220V LED Flasher
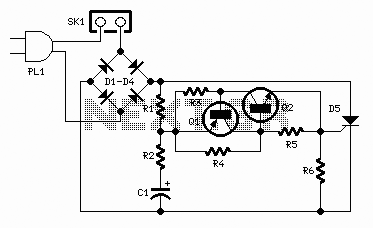
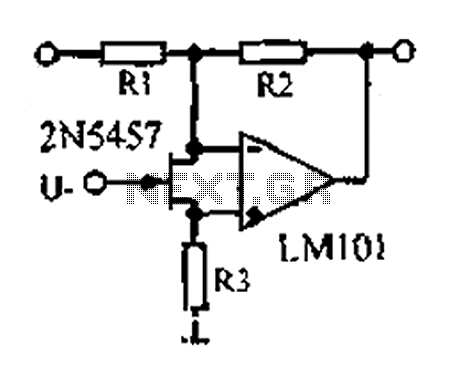
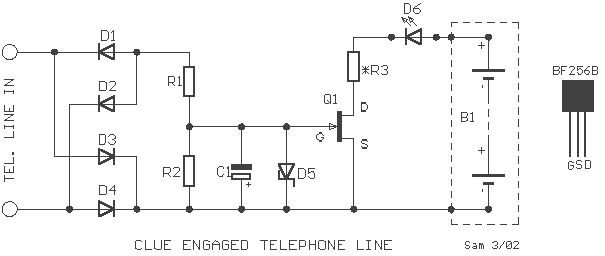
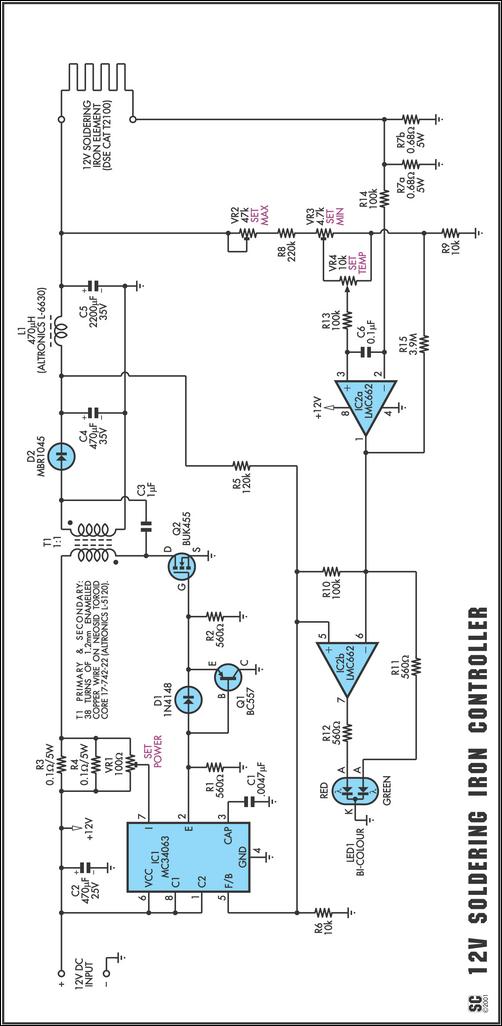
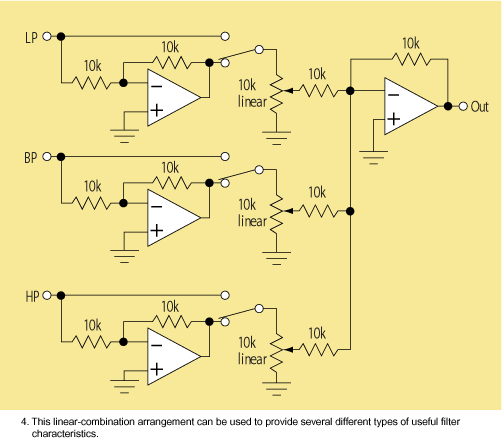
This is a 220V LED flasher circuit designed as a reliable alternative to thermally-activated switches for flashing Christmas tree lamps. The circuit is cost-effective and easy to assemble. Schematic diagram: Component Parts: R1 10Ω.
The 220V LED flasher circuit operates by utilizing a simple arrangement of components to create a flashing effect suitable for decorative lighting applications, such as Christmas tree lamps. The primary components include a resistor (R1), which is essential for controlling the current flow through the LED, ensuring it operates within safe limits. The circuit may also include additional components such as a capacitor for timing, a diode for rectification, and a transistor to switch the LED on and off.
In a typical configuration, the resistor R1 is connected in series with the LED, which is powered by a 220V AC supply. The capacitor, when included, is connected in parallel with the LED, forming an RC timing circuit that determines the flashing rate. The diode is used to convert the AC voltage to DC, allowing the LED to flash appropriately. The transistor acts as a switch, controlled by the charging and discharging of the capacitor, enabling the LED to turn on and off at a specified frequency.
This circuit can be assembled on a breadboard or a printed circuit board (PCB) for more permanent installations. The simplicity of the design, combined with readily available components, makes this LED flasher circuit an ideal choice for festive lighting applications, providing an energy-efficient and visually appealing solution. Proper safety precautions should be taken when working with high-voltage circuits, including the use of insulated tools and components rated for the operating voltage.This is a 220V LED flasher circuit which is intended as a reliable replacement to thermally-activated switches used for Christmas tree lamp-flashing. This a cheap circuit and easy to build. Schematic diagram: Component Parts: R1_________ 10.. 🔗 External reference
The 220V LED flasher circuit operates by utilizing a simple arrangement of components to create a flashing effect suitable for decorative lighting applications, such as Christmas tree lamps. The primary components include a resistor (R1), which is essential for controlling the current flow through the LED, ensuring it operates within safe limits. The circuit may also include additional components such as a capacitor for timing, a diode for rectification, and a transistor to switch the LED on and off.
In a typical configuration, the resistor R1 is connected in series with the LED, which is powered by a 220V AC supply. The capacitor, when included, is connected in parallel with the LED, forming an RC timing circuit that determines the flashing rate. The diode is used to convert the AC voltage to DC, allowing the LED to flash appropriately. The transistor acts as a switch, controlled by the charging and discharging of the capacitor, enabling the LED to turn on and off at a specified frequency.
This circuit can be assembled on a breadboard or a printed circuit board (PCB) for more permanent installations. The simplicity of the design, combined with readily available components, makes this LED flasher circuit an ideal choice for festive lighting applications, providing an energy-efficient and visually appealing solution. Proper safety precautions should be taken when working with high-voltage circuits, including the use of insulated tools and components rated for the operating voltage.This is a 220V LED flasher circuit which is intended as a reliable replacement to thermally-activated switches used for Christmas tree lamp-flashing. This a cheap circuit and easy to build. Schematic diagram: Component Parts: R1_________ 10.. 🔗 External reference