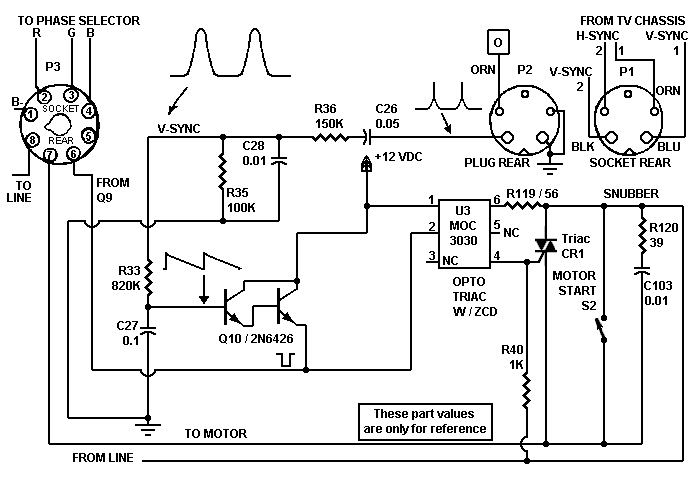
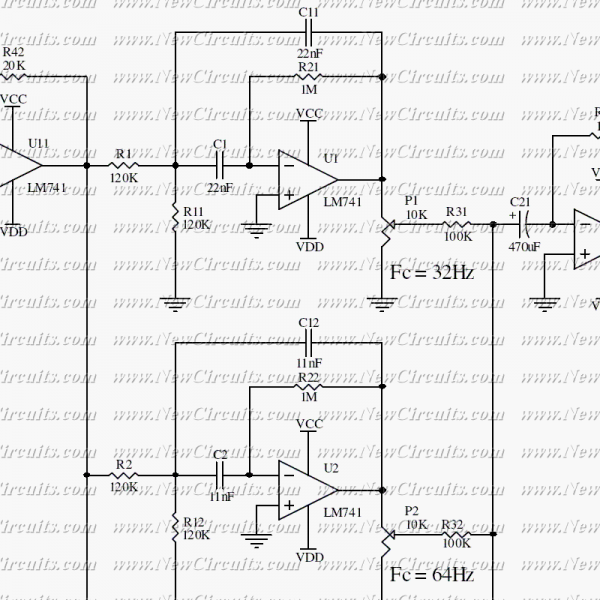
5 channel graphic equalizer by BC548 transistor
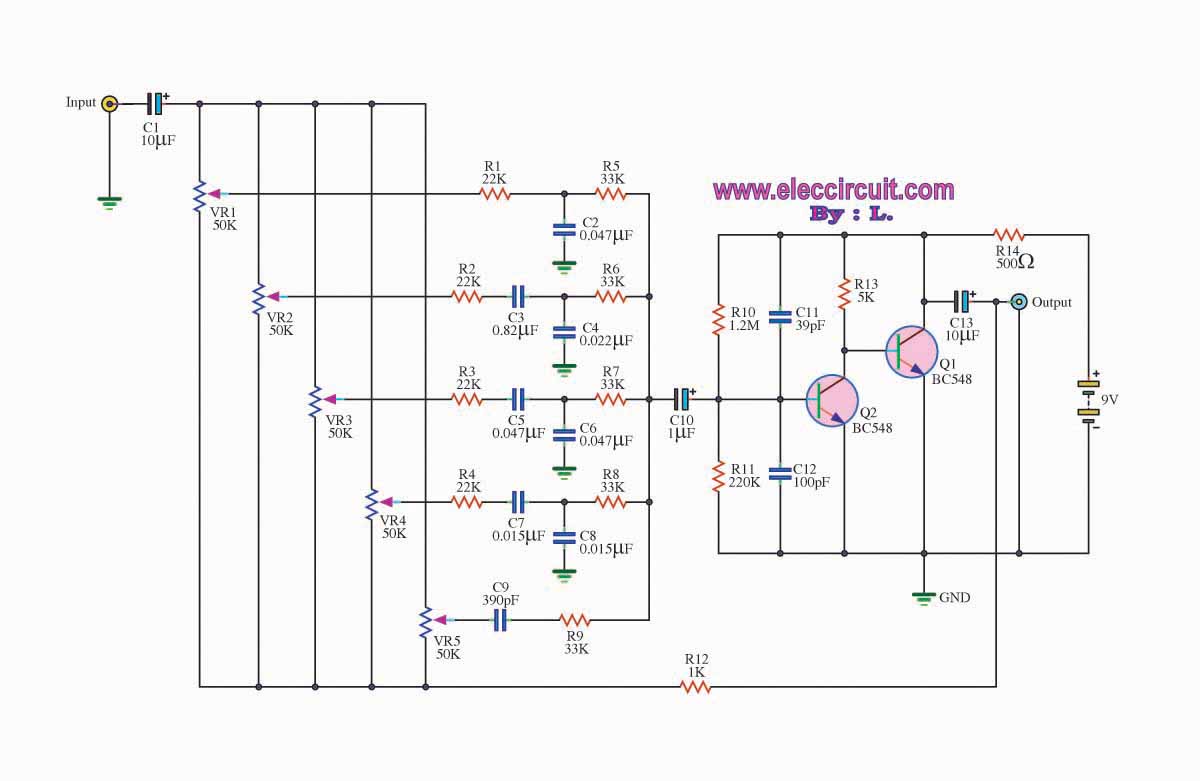
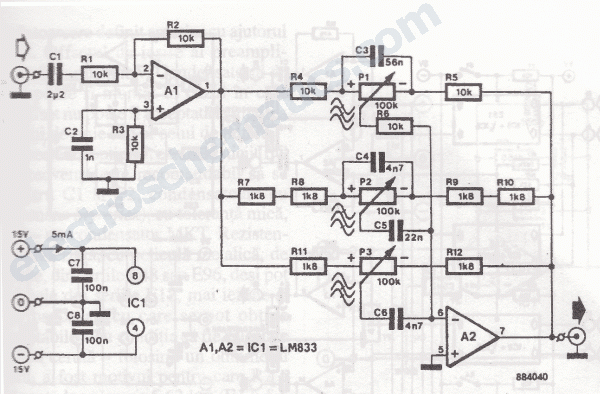
The graphic equalizer circuit is designed to adjust frequency response in audio systems. Certain audio frequency responses may not be smooth.
The graphic equalizer circuit functions by providing the ability to adjust specific frequency bands of an audio signal, allowing for tailored sound reproduction. Typically, this circuit consists of multiple band-pass filters, each tuned to a specific frequency range. The output of each filter can be adjusted using potentiometers, which control the gain for that particular frequency band.
The circuit usually comprises operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured as active filters. Each filter section can be designed as a second-order or higher filter to achieve a steeper roll-off and better separation between adjacent frequency bands. The standard configuration may include several bands, such as 31, 15, or 10 bands, covering the audible spectrum from approximately 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
In a typical implementation, the input audio signal is fed into the circuit, and each filter section processes the signal by boosting or attenuating the amplitude of the specific frequency range. The overall output is a composite of all the adjusted signals, providing a customized audio output that compensates for deficiencies in the original audio source or the acoustics of the listening environment.
To ensure optimal performance, components such as resistors and capacitors must be selected with precision, as they determine the center frequency and bandwidth of each filter. Additionally, feedback mechanisms may be employed to stabilize the circuit and reduce distortion, ensuring high fidelity in audio reproduction.
The graphic equalizer circuit is widely used in various applications, including home audio systems, professional sound reinforcement, and music production, making it an essential tool for audio engineers and enthusiasts alike.The graphic equalizer circuit the frequency adjust circuit. For some kinds of audio frequency response is not smooth. The.. 🔗 External reference
The graphic equalizer circuit functions by providing the ability to adjust specific frequency bands of an audio signal, allowing for tailored sound reproduction. Typically, this circuit consists of multiple band-pass filters, each tuned to a specific frequency range. The output of each filter can be adjusted using potentiometers, which control the gain for that particular frequency band.
The circuit usually comprises operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured as active filters. Each filter section can be designed as a second-order or higher filter to achieve a steeper roll-off and better separation between adjacent frequency bands. The standard configuration may include several bands, such as 31, 15, or 10 bands, covering the audible spectrum from approximately 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
In a typical implementation, the input audio signal is fed into the circuit, and each filter section processes the signal by boosting or attenuating the amplitude of the specific frequency range. The overall output is a composite of all the adjusted signals, providing a customized audio output that compensates for deficiencies in the original audio source or the acoustics of the listening environment.
To ensure optimal performance, components such as resistors and capacitors must be selected with precision, as they determine the center frequency and bandwidth of each filter. Additionally, feedback mechanisms may be employed to stabilize the circuit and reduce distortion, ensuring high fidelity in audio reproduction.
The graphic equalizer circuit is widely used in various applications, including home audio systems, professional sound reinforcement, and music production, making it an essential tool for audio engineers and enthusiasts alike.The graphic equalizer circuit the frequency adjust circuit. For some kinds of audio frequency response is not smooth. The.. 🔗 External reference