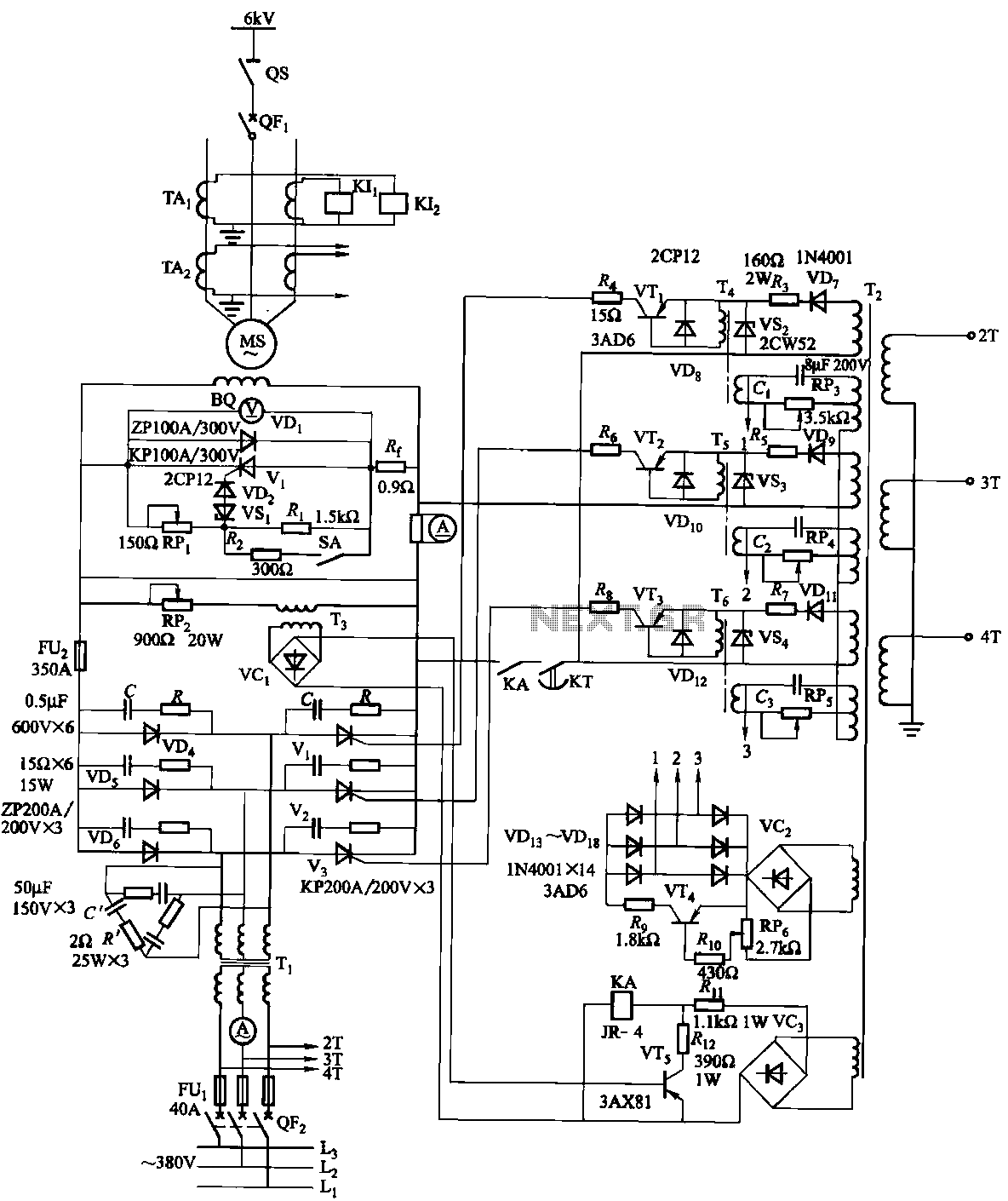
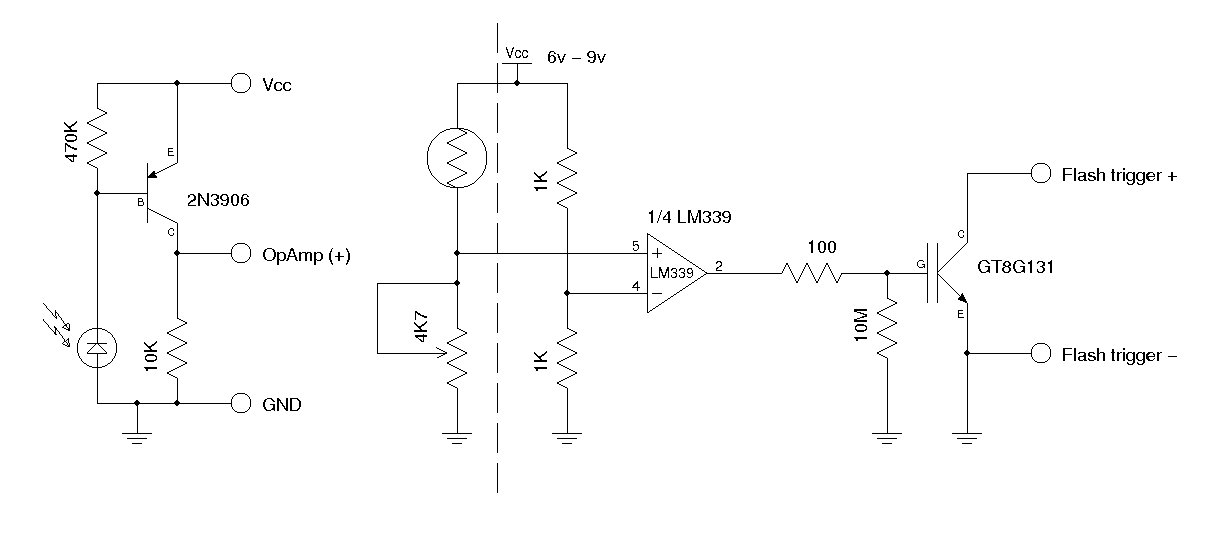
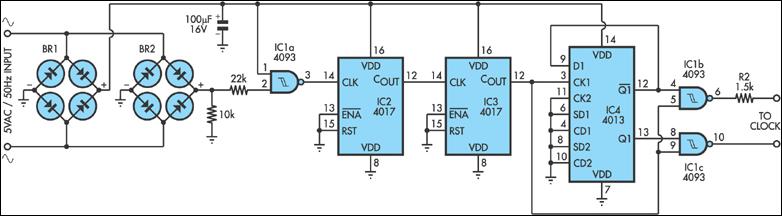
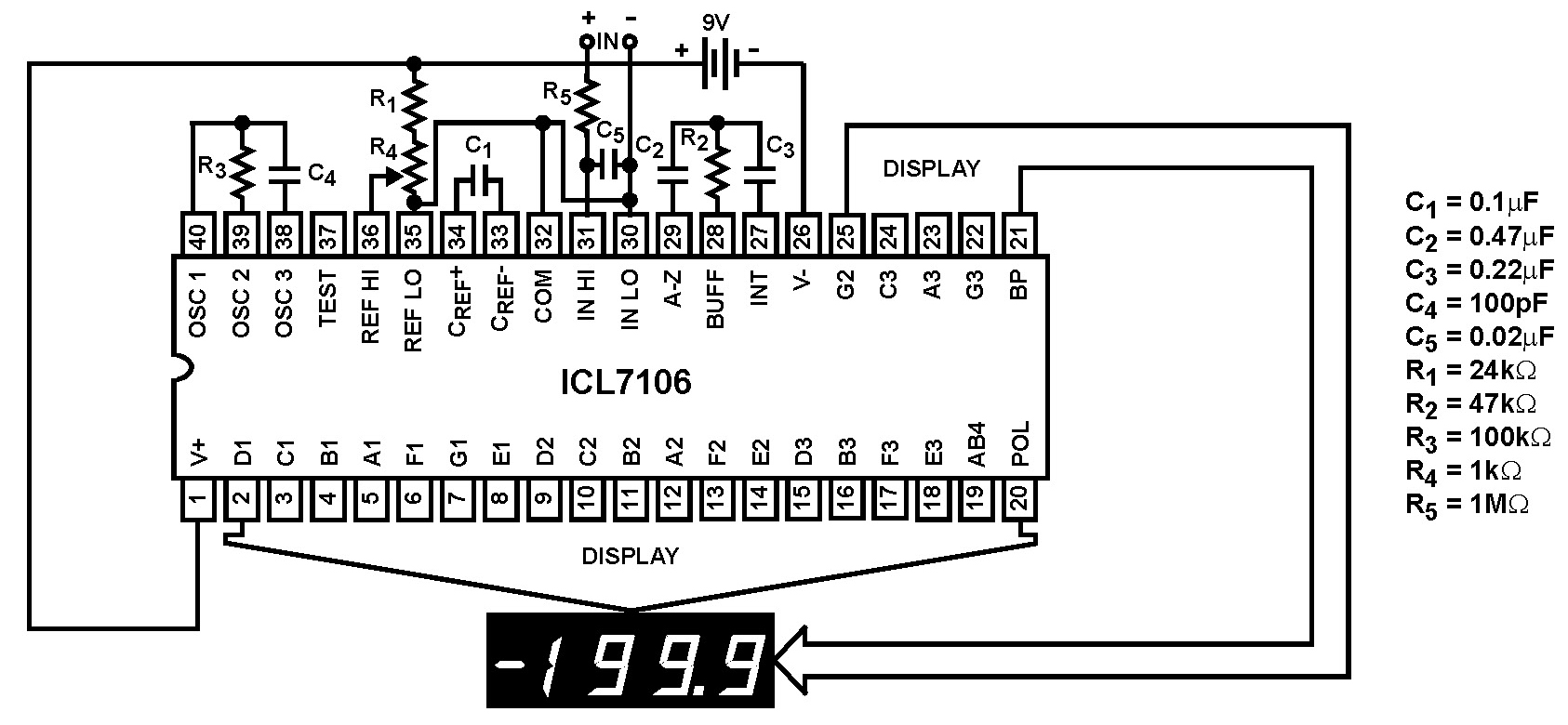
200mA Buck-Boost Synchronous DC/DC Converters
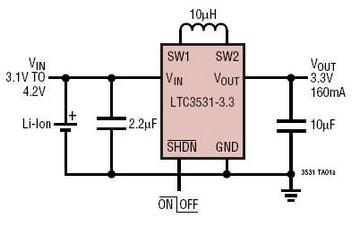
The LTC3531, LTC3531-3.3, and LTC3531-3 are synchronous buck-boost DC/DC converters that function with input voltages that can be above, below, or equal to the output voltage. The topology utilized in these integrated circuits (ICs) enables continuous power transfer across all operating modes, making them suitable for applications involving single-cell Li-Ion batteries and multicell alkaline or nickel batteries. The converters operate in Burst Mode, which reduces the solution footprint and component count while maintaining high conversion efficiency across a wide range of load currents. Each device incorporates two 0.5 A N-channel MOSFET switches and two P-channel switches (0.5 A, 0.8 A). The typical quiescent current is 16 µA, making these devices well-suited for battery-powered applications. Additional features include a shutdown current of less than 1 µA, current limiting, thermal shutdown, and output disconnect functionality. The devices are available in a 6-pin ThinSOT package for fixed voltage versions or a 3mm x 3mm DFN package for both fixed and adjustable versions.
The LTC3531 series of synchronous buck-boost converters is designed to provide efficient voltage regulation in applications where the input voltage may vary significantly in relation to the output voltage. This flexibility is crucial for battery-operated devices, where the input voltage from batteries can fluctuate as they discharge. The converters utilize a sophisticated control scheme that allows seamless transitions between buck, boost, and buck-boost modes, ensuring optimal efficiency regardless of the operating conditions.
In Burst Mode operation, the ICs minimize power loss during low load conditions by reducing the switching frequency and entering a low-power state, which significantly lowers the quiescent current to approximately 16 µA. This feature is particularly advantageous for battery-powered applications, as it extends battery life by reducing the overall current draw when the device is idle.
The inclusion of two N-channel MOSFETs and two P-channel MOSFETs in the converter design allows for efficient switching and power management. The devices are capable of handling output currents up to 0.8 A, making them suitable for a variety of load requirements. Furthermore, the built-in current limiting and thermal shutdown features protect the device from overcurrent and overheating conditions, enhancing reliability in demanding applications.
The LTC3531 devices are offered in compact packages, such as the 6-pin ThinSOT and 3mm x 3mm DFN, facilitating integration into space-constrained designs. This compact packaging, combined with the high efficiency and versatility of the converters, makes the LTC3531 series an excellent choice for powering portable electronics, sensors, and other battery-operated devices.The LTC3531/LTC3531-3. 3/LTC3531-3 are synchronous buck-boost DC/DC converters that operate from input voltages above, below or equal to the output voltage. The topology incorporated in the ICs provides a continuous transfer through all operating modes, making the product ideal for single cell Li-Ion and multicell alkaline or nickel applications.
T he converters operate in Burst Mode, minimizing solution footprint and component count as well as providing high conversion efficiency over a wide range of load currents. The devices include two 0. 5 © N-channel MOSFET switches and two P-channel switches (0. 5 ©, 0. 8 ©). Quiescent current is typically 16 A, making the parts ideal for battery power applications. Other features include a <1uA shutdown current, current limiting, thermal shutdown and output disconnect. The parts are offered in a 6-pin ThinSOT package for fi xed voltage versions or a 3mm G— 3mm DFN package for fixed and adjustable versions.
🔗 External reference
The LTC3531 series of synchronous buck-boost converters is designed to provide efficient voltage regulation in applications where the input voltage may vary significantly in relation to the output voltage. This flexibility is crucial for battery-operated devices, where the input voltage from batteries can fluctuate as they discharge. The converters utilize a sophisticated control scheme that allows seamless transitions between buck, boost, and buck-boost modes, ensuring optimal efficiency regardless of the operating conditions.
In Burst Mode operation, the ICs minimize power loss during low load conditions by reducing the switching frequency and entering a low-power state, which significantly lowers the quiescent current to approximately 16 µA. This feature is particularly advantageous for battery-powered applications, as it extends battery life by reducing the overall current draw when the device is idle.
The inclusion of two N-channel MOSFETs and two P-channel MOSFETs in the converter design allows for efficient switching and power management. The devices are capable of handling output currents up to 0.8 A, making them suitable for a variety of load requirements. Furthermore, the built-in current limiting and thermal shutdown features protect the device from overcurrent and overheating conditions, enhancing reliability in demanding applications.
The LTC3531 devices are offered in compact packages, such as the 6-pin ThinSOT and 3mm x 3mm DFN, facilitating integration into space-constrained designs. This compact packaging, combined with the high efficiency and versatility of the converters, makes the LTC3531 series an excellent choice for powering portable electronics, sensors, and other battery-operated devices.The LTC3531/LTC3531-3. 3/LTC3531-3 are synchronous buck-boost DC/DC converters that operate from input voltages above, below or equal to the output voltage. The topology incorporated in the ICs provides a continuous transfer through all operating modes, making the product ideal for single cell Li-Ion and multicell alkaline or nickel applications.
T he converters operate in Burst Mode, minimizing solution footprint and component count as well as providing high conversion efficiency over a wide range of load currents. The devices include two 0. 5 © N-channel MOSFET switches and two P-channel switches (0. 5 ©, 0. 8 ©). Quiescent current is typically 16 A, making the parts ideal for battery power applications. Other features include a <1uA shutdown current, current limiting, thermal shutdown and output disconnect. The parts are offered in a 6-pin ThinSOT package for fi xed voltage versions or a 3mm G— 3mm DFN package for fixed and adjustable versions.
🔗 External reference