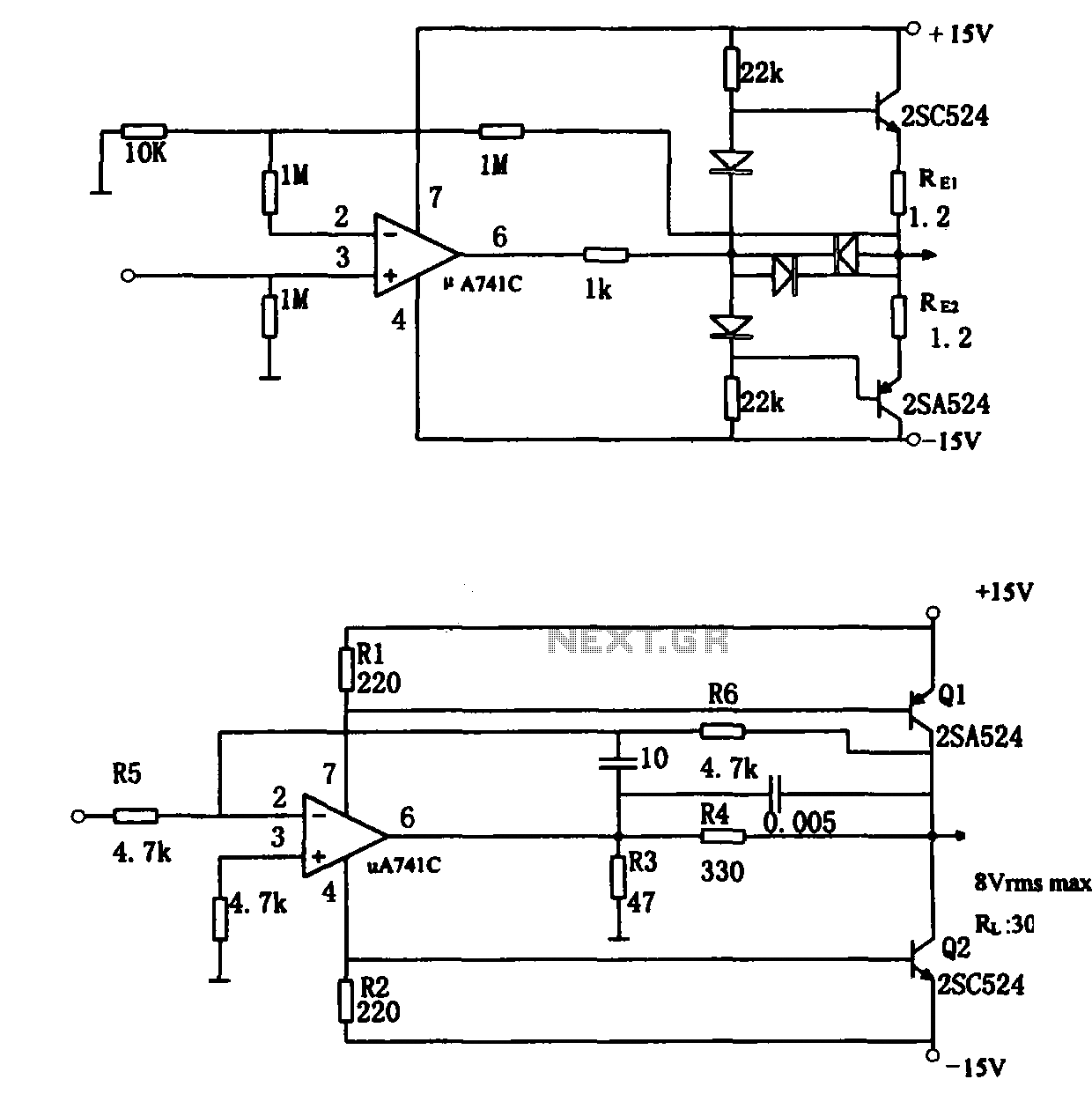
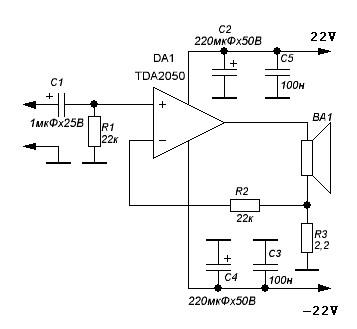
The direct coupling audio power amplifier utilizes an integrated operational amplifier. There are typically two practical configurations. The first configuration, depicted in (a), features a circuit structure that includes the output of the operational amplifier and a complementary symmetry emitter follower. This configuration is simple and user-friendly but has lower power utilization. In Figure (a), two transistors are connected in series with a pole resistance (RE) of 1.2 ohms, which serves to implement over-current protection for the amplifier transistor at the output terminal of the integrated operational amplifier (pin 6). An external 1k ohm resistor connected to the A741 also contributes to overcurrent protection. The voltage amplification factor in this configuration is approximately 101.4, with diodes specified as 1S953 and amplifier tubes as 2SC524 and 2SA524. The second configuration, illustrated in (b), employs the operational amplifier to supply current excitation to a complementary symmetry common emitter amplifier, with power output parameters around 2W. The A741C power operational amplifier is compact, and the output stage consists of two class AB amplifier tubes operating in an enlarged state, resulting in low power consumption and higher efficiency. The output current is typically a few milliamps, with the supply current closely matching the load current. The positive and negative power terminals of the operational amplifier (pins 7 and 4) are connected to the bases of transistors Q1 and Q2, respectively, providing the necessary base excitation current. In Figure (b), resistor R3 (47 ohms) is used to increase the power supply current, thereby enhancing the base excitation current of the power amplifier tubes. Resistor R4 serves as a current limiting device, providing overcurrent protection for the A741C.
The direct coupling audio power amplifier circuit can be divided into two distinct configurations, each catering to specific performance requirements. The first configuration (a) employs a straightforward design that integrates an operational amplifier with a complementary symmetry emitter follower. This design is characterized by its simplicity and ease of implementation, making it suitable for a variety of applications. However, it is important to note that this configuration yields lower power utilization due to inherent limitations in the design.
In this configuration, two transistors are arranged in series with a pole resistance of 1.2 ohms, which plays a crucial role in safeguarding the amplifier transistor at the output terminal of the operational amplifier. The external 1k ohm resistor connected to pin 6 of the A741 operational amplifier further enhances overcurrent protection, ensuring the reliability of the circuit during operation. The voltage amplification factor of approximately 101.4 indicates the circuit's capability to amplify audio signals effectively. The choice of diodes (1S953) and amplifier tubes (2SC524 and 2SA524) is critical, as these components determine the overall performance and efficiency of the amplifier.
The second configuration (b) shifts the focus to a more efficient design by utilizing the operational amplifier to supply current excitation to a complementary symmetry common emitter amplifier. This approach allows for a power output of around 2W, which is suitable for driving various audio loads. The A741C operational amplifier, known for its compact size, operates in conjunction with two class AB amplifier tubes that function in an enlarged state, optimizing power consumption while maintaining high efficiency. The output current, typically in the range of a few milliamps, aligns closely with the supply current, ensuring that the circuit operates efficiently under varying load conditions.
In this configuration, the positive and negative power terminals of the operational amplifier are strategically connected to the bases of transistors Q1 and Q2, facilitating the necessary base excitation current for optimal performance. Resistor R3, valued at 47 ohms, is instrumental in augmenting the power supply current, thereby increasing the base excitation current for the power amplifier tubes. Additionally, resistor R4 serves as a vital current limiting component, providing overcurrent protection for the A741C operational amplifier, thereby enhancing the circuit's reliability and longevity. Overall, these configurations exemplify effective design strategies in audio power amplification, balancing simplicity, efficiency, and performance.As shown for the direct coupling audio power amplifier. When using an integrated operational amplifier constituting the audio power amplifier, there are usually two practical forms.The first practical form as shown in (a), the structure of the circuit is in the output of op amp plus complementary symmetry emitter follower, this form of structure is simple, easy to use, but lower power utilization. Figure (a) know, shoot the circuit two transistors are connected in series pole resistance RE (1.2 ), whose role is to implement over-current amplifier transistor in the integrated operational amplifier output terminal (pin 6) External 1k resistor to A741 also play the role of overcurrent protection.
Figure (a) in which the voltage amplification factor of about 101,4 diodes are 1S953, amplifier tube for the tube, model 2SC524 and 2SA524.The second practical form as shown in (b), the circuit is the use of the operational amplifier supply current excitation complementary symmetry common emitter amplifier, power output parameters as shown in the figure is about 2W. A741C power operational amplifier itself is small, the output stage of the two class AB amplifier tube operating in the enlarged state, the power consumption is also small, and thus a higher efficiency when taking a few milliamps of output current, supply current is substantially close to the load current.
Positive and negative power terminal of the operational amplifier (pin 7,4), respectively, with the base of transistor Q1 and Q2 is connected to that supply current to become operational amplifier Q1 and Q2 base excitation current. Role Figure (b) of the resistor R3 (47 ) is to increase the power supply current, which increases both the power amplifier tube base excitation current.
Resistor current limiting resistor R4, to A741C play the role of overcurrent protection.
The direct coupling audio power amplifier circuit can be divided into two distinct configurations, each catering to specific performance requirements. The first configuration (a) employs a straightforward design that integrates an operational amplifier with a complementary symmetry emitter follower. This design is characterized by its simplicity and ease of implementation, making it suitable for a variety of applications. However, it is important to note that this configuration yields lower power utilization due to inherent limitations in the design.
In this configuration, two transistors are arranged in series with a pole resistance of 1.2 ohms, which plays a crucial role in safeguarding the amplifier transistor at the output terminal of the operational amplifier. The external 1k ohm resistor connected to pin 6 of the A741 operational amplifier further enhances overcurrent protection, ensuring the reliability of the circuit during operation. The voltage amplification factor of approximately 101.4 indicates the circuit's capability to amplify audio signals effectively. The choice of diodes (1S953) and amplifier tubes (2SC524 and 2SA524) is critical, as these components determine the overall performance and efficiency of the amplifier.
The second configuration (b) shifts the focus to a more efficient design by utilizing the operational amplifier to supply current excitation to a complementary symmetry common emitter amplifier. This approach allows for a power output of around 2W, which is suitable for driving various audio loads. The A741C operational amplifier, known for its compact size, operates in conjunction with two class AB amplifier tubes that function in an enlarged state, optimizing power consumption while maintaining high efficiency. The output current, typically in the range of a few milliamps, aligns closely with the supply current, ensuring that the circuit operates efficiently under varying load conditions.
In this configuration, the positive and negative power terminals of the operational amplifier are strategically connected to the bases of transistors Q1 and Q2, facilitating the necessary base excitation current for optimal performance. Resistor R3, valued at 47 ohms, is instrumental in augmenting the power supply current, thereby increasing the base excitation current for the power amplifier tubes. Additionally, resistor R4 serves as a vital current limiting component, providing overcurrent protection for the A741C operational amplifier, thereby enhancing the circuit's reliability and longevity. Overall, these configurations exemplify effective design strategies in audio power amplification, balancing simplicity, efficiency, and performance.As shown for the direct coupling audio power amplifier. When using an integrated operational amplifier constituting the audio power amplifier, there are usually two practical forms.The first practical form as shown in (a), the structure of the circuit is in the output of op amp plus complementary symmetry emitter follower, this form of structure is simple, easy to use, but lower power utilization. Figure (a) know, shoot the circuit two transistors are connected in series pole resistance RE (1.2 ), whose role is to implement over-current amplifier transistor in the integrated operational amplifier output terminal (pin 6) External 1k resistor to A741 also play the role of overcurrent protection.
Figure (a) in which the voltage amplification factor of about 101,4 diodes are 1S953, amplifier tube for the tube, model 2SC524 and 2SA524.The second practical form as shown in (b), the circuit is the use of the operational amplifier supply current excitation complementary symmetry common emitter amplifier, power output parameters as shown in the figure is about 2W. A741C power operational amplifier itself is small, the output stage of the two class AB amplifier tube operating in the enlarged state, the power consumption is also small, and thus a higher efficiency when taking a few milliamps of output current, supply current is substantially close to the load current.
Positive and negative power terminal of the operational amplifier (pin 7,4), respectively, with the base of transistor Q1 and Q2 is connected to that supply current to become operational amplifier Q1 and Q2 base excitation current. Role Figure (b) of the resistor R3 (47 ) is to increase the power supply current, which increases both the power amplifier tube base excitation current.
Resistor current limiting resistor R4, to A741C play the role of overcurrent protection.