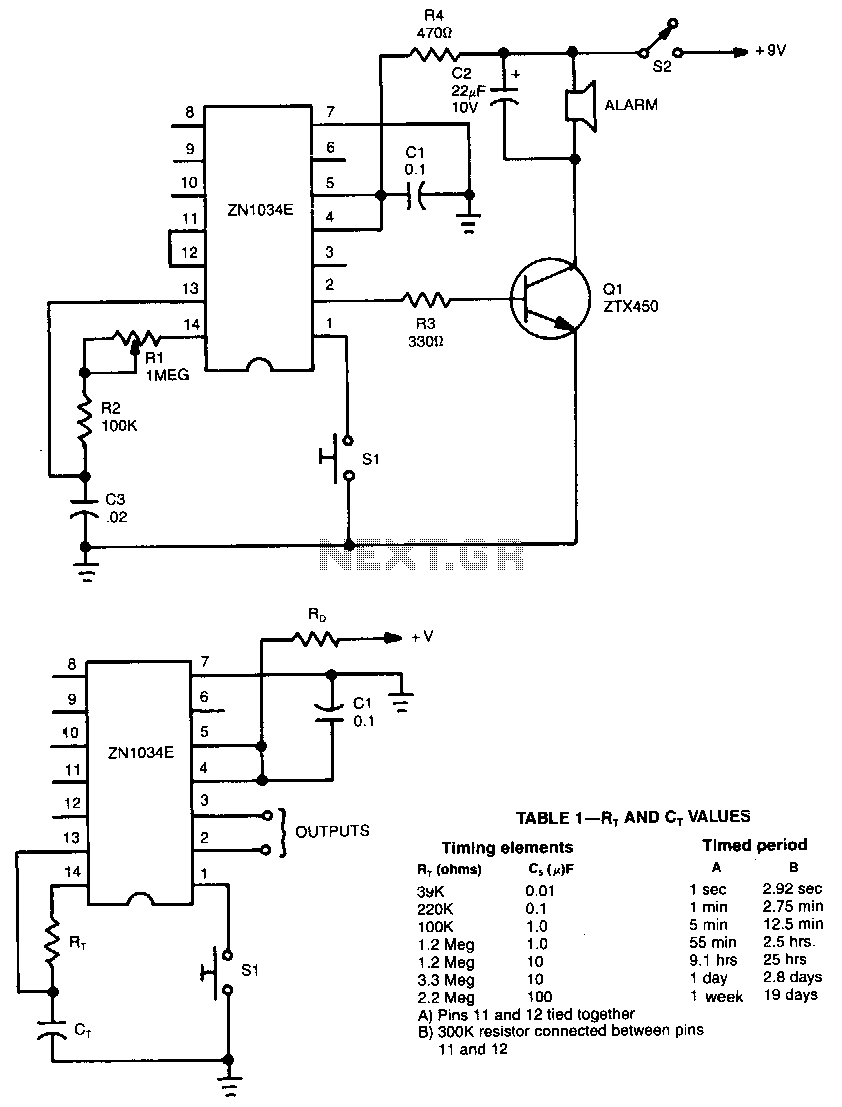
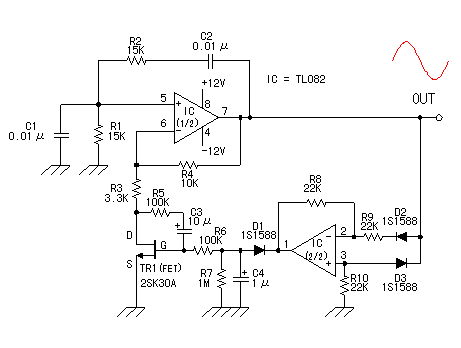
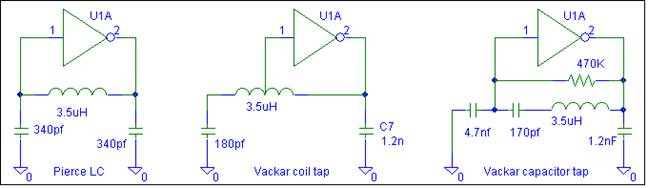
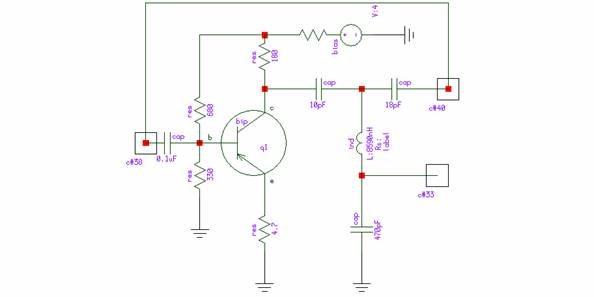
555 Timer Oscillator
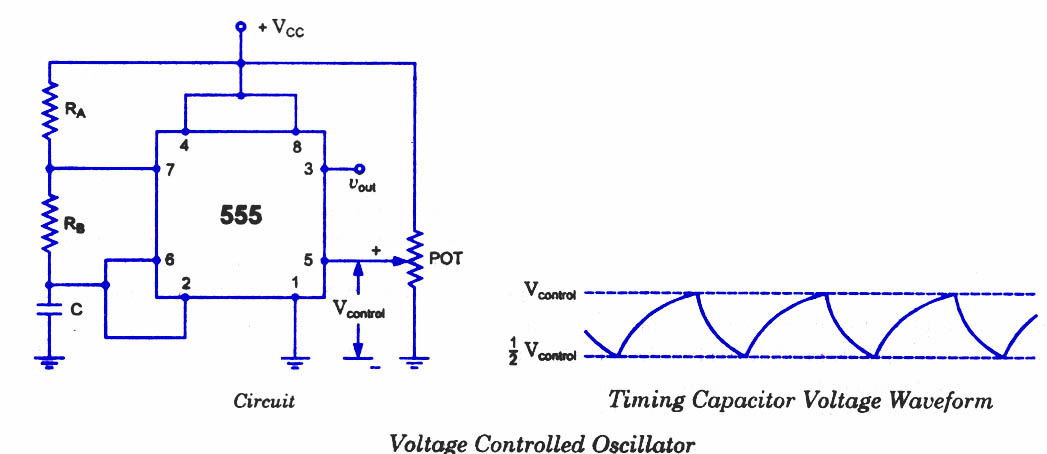
As discussed in previous blog posts, the pin 5 terminal serves as a voltage control terminal, allowing for the adjustment of threshold and trigger levels. Typically, the control voltage is set at +2/3VCC due to the internal voltage divider. However, an external voltage can be applied to this terminal directly or through a potentiometer. By adjusting the potentiometer, the control voltage can be varied. The voltage across the timing capacitor fluctuates between +Vcontrol and ½ Vcontrol. When the control voltage is increased, the capacitor takes longer to charge and discharge, resulting in a decrease in frequency. Therefore, the frequency can be altered by modifying the control voltage. The control voltage may be sourced from a potentiometer or could be the output from a transistor circuit, operational amplifier, or another device.
The circuit involving the pin 5 terminal typically functions within a timing application, such as a 555 timer configured in astable or monostable mode. The voltage control terminal provides an important means of adjusting the timing characteristics of the circuit. The internal voltage divider sets a default control voltage at approximately +2/3VCC, which is crucial for establishing the baseline operation of the timing mechanism.
When an external voltage is applied, either directly or through a potentiometer, the effective control voltage can be modified. This variation influences the behavior of the timing capacitor, which is essential for generating the desired output frequency. The capacitor's charge and discharge times are directly proportional to the control voltage; thus, an increase in control voltage leads to extended charge and discharge cycles, resulting in a lower output frequency.
The schematic representation of this circuit typically includes the timing capacitor connected to the threshold and trigger pins of the 555 timer, with the control voltage input at pin 5. The potentiometer can be depicted in series with the control voltage source, illustrating how the user can adjust the voltage applied to the terminal. Additionally, alternative sources for the control voltage, such as a transistor circuit or an operational amplifier, can be integrated into the schematic to showcase the versatility of this configuration.
Overall, this voltage control mechanism provides a flexible approach to modifying the timing characteristics of the circuit, enabling a wide range of applications in frequency generation and timing control. The capability to adjust the control voltage through various means enhances the functionality and adaptability of the circuit design in practical electronic applications.As discussed in previous blog posts, pin 5 terminal is voltage control terminal and its function is to control the threshold and trigger levels. Normally, the control voltage is +2/3VCC because of the internal voltage divider. However, an external voltage can be applied to thisterminal directly or through a pot, as illustrated in figure, and by a
djusting the pot, control voltage can be varied. Voltage across the timing capacitor is depicted in figure, which varies between +Vcontrol and ½ Vcontrol. If control voltage is increased, the capacitor takes a longer to charge and discharge; the frequency, therefore, decreases.
Thus the fre quency can be changed by changing the control volt age. Incidentally, the control voltage may be made available through a pot, or it may be output of a transistor circuit, op-amp, or some other device. 🔗 External reference
The circuit involving the pin 5 terminal typically functions within a timing application, such as a 555 timer configured in astable or monostable mode. The voltage control terminal provides an important means of adjusting the timing characteristics of the circuit. The internal voltage divider sets a default control voltage at approximately +2/3VCC, which is crucial for establishing the baseline operation of the timing mechanism.
When an external voltage is applied, either directly or through a potentiometer, the effective control voltage can be modified. This variation influences the behavior of the timing capacitor, which is essential for generating the desired output frequency. The capacitor's charge and discharge times are directly proportional to the control voltage; thus, an increase in control voltage leads to extended charge and discharge cycles, resulting in a lower output frequency.
The schematic representation of this circuit typically includes the timing capacitor connected to the threshold and trigger pins of the 555 timer, with the control voltage input at pin 5. The potentiometer can be depicted in series with the control voltage source, illustrating how the user can adjust the voltage applied to the terminal. Additionally, alternative sources for the control voltage, such as a transistor circuit or an operational amplifier, can be integrated into the schematic to showcase the versatility of this configuration.
Overall, this voltage control mechanism provides a flexible approach to modifying the timing characteristics of the circuit, enabling a wide range of applications in frequency generation and timing control. The capability to adjust the control voltage through various means enhances the functionality and adaptability of the circuit design in practical electronic applications.As discussed in previous blog posts, pin 5 terminal is voltage control terminal and its function is to control the threshold and trigger levels. Normally, the control voltage is +2/3VCC because of the internal voltage divider. However, an external voltage can be applied to thisterminal directly or through a pot, as illustrated in figure, and by a
djusting the pot, control voltage can be varied. Voltage across the timing capacitor is depicted in figure, which varies between +Vcontrol and ½ Vcontrol. If control voltage is increased, the capacitor takes a longer to charge and discharge; the frequency, therefore, decreases.
Thus the fre quency can be changed by changing the control volt age. Incidentally, the control voltage may be made available through a pot, or it may be output of a transistor circuit, op-amp, or some other device. 🔗 External reference