2Watt Audio Amplifier
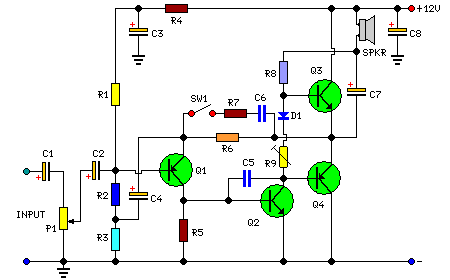
The circuit was intentionally designed without integrated circuits (ICs) and follows a traditional approach to achieve favorable harmonic distortion characteristics while avoiding the use of hard-to-find components. The amplifier can be powered conveniently using a 12V wall plug-in adapter. Activating switch SW1 enables a bass boost feature; however, it is necessary to increase the volume control to compensate for power loss at higher frequencies. During operation, resistor R9 should be adjusted carefully to minimize audible signal crossover distortion while maintaining low quiescent current consumption. A suitable compromise is to set the quiescent current at approximately 10-15 mA. To measure this current, a DC current meter should be temporarily connected in series with the collector of transistor Q3.
The circuit is designed as a discrete amplifier that emphasizes simplicity and ease of assembly. By avoiding integrated circuits, the design offers a hands-on approach, appealing to hobbyists and engineers who appreciate traditional circuit-building techniques. The choice of a 12V wall adapter for power supply ensures compatibility with common power sources, making the amplifier suitable for various applications.
The bass boost feature, activated by switch SW1, enhances low-frequency response, which is particularly beneficial for applications requiring richer sound quality. However, users must be aware that engaging this feature necessitates an increase in volume control to counterbalance the inherent power loss at higher frequencies, ensuring that the output remains consistent and clear across the audio spectrum.
Resistor R9 plays a critical role in managing crossover distortion, which can adversely affect audio quality if not properly adjusted. The recommendation to set the quiescent current at 10-15 mA strikes a balance between performance and efficiency, allowing the amplifier to operate effectively while minimizing heat generation and power consumption. The inclusion of a DC current meter for measuring quiescent current provides a practical method for users to fine-tune the amplifier's performance, ensuring optimal operation.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a classic approach to audio amplification, combining simplicity, functionality, and ease of use, making it a valuable project for those interested in exploring the fundamentals of electronic amplifiers.The circuit was deliberately designed using no ICs and in a rather old-fashioned manner in order to obtain good harmonic distortion behavior and to avoid hard to find components. The amplifier(s) can be conveniently supplied by a 12V wall plug-in adapter. Closing SW1 a bass-boost is provided but, at the same time, volume control must be increased to compensate for power loss at higher frequencies. In use, R9 should be carefully adjusted to provide minimal audible signal cross-over distortion consistent with minimal measured quiescent current consumption; a good compromise is to set the quiescent current at about 10-15 mA. To measure this current, wire a DC current meter temporarily in series with the collector of Q3. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed as a discrete amplifier that emphasizes simplicity and ease of assembly. By avoiding integrated circuits, the design offers a hands-on approach, appealing to hobbyists and engineers who appreciate traditional circuit-building techniques. The choice of a 12V wall adapter for power supply ensures compatibility with common power sources, making the amplifier suitable for various applications.
The bass boost feature, activated by switch SW1, enhances low-frequency response, which is particularly beneficial for applications requiring richer sound quality. However, users must be aware that engaging this feature necessitates an increase in volume control to counterbalance the inherent power loss at higher frequencies, ensuring that the output remains consistent and clear across the audio spectrum.
Resistor R9 plays a critical role in managing crossover distortion, which can adversely affect audio quality if not properly adjusted. The recommendation to set the quiescent current at 10-15 mA strikes a balance between performance and efficiency, allowing the amplifier to operate effectively while minimizing heat generation and power consumption. The inclusion of a DC current meter for measuring quiescent current provides a practical method for users to fine-tune the amplifier's performance, ensuring optimal operation.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a classic approach to audio amplification, combining simplicity, functionality, and ease of use, making it a valuable project for those interested in exploring the fundamentals of electronic amplifiers.The circuit was deliberately designed using no ICs and in a rather old-fashioned manner in order to obtain good harmonic distortion behavior and to avoid hard to find components. The amplifier(s) can be conveniently supplied by a 12V wall plug-in adapter. Closing SW1 a bass-boost is provided but, at the same time, volume control must be increased to compensate for power loss at higher frequencies. In use, R9 should be carefully adjusted to provide minimal audible signal cross-over distortion consistent with minimal measured quiescent current consumption; a good compromise is to set the quiescent current at about 10-15 mA. To measure this current, wire a DC current meter temporarily in series with the collector of Q3. 🔗 External reference