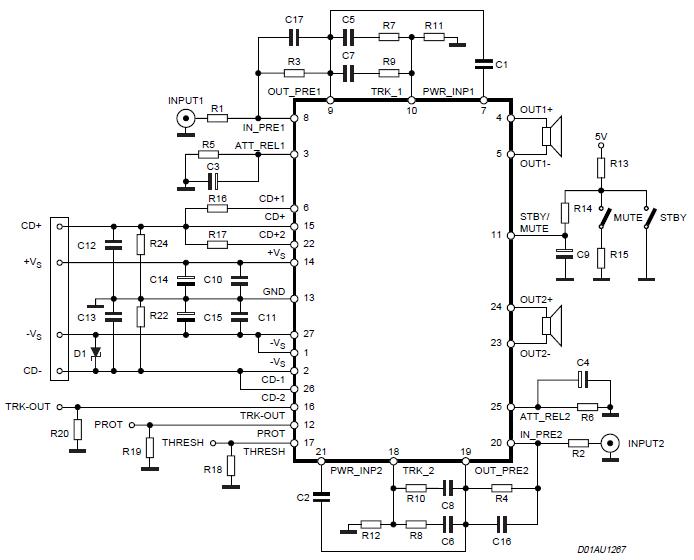
22 Watt Stereo Amplifier
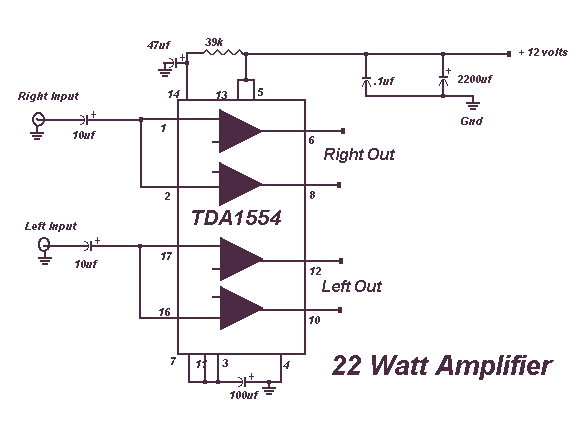
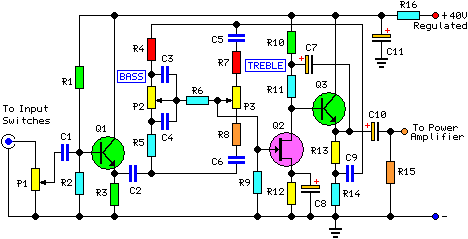
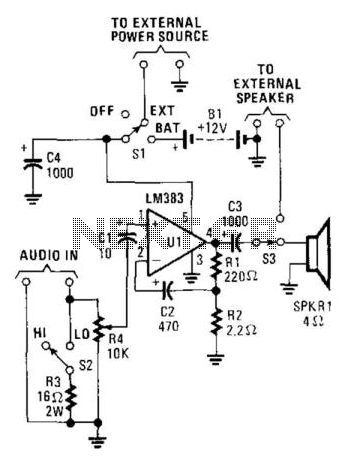
This circuit is very basic to build and puts out great power for your car or home. Keep all leads as short as possible.
The described circuit is a fundamental power amplifier, suitable for applications in automotive or residential settings. The design aims to deliver high output power while maintaining simplicity in construction. It is essential to minimize lead lengths to reduce parasitic inductance and resistance, which can adversely affect performance.
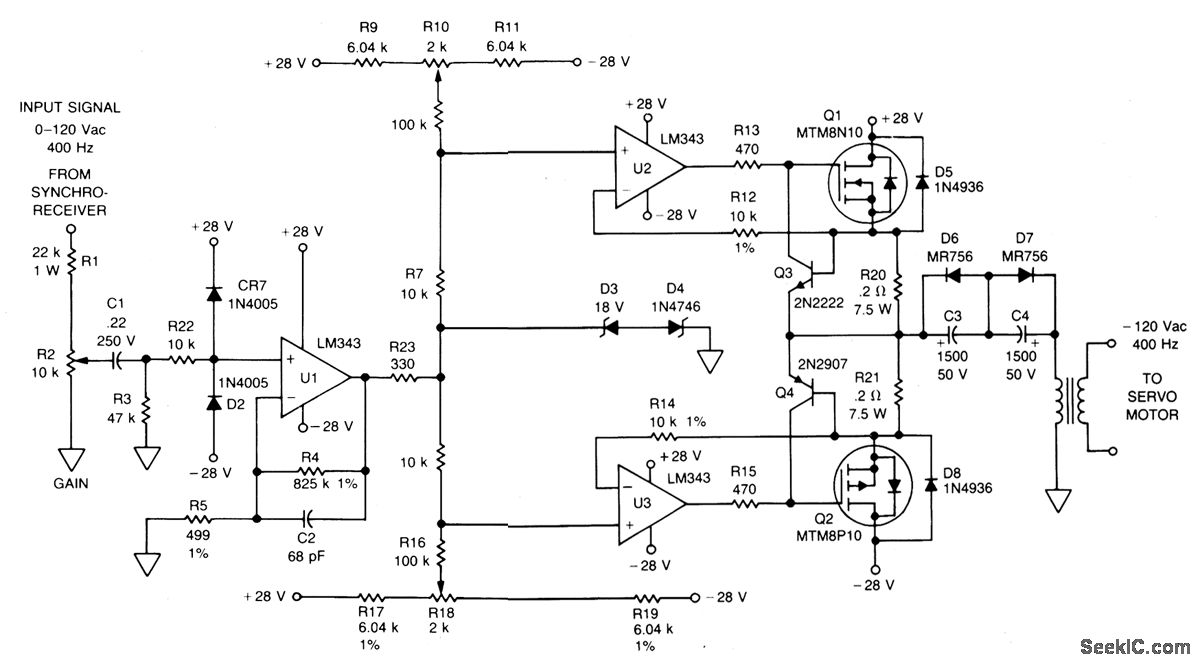
The circuit typically consists of a power supply, an amplifier stage, and output transistors. The power supply should be capable of providing adequate current and voltage levels to support the desired output power. A common configuration might include a transformer-based supply for AC applications or a battery for DC applications.
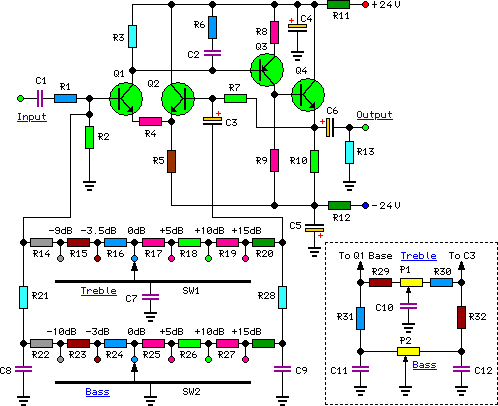
The amplifier stage can be built using operational amplifiers or discrete transistors, depending on the required power output and frequency response. For higher power applications, using complementary push-pull transistor configurations can enhance efficiency and reduce distortion.
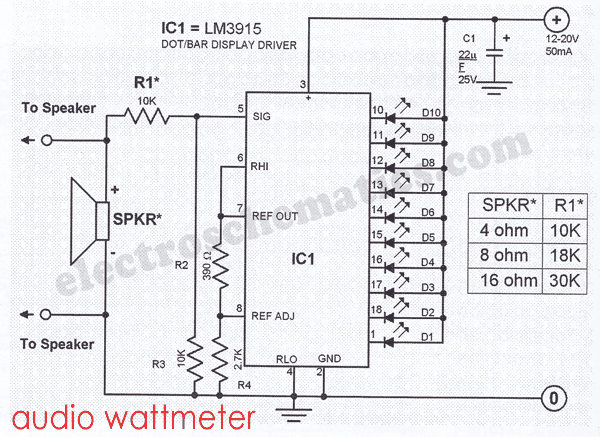
Output transistors are crucial for driving the load, which could be speakers in a car audio system or appliances in a home. Heat sinks may be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring the transistors operate within safe temperature limits.
Circuit protection features, such as fuses or circuit breakers, should be incorporated to prevent damage from overcurrent situations. Additionally, decoupling capacitors can be placed near the power supply pins of the amplifier to stabilize the voltage during transient conditions.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes robustness and efficiency, making it suitable for various high-power applications. Proper layout and component selection are critical for achieving optimal performance.This circuit is very basic to build and puts out great power for your car or home. Keep all leads as short as possible. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a fundamental power amplifier, suitable for applications in automotive or residential settings. The design aims to deliver high output power while maintaining simplicity in construction. It is essential to minimize lead lengths to reduce parasitic inductance and resistance, which can adversely affect performance.
The circuit typically consists of a power supply, an amplifier stage, and output transistors. The power supply should be capable of providing adequate current and voltage levels to support the desired output power. A common configuration might include a transformer-based supply for AC applications or a battery for DC applications.
The amplifier stage can be built using operational amplifiers or discrete transistors, depending on the required power output and frequency response. For higher power applications, using complementary push-pull transistor configurations can enhance efficiency and reduce distortion.
Output transistors are crucial for driving the load, which could be speakers in a car audio system or appliances in a home. Heat sinks may be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring the transistors operate within safe temperature limits.
Circuit protection features, such as fuses or circuit breakers, should be incorporated to prevent damage from overcurrent situations. Additionally, decoupling capacitors can be placed near the power supply pins of the amplifier to stabilize the voltage during transient conditions.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes robustness and efficiency, making it suitable for various high-power applications. Proper layout and component selection are critical for achieving optimal performance.This circuit is very basic to build and puts out great power for your car or home. Keep all leads as short as possible. 🔗 External reference