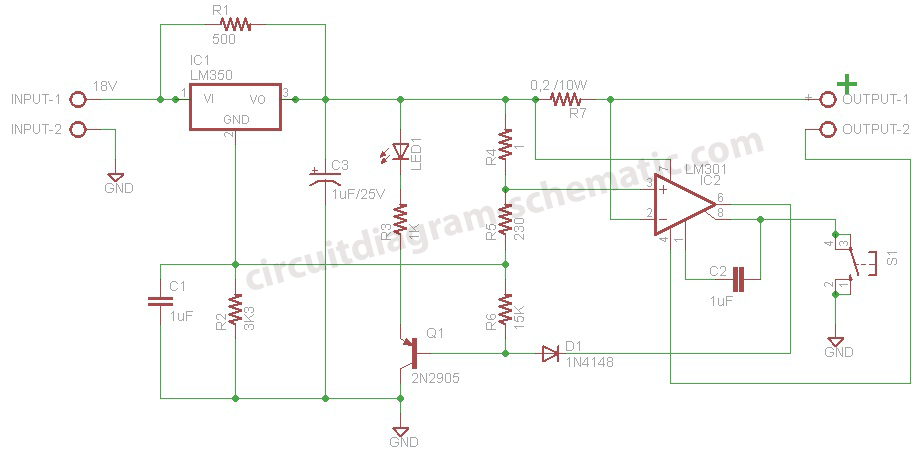
20dB antenna amplifier circuit diagram electronic project
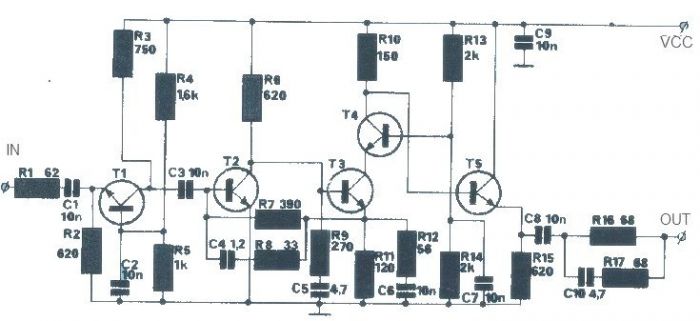
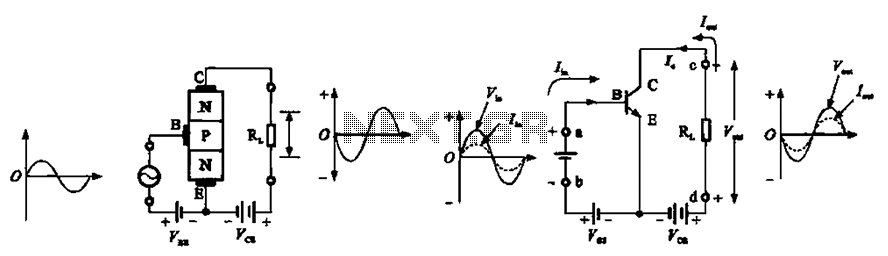
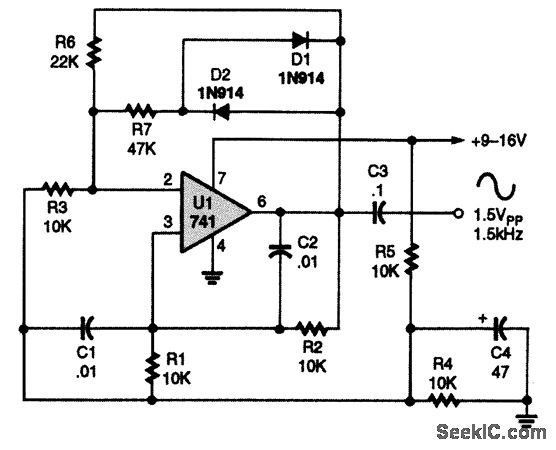
The T1 transistor must be of the BF200 type (or a similar variant), while the other transistors can be of the BF214 type. To achieve high efficiency, the antenna amplifier should be positioned at a short distance from the antenna. This amplifier circuit can be powered by a power supply that provides an output voltage between 6 and 12 volts DC. It is recommended to use a shielded cable or coaxial cable for powering this device.
The circuit design involves utilizing a BF200 transistor as the primary amplification element, which is known for its high-frequency performance and low noise characteristics. The BF214 transistors serve as additional amplification stages, enhancing the overall gain of the circuit.
To ensure optimal performance, the placement of the antenna amplifier is crucial; it should be installed as close to the antenna as possible to minimize signal loss and maintain signal integrity. The use of a power supply that delivers a voltage range of 6 to 12 volts DC allows for flexibility in powering the circuit, accommodating various power supply options available in the field.
For the connection of the power supply to the amplifier circuit, employing a shielded cable or coaxial cable is vital. This choice helps to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensures that the signal remains clean as it travels from the power source to the amplifier. Additionally, the shielded cable provides protection against external noise, which is especially important in RF applications.
The overall design should consider the thermal management of the transistors, ensuring that adequate heat dissipation is provided, especially under high load conditions. Proper grounding techniques should also be implemented to prevent ground loops and enhance circuit stability.
In summary, the circuit requires careful attention to component selection, placement, and interconnection methods to achieve the desired performance in antenna amplification applications.T1 transistor must be BF200 type (or similar ) and the other transistors can be BF214 type. For high efficiency, the antenna amplifier must be placed at a small distance from antenna. This amplifier circuit can be powered using a power supply that supply an output voltage between 6 and 12 volts DC. For powering this device you need to use a sh ielded cable or a coaxial cable. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design involves utilizing a BF200 transistor as the primary amplification element, which is known for its high-frequency performance and low noise characteristics. The BF214 transistors serve as additional amplification stages, enhancing the overall gain of the circuit.
To ensure optimal performance, the placement of the antenna amplifier is crucial; it should be installed as close to the antenna as possible to minimize signal loss and maintain signal integrity. The use of a power supply that delivers a voltage range of 6 to 12 volts DC allows for flexibility in powering the circuit, accommodating various power supply options available in the field.
For the connection of the power supply to the amplifier circuit, employing a shielded cable or coaxial cable is vital. This choice helps to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensures that the signal remains clean as it travels from the power source to the amplifier. Additionally, the shielded cable provides protection against external noise, which is especially important in RF applications.
The overall design should consider the thermal management of the transistors, ensuring that adequate heat dissipation is provided, especially under high load conditions. Proper grounding techniques should also be implemented to prevent ground loops and enhance circuit stability.
In summary, the circuit requires careful attention to component selection, placement, and interconnection methods to achieve the desired performance in antenna amplification applications.T1 transistor must be BF200 type (or similar ) and the other transistors can be BF214 type. For high efficiency, the antenna amplifier must be placed at a small distance from antenna. This amplifier circuit can be powered using a power supply that supply an output voltage between 6 and 12 volts DC. For powering this device you need to use a sh ielded cable or a coaxial cable. 🔗 External reference