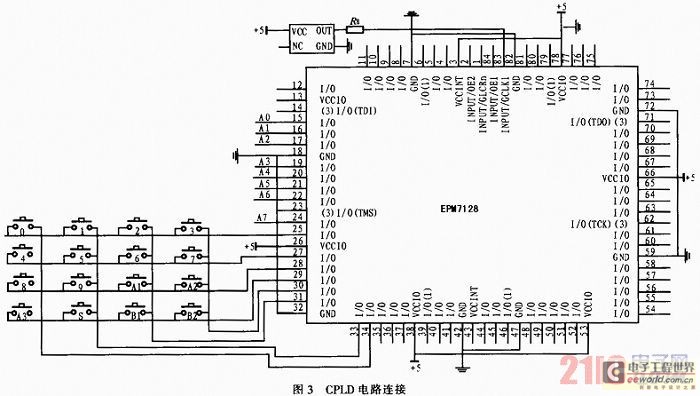
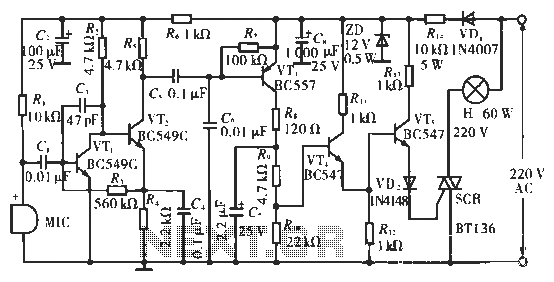
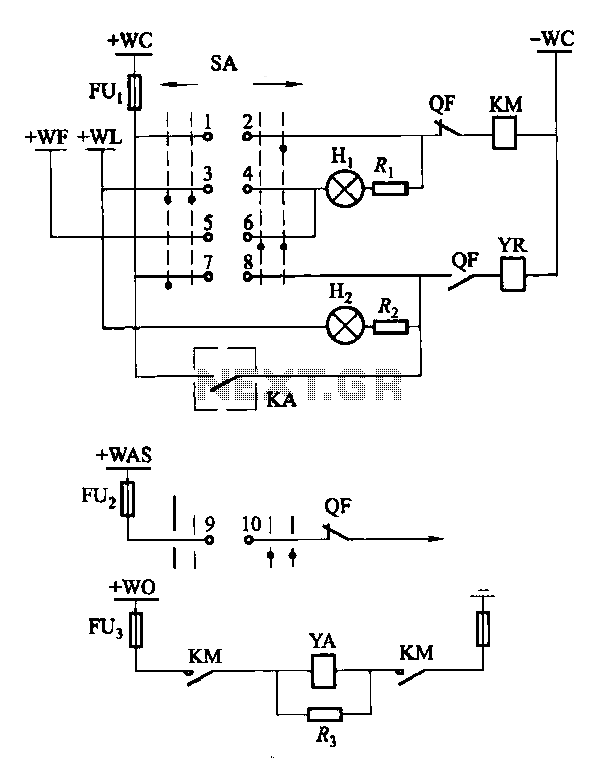
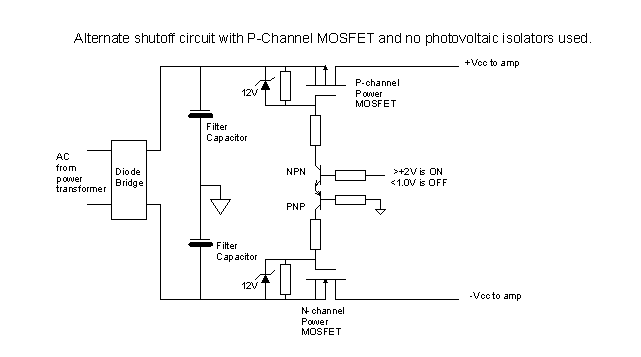
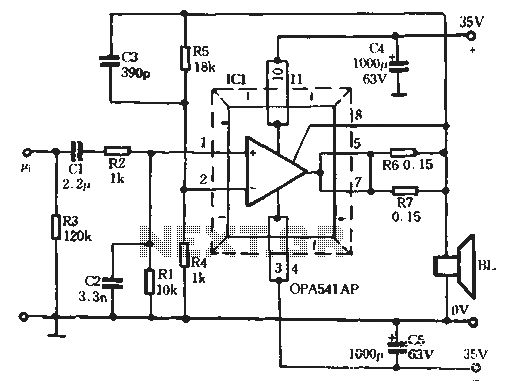
4 Direct drive LCD display circuit diagram
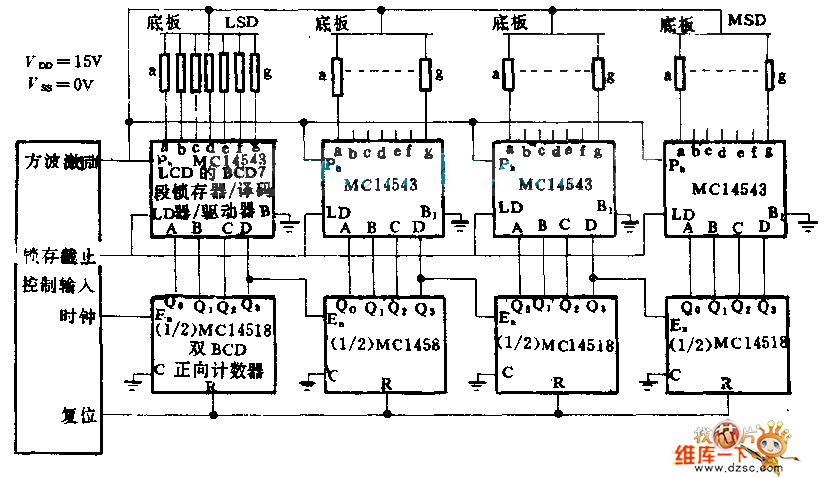
Each part of the LCD has an individual counter, latch, decoder, and driver. The pumping signal is fed back to the motherboard of the LCD. When the display section is disconnected, the phase and amplitude of the motherboard and display segment drive signal are identical, resulting in no voltage being present at the two ends of the display. When the display segment is triggered, its pumping signal is activated.
The LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) system operates through a series of interconnected components that manage the visual output. Each segment of the LCD is equipped with its own counter, latch, decoder, and driver, allowing for precise control over the displayed information. The counter is responsible for counting the incoming signals, while the latch holds the current state of the display until it is updated. The decoder translates the binary input data into signals that can be understood by the driver, which ultimately activates the individual pixels of the display.
Feedback from the pumping signal to the motherboard is crucial for maintaining synchronization between the display and the control circuitry. This feedback mechanism ensures that when the display section is disconnected, the signals from the motherboard and the display segment are in phase and have the same amplitude. As a result, no voltage is detected across the terminals of the display, indicating that the system is in a safe state and preventing potential damage.
When the display segment is triggered, the pumping signal is energized, allowing the individual pixels to change their state and produce the desired visual output. This activation process requires careful timing and control to ensure that the display functions correctly and responds accurately to input signals. The design of the LCD system emphasizes reliability and precision, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in consumer electronics, industrial displays, and other fields where visual information is critical.Each part of LCD has individual counter, latch, decoder and driver. Pumping signal feeds back to the motherboard of LCD. When the display section is disconnected, the phase and amplitude of the motherboard and display segment drive signal are the same. It shows no voltage on the 2 ends of display. When the display segment is triggered, its pumping signal p.. 🔗 External reference
The LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) system operates through a series of interconnected components that manage the visual output. Each segment of the LCD is equipped with its own counter, latch, decoder, and driver, allowing for precise control over the displayed information. The counter is responsible for counting the incoming signals, while the latch holds the current state of the display until it is updated. The decoder translates the binary input data into signals that can be understood by the driver, which ultimately activates the individual pixels of the display.
Feedback from the pumping signal to the motherboard is crucial for maintaining synchronization between the display and the control circuitry. This feedback mechanism ensures that when the display section is disconnected, the signals from the motherboard and the display segment are in phase and have the same amplitude. As a result, no voltage is detected across the terminals of the display, indicating that the system is in a safe state and preventing potential damage.
When the display segment is triggered, the pumping signal is energized, allowing the individual pixels to change their state and produce the desired visual output. This activation process requires careful timing and control to ensure that the display functions correctly and responds accurately to input signals. The design of the LCD system emphasizes reliability and precision, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in consumer electronics, industrial displays, and other fields where visual information is critical.Each part of LCD has individual counter, latch, decoder and driver. Pumping signal feeds back to the motherboard of LCD. When the display section is disconnected, the phase and amplitude of the motherboard and display segment drive signal are the same. It shows no voltage on the 2 ends of display. When the display segment is triggered, its pumping signal p.. 🔗 External reference