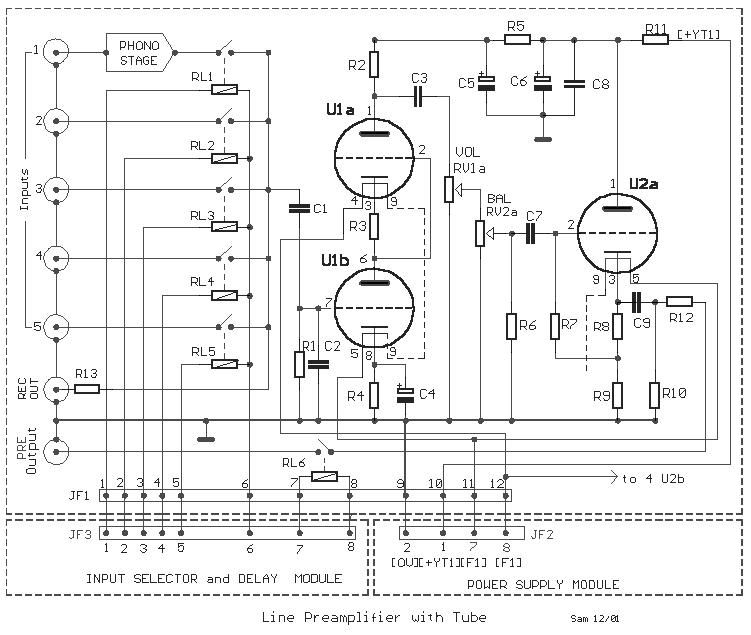
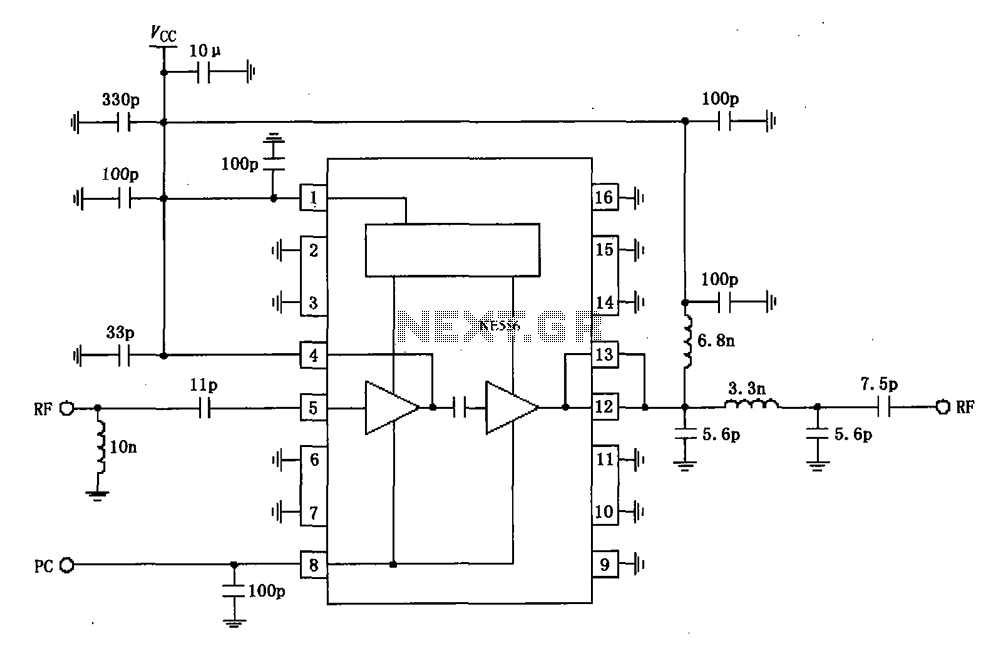
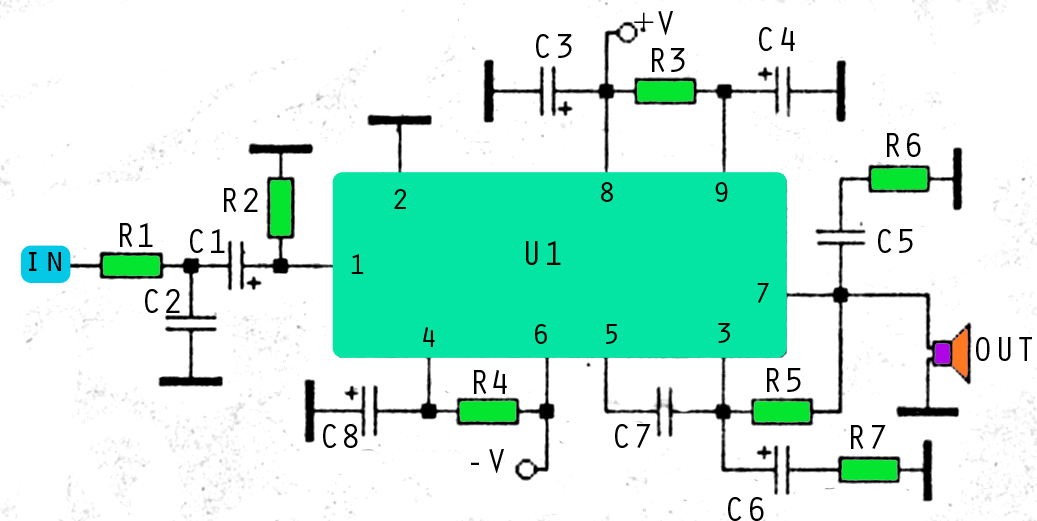
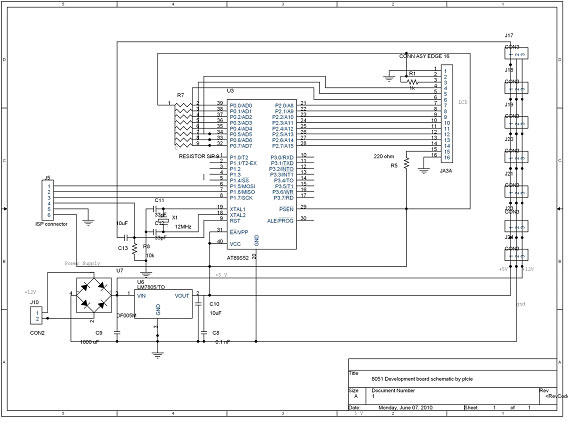
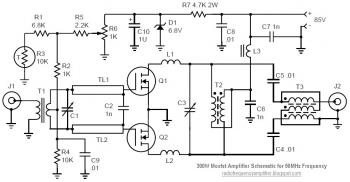
50mhz 300w mosfet amplifier circuit
An RF power amplifier is an electronic amplifier used to convert a low-power radio-frequency signal into a larger signal of significant power, typically for driving the antenna of a transmitter. It is optimized for high efficiency, high output power (P1dB) compression, good gain, good return loss on both the input and output, and optimal heat dissipation. The primary applications of RF power amplifiers include driving high-power sources, transmitting antennas, microwave heating, and exciting resonant cavity structures. Among these applications, driving transmitter antennas is the most recognized.
An RF power amplifier is a critical component in various communication systems, serving to enhance the power level of radio frequency signals for effective transmission. The design of an RF power amplifier involves several key parameters that must be optimized to ensure performance and reliability.
Firstly, efficiency is paramount; it is defined as the ratio of output power to input power. High efficiency minimizes heat generation, which is crucial for maintaining performance and prolonging the lifespan of the amplifier. The output power, often expressed in terms of P1dB, is the power level at which the amplifier begins to compress the output signal. This parameter is essential for understanding the amplifier's linearity and overall performance under varying load conditions.
Gain is another critical factor, representing the ratio of output signal power to input signal power. A good gain ensures that the amplifier can effectively boost weak signals to usable levels without introducing excessive noise. Return loss on both input and output is also significant; it measures how well the amplifier matches the impedance of connected components, impacting signal integrity and minimizing reflections that can degrade performance.
Heat dissipation is a design consideration that directly affects both the efficiency and reliability of the amplifier. Effective thermal management strategies, such as heat sinks and thermal pads, are often incorporated to dissipate heat generated during operation.
RF power amplifiers find applications in various fields, including telecommunications, broadcasting, and industrial heating. In telecommunications, they are vital for driving antennas that transmit signals over long distances, ensuring that the signal maintains its integrity and strength. In microwave heating applications, RF power amplifiers are utilized to generate heat for processes such as cooking or material processing. Additionally, they play a role in exciting resonant cavity structures, which are essential in various scientific and industrial applications.
Overall, the design and application of RF power amplifiers are crucial for enhancing the performance of radio frequency systems, ensuring that signals are transmitted efficiently and effectively across various platforms.An RF power amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier which is utilised to convert a low-power radio-frequency signal into a larger signal of significant power, usually for driving the antenna of a transmitter. It is usually optimized to have high efficiency, high output Power (P1dB) compression, good gain, good return loss on the input and outp
ut, and optimum heat dissipation. The basic applications of the RF power amplifier include driving to another high power source, driving a transmitting antenna, microwave heating, and exciting resonant cavity structures. Among these applications, driving transmitter antennas is most well known. 🔗 External reference
An RF power amplifier is a critical component in various communication systems, serving to enhance the power level of radio frequency signals for effective transmission. The design of an RF power amplifier involves several key parameters that must be optimized to ensure performance and reliability.
Firstly, efficiency is paramount; it is defined as the ratio of output power to input power. High efficiency minimizes heat generation, which is crucial for maintaining performance and prolonging the lifespan of the amplifier. The output power, often expressed in terms of P1dB, is the power level at which the amplifier begins to compress the output signal. This parameter is essential for understanding the amplifier's linearity and overall performance under varying load conditions.
Gain is another critical factor, representing the ratio of output signal power to input signal power. A good gain ensures that the amplifier can effectively boost weak signals to usable levels without introducing excessive noise. Return loss on both input and output is also significant; it measures how well the amplifier matches the impedance of connected components, impacting signal integrity and minimizing reflections that can degrade performance.
Heat dissipation is a design consideration that directly affects both the efficiency and reliability of the amplifier. Effective thermal management strategies, such as heat sinks and thermal pads, are often incorporated to dissipate heat generated during operation.
RF power amplifiers find applications in various fields, including telecommunications, broadcasting, and industrial heating. In telecommunications, they are vital for driving antennas that transmit signals over long distances, ensuring that the signal maintains its integrity and strength. In microwave heating applications, RF power amplifiers are utilized to generate heat for processes such as cooking or material processing. Additionally, they play a role in exciting resonant cavity structures, which are essential in various scientific and industrial applications.
Overall, the design and application of RF power amplifiers are crucial for enhancing the performance of radio frequency systems, ensuring that signals are transmitted efficiently and effectively across various platforms.An RF power amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier which is utilised to convert a low-power radio-frequency signal into a larger signal of significant power, usually for driving the antenna of a transmitter. It is usually optimized to have high efficiency, high output Power (P1dB) compression, good gain, good return loss on the input and outp
ut, and optimum heat dissipation. The basic applications of the RF power amplifier include driving to another high power source, driving a transmitting antenna, microwave heating, and exciting resonant cavity structures. Among these applications, driving transmitter antennas is most well known. 🔗 External reference