2000V Low-Current Power Supply
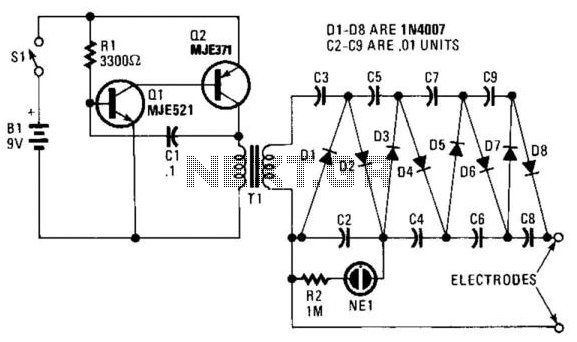
This circuit consists of components Q1, Q2, R1, and C1, which together create a multivibrator. The oscillation produced results in a square wave with a voltage peak-to-peak (Vpp) ranging from 20 to 30 volts. This output is then amplified by T1, an audio transformer typically found in radios or small televisions. The impedance ratio of 8 to 1,200 ohms corresponds to a turn ratio of 12:1. The alternating current from the secondary winding of T1 is directed to the multiplier circuit, which includes diodes D1 to D8 and capacitors C2 to C9. NE1 and resistor R2 function as an operational indicator for the circuit. The output voltage from this circuit can reach approximately 2,000 volts, and capacitors C2 to C9 must have a voltage rating of 400 volts or higher.
The circuit described operates as a high-voltage generator utilizing a multivibrator configuration. The multivibrator, formed by transistors Q1 and Q2, generates a square wave signal. This square wave oscillation is essential for driving the transformer T1, which steps up the voltage to a significantly higher level. The transformer is designed with a specific impedance ratio, allowing for efficient energy transfer and voltage amplification.
The output from the transformer is an alternating current (AC) signal, which is then fed into a multiplier circuit composed of eight diodes (D1 to D8) arranged in a configuration suitable for voltage multiplication. This arrangement effectively increases the peak voltage output from the transformer, allowing the circuit to achieve the desired high voltage of approximately 2,000 volts.
Capacitors C2 to C9 play a critical role in the multiplier circuit, storing energy and smoothing the output voltage. The requirement for these capacitors to have a voltage rating of 400 volts or higher is essential to ensure reliability and prevent breakdown under high-voltage conditions.
The operational indicator, consisting of NE1 and resistor R2, provides a visual or functional indication of the circuit's performance, ensuring that the system is functioning correctly and safely. Overall, this circuit design is suitable for applications requiring high-voltage generation, leveraging the principles of oscillation and voltage multiplication effectively. In this circuit Ql, Q2, Rl, and CI form a multivibrator. The square wave that results from the oscillation of this circuit (20 to 30 Vpp) is stepped up by T1 (an audio transformer of the type used in radios or small TVs). An 8- to 1,200-Q impedance ratio equates to a turn ratio of 12:1. The ac from the secondary of T1 is applied to the multiplier circuit (D1 to D8 and C2 to C9). NE1/R2 are used as an operating indicator. The circuit will supply about 2,000 V. C2 to C9 should have a 400-V or higher voltage rating.
The circuit described operates as a high-voltage generator utilizing a multivibrator configuration. The multivibrator, formed by transistors Q1 and Q2, generates a square wave signal. This square wave oscillation is essential for driving the transformer T1, which steps up the voltage to a significantly higher level. The transformer is designed with a specific impedance ratio, allowing for efficient energy transfer and voltage amplification.
The output from the transformer is an alternating current (AC) signal, which is then fed into a multiplier circuit composed of eight diodes (D1 to D8) arranged in a configuration suitable for voltage multiplication. This arrangement effectively increases the peak voltage output from the transformer, allowing the circuit to achieve the desired high voltage of approximately 2,000 volts.
Capacitors C2 to C9 play a critical role in the multiplier circuit, storing energy and smoothing the output voltage. The requirement for these capacitors to have a voltage rating of 400 volts or higher is essential to ensure reliability and prevent breakdown under high-voltage conditions.
The operational indicator, consisting of NE1 and resistor R2, provides a visual or functional indication of the circuit's performance, ensuring that the system is functioning correctly and safely. Overall, this circuit design is suitable for applications requiring high-voltage generation, leveraging the principles of oscillation and voltage multiplication effectively. In this circuit Ql, Q2, Rl, and CI form a multivibrator. The square wave that results from the oscillation of this circuit (20 to 30 Vpp) is stepped up by T1 (an audio transformer of the type used in radios or small TVs). An 8- to 1,200-Q impedance ratio equates to a turn ratio of 12:1. The ac from the secondary of T1 is applied to the multiplier circuit (D1 to D8 and C2 to C9). NE1/R2 are used as an operating indicator. The circuit will supply about 2,000 V. C2 to C9 should have a 400-V or higher voltage rating.