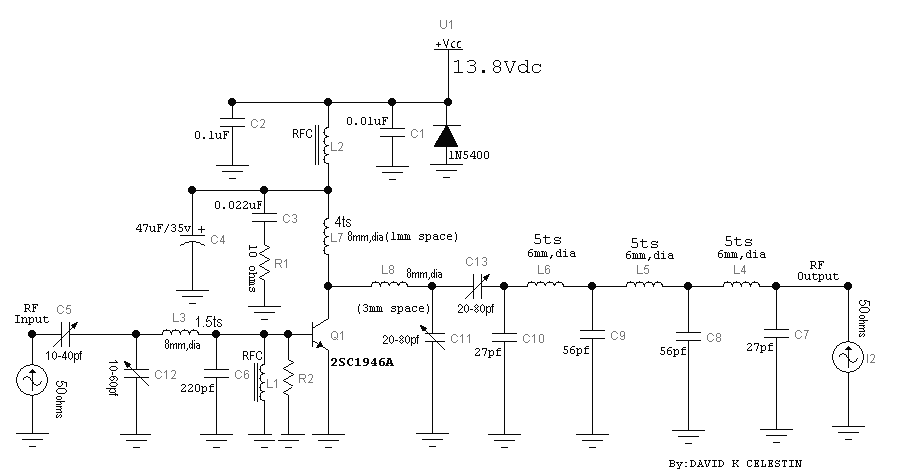
200Mhz cascode amplifier
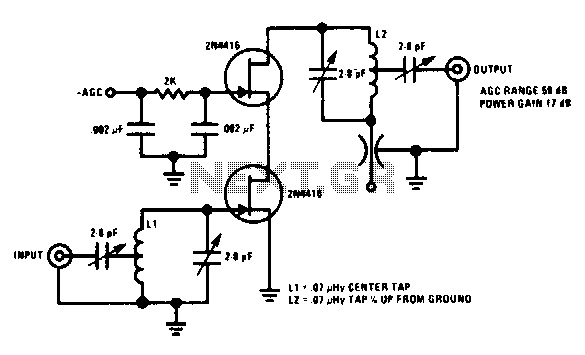
This 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit features low cross-modulation, large signal handling ability, no neutralization, and automatic gain control (AGC) managed by biasing the upper cascode JFET. The only special requirement of this circuit is that the drain-source saturation current (Idss) of the upper unit must be greater than that of the lower unit.
The 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit is designed to achieve high-frequency performance while minimizing undesirable effects such as cross-modulation. The cascode configuration, which consists of two JFETs arranged in series, allows for improved gain stability and bandwidth. The upper JFET is responsible for providing a high impedance to the input signal, while the lower JFET amplifies the signal with a lower output impedance.
In this circuit, the automatic gain control (AGC) is implemented by adjusting the biasing of the upper cascode JFET. This allows for dynamic control of the gain based on the input signal level, ensuring that the output remains within a specified range despite variations in the input. The absence of neutralization simplifies the design and enhances reliability, making it suitable for applications where consistent performance is critical.
The requirement that the Idss of the upper JFET exceeds that of the lower JFET is vital for maintaining the desired operating point and ensuring that the upper device can effectively handle the larger signal levels without distortion. This design consideration is critical for achieving optimal performance in high-frequency applications, where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, this JFET cascode circuit is an effective solution for high-frequency amplification needs, balancing performance with simplicity and reliability.This 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit features low cross-modulation, large signal handling ability, no neutralization, and AGC controlled by biasing the upper cascode JFET The only special requirement of this circuit is that Idss of the upper unit must be greater than that of the lower unit.
The 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit is designed to achieve high-frequency performance while minimizing undesirable effects such as cross-modulation. The cascode configuration, which consists of two JFETs arranged in series, allows for improved gain stability and bandwidth. The upper JFET is responsible for providing a high impedance to the input signal, while the lower JFET amplifies the signal with a lower output impedance.
In this circuit, the automatic gain control (AGC) is implemented by adjusting the biasing of the upper cascode JFET. This allows for dynamic control of the gain based on the input signal level, ensuring that the output remains within a specified range despite variations in the input. The absence of neutralization simplifies the design and enhances reliability, making it suitable for applications where consistent performance is critical.
The requirement that the Idss of the upper JFET exceeds that of the lower JFET is vital for maintaining the desired operating point and ensuring that the upper device can effectively handle the larger signal levels without distortion. This design consideration is critical for achieving optimal performance in high-frequency applications, where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, this JFET cascode circuit is an effective solution for high-frequency amplification needs, balancing performance with simplicity and reliability.This 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit features low cross-modulation, large signal handling ability, no neutralization, and AGC controlled by biasing the upper cascode JFET The only special requirement of this circuit is that Idss of the upper unit must be greater than that of the lower unit.