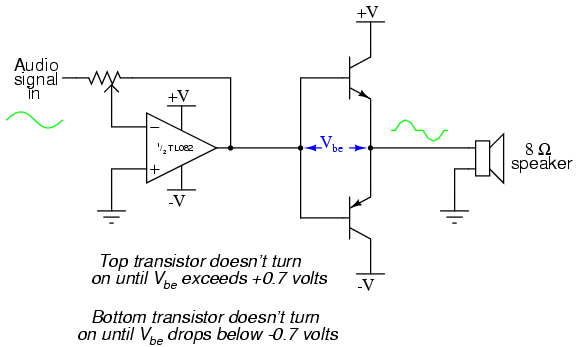
1W BTL Audio Amplifier
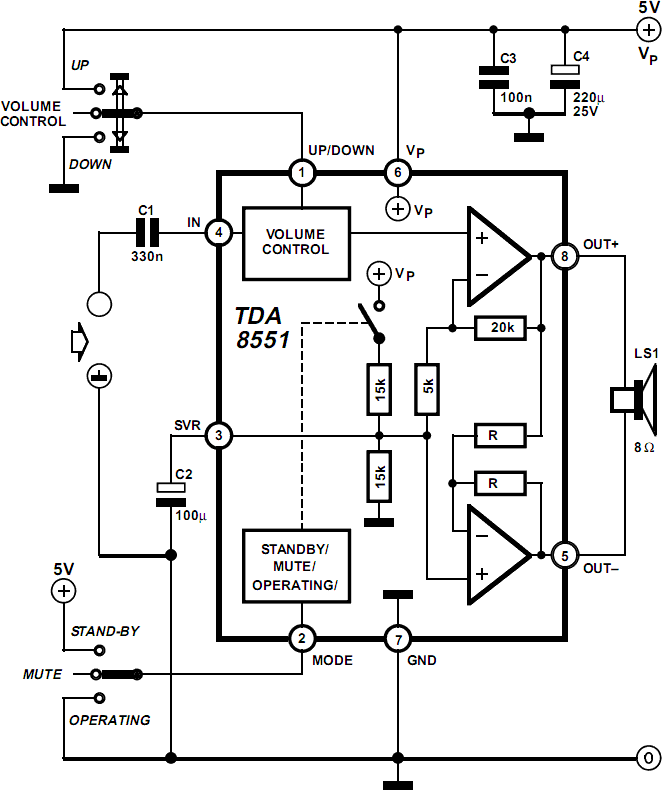
The TDA8581(T) from Philips Semiconductors is a 1-watt Bridge Tied Load (BTL) audio power amplifier capable of delivering 1 watt of output power into an 8-ohm load at a total harmonic distortion (THD) of 10% while using a 5V power supply. The schematic presented combines the functional diagram of the TDA8551 with its typical application circuit. The amplifier's gain can be adjusted via a digital volume control input, with a maximum gain of 20 dB at the highest volume setting. The MODE pin allows the device to be switched among three modes: standby (MODE level between Vp and Vp - 0.5 V), muted (MODE level between 1 V and Vp - 1.4 V), or normal (MODE level less than 0.5 V). The TDA8551 includes an internal thermal shutdown protection mechanism. The total voltage drop across both MOS transistors in the complementary output stage is less than 1 V. With a 5-V supply and an 8-ohm loudspeaker, an output power of 1 watt can be achieved. The volume control provides an attenuation range from 0 dB to 80 dB in 64 steps, controlled by the 3-state level at the UP/DOWN pin: floating (volume unchanged), negative pulses (decrease volume), and positive pulses (increase volume). Each pulse at the UP/DOWN pin results in a gain change of 80/64 = 1.25 dB (typical value). Upon initial power connection, the attenuator defaults to 40 dB (low volume), resulting in a total amplifier gain of 20 dB. Positive pulses must be applied to the UP/DOWN pin to reach listening volume. Additionally, the graph illustrates the THD as a function of output power. The maximum quiescent current consumption for the amplifier is specified at 10 mA, plus the current resulting from the output offset voltage divided by the load impedance.
The TDA8581(T) audio power amplifier is designed for compact and efficient audio amplification applications. It operates using a BTL configuration, which enhances the output power by allowing both output terminals to drive the load effectively. This configuration is particularly advantageous for driving speakers in portable or space-constrained devices.
The device's gain control through a digital volume control input allows for precise audio level adjustments, facilitating user-friendly operation. The maximum gain of 20 dB ensures sufficient amplification for various audio signals, while the ability to attenuate down to 0 dB provides flexibility in tailoring the output to specific requirements.
The three operational modes—standby, muted, and normal—offer versatility in managing power consumption and audio output. The internal thermal shutdown feature is a critical safety aspect, preventing damage to the amplifier under excessive thermal conditions, thus enhancing reliability.
With respect to performance metrics, the low voltage drop across the output stage MOS transistors ensures efficient power delivery, minimizing heat generation and maximizing output power. The specified output capability of 1 watt into an 8-ohm load at a 5V supply is indicative of the amplifier's suitability for driving small speakers in consumer electronics.
The volume control mechanism, which operates in 64 discrete steps, provides a fine-tuned adjustment of the audio output, allowing users to achieve their preferred listening levels. The default setting upon power-up ensures that the device is safe for initial use, protecting against sudden loud outputs.
In summary, the TDA8581(T) is a robust, efficient, and versatile audio power amplifier that caters to modern audio applications, providing essential features for audio control and protection while delivering high-quality sound output.The TDA8581(T) from Philips Semiconductors is a 1-watt Bridge Tied Load (BTL) audio power amplifier capable of delivering 1 watt output power into an 8-Wload at THD (total harmonic distortion) of 10% and using a 5V power supply. The schematic shown here combines the functional diagram of the TDA8551 with its typical application circuit.
The gain o f the amplifier can be set by the digital volume control input. At the highest volume setting, the gain is 20 dB. Using the MODE pin the device can be switched to one of three modes: standby (MODE level between Vp and Vp 0. 5 V), muted (MODE level between 1 V and Vp 1. 4 V) or normal (MODE level less than 0. 5 V). The TDA8551 is protected by an internal thermal shutdown protection mechanism. The total voltage loss for both MOS transistors in the complementary output stage is less than 1 V. Using a 5-V supply and an 8-W loudspeaker, an output power of 1 watt can be delivered. The volume control has an attenuation range of between 0 dB and 80 dB in 64 steps set by the 3-state level at the UP/DOWN pin: floating: volume remains unchanged; negative pulses: decrease volume; positive pulses: increase volume Each pulse at he Up/DOWN pin causes a change in gain of 80/64 = 1.
25 dB (typical value). When the supply voltage is first connected, the attenuator is set to 40 dB (low volume), so the gain of the total amplifier is then 20 dB. Some positive pulses have to be applied to the UP/DOWN pin to achieve listening volume. The graph shows the THD as a function of output power. The maximum quiescent current consumption of the amplifier is specified at 10 mA, to which should be added the current resulting from the output offset voltage divided by the load impedance.
🔗 External reference
The TDA8581(T) audio power amplifier is designed for compact and efficient audio amplification applications. It operates using a BTL configuration, which enhances the output power by allowing both output terminals to drive the load effectively. This configuration is particularly advantageous for driving speakers in portable or space-constrained devices.
The device's gain control through a digital volume control input allows for precise audio level adjustments, facilitating user-friendly operation. The maximum gain of 20 dB ensures sufficient amplification for various audio signals, while the ability to attenuate down to 0 dB provides flexibility in tailoring the output to specific requirements.
The three operational modes—standby, muted, and normal—offer versatility in managing power consumption and audio output. The internal thermal shutdown feature is a critical safety aspect, preventing damage to the amplifier under excessive thermal conditions, thus enhancing reliability.
With respect to performance metrics, the low voltage drop across the output stage MOS transistors ensures efficient power delivery, minimizing heat generation and maximizing output power. The specified output capability of 1 watt into an 8-ohm load at a 5V supply is indicative of the amplifier's suitability for driving small speakers in consumer electronics.
The volume control mechanism, which operates in 64 discrete steps, provides a fine-tuned adjustment of the audio output, allowing users to achieve their preferred listening levels. The default setting upon power-up ensures that the device is safe for initial use, protecting against sudden loud outputs.
In summary, the TDA8581(T) is a robust, efficient, and versatile audio power amplifier that caters to modern audio applications, providing essential features for audio control and protection while delivering high-quality sound output.The TDA8581(T) from Philips Semiconductors is a 1-watt Bridge Tied Load (BTL) audio power amplifier capable of delivering 1 watt output power into an 8-Wload at THD (total harmonic distortion) of 10% and using a 5V power supply. The schematic shown here combines the functional diagram of the TDA8551 with its typical application circuit.
The gain o f the amplifier can be set by the digital volume control input. At the highest volume setting, the gain is 20 dB. Using the MODE pin the device can be switched to one of three modes: standby (MODE level between Vp and Vp 0. 5 V), muted (MODE level between 1 V and Vp 1. 4 V) or normal (MODE level less than 0. 5 V). The TDA8551 is protected by an internal thermal shutdown protection mechanism. The total voltage loss for both MOS transistors in the complementary output stage is less than 1 V. Using a 5-V supply and an 8-W loudspeaker, an output power of 1 watt can be delivered. The volume control has an attenuation range of between 0 dB and 80 dB in 64 steps set by the 3-state level at the UP/DOWN pin: floating: volume remains unchanged; negative pulses: decrease volume; positive pulses: increase volume Each pulse at he Up/DOWN pin causes a change in gain of 80/64 = 1.
25 dB (typical value). When the supply voltage is first connected, the attenuator is set to 40 dB (low volume), so the gain of the total amplifier is then 20 dB. Some positive pulses have to be applied to the UP/DOWN pin to achieve listening volume. The graph shows the THD as a function of output power. The maximum quiescent current consumption of the amplifier is specified at 10 mA, to which should be added the current resulting from the output offset voltage divided by the load impedance.
🔗 External reference