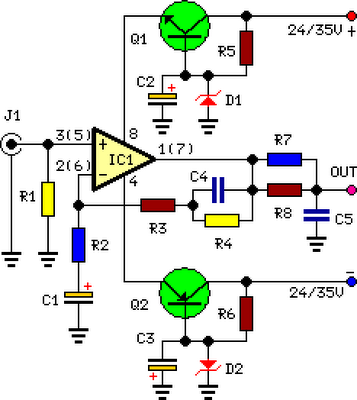
600W rf power amplifier
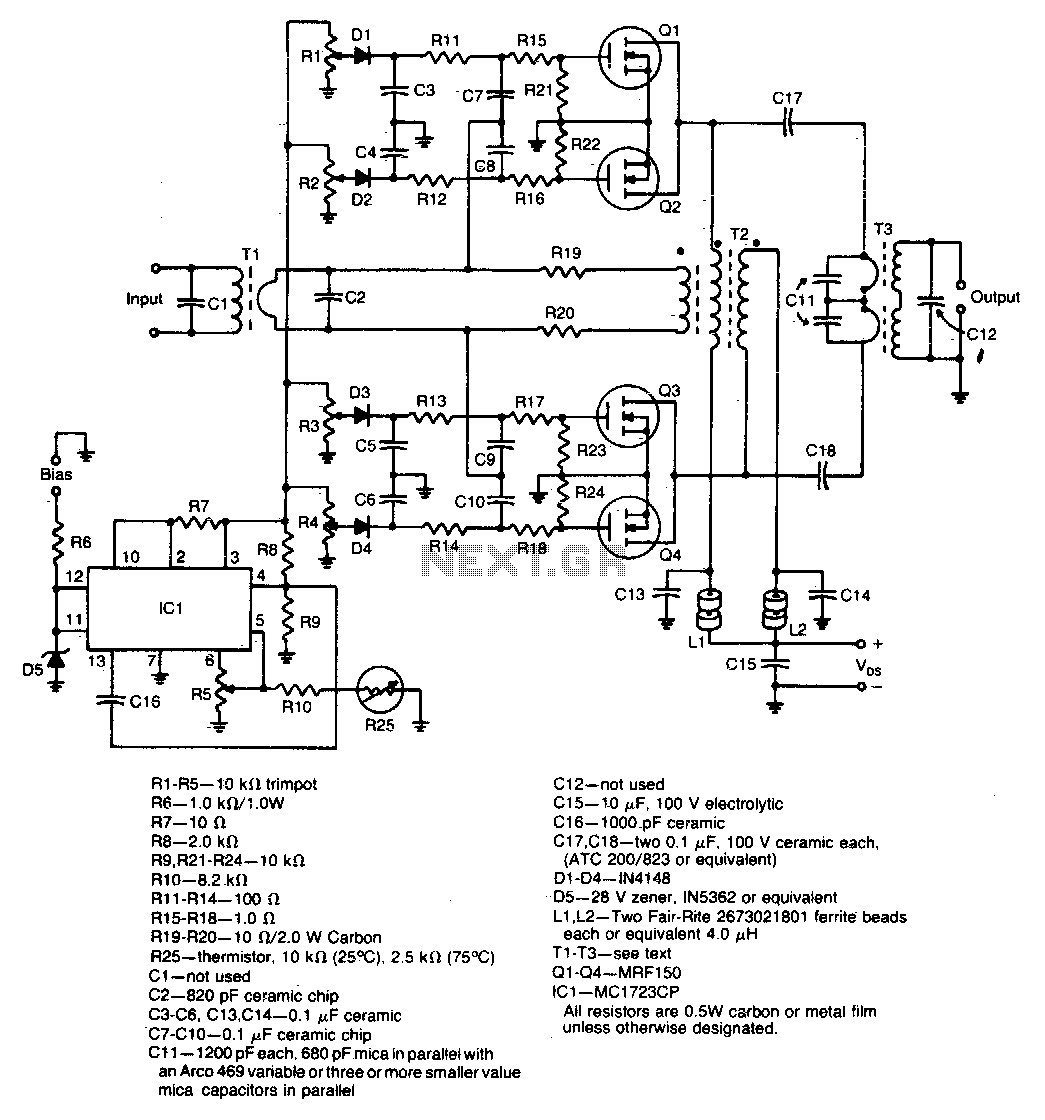
A unique push-pull parallel circuit utilizes four MRF150 RF power FETs connected in parallel at relatively high power levels. Supply voltages ranging from 40 to 50 Vdc can be employed, contingent on the linearity requirements. The bias for each device is independently adjustable, eliminating the need for matching the gate threshold voltages.
The described push-pull parallel circuit configuration is designed to operate with four MRF150 RF power FETs, which are known for their high efficiency and capability to handle substantial power levels. By paralleling these FETs, the circuit can effectively distribute the load, thereby enhancing the overall output power while minimizing the thermal stress on individual devices.
The supply voltage range of 40 to 50 Vdc allows for flexibility in operation, enabling the designer to select an appropriate voltage based on the specific linearity requirements of the application. This voltage range is critical in ensuring that the FETs operate within their optimal performance envelope, thus achieving desired amplification characteristics without distortion.
A notable feature of this circuit design is the independently adjustable bias for each FET. This adjustability allows for fine-tuning of the operating point of each transistor, facilitating optimal performance across various operating conditions. The ability to set the bias independently negates the necessity for matching the gate threshold voltages among the FETs, simplifying the design process. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in applications where variations in device characteristics might otherwise lead to performance inconsistencies.
In summary, this push-pull parallel circuit configuration, leveraging the capabilities of the MRF150 RF power FETs, presents a robust solution for high-power RF applications, with adjustable biasing that enhances performance and simplifies circuit design.A unique push-pull parallel circuit. It uses four MRF150 RF power FETs paralleled at relatively high power levels. Supply voltages of 40 to 50 Vdc can be used, depending on linearity requirements The bias for each device is independently adjustable; therefore, no matching is required for the gate threshold voltages.
The described push-pull parallel circuit configuration is designed to operate with four MRF150 RF power FETs, which are known for their high efficiency and capability to handle substantial power levels. By paralleling these FETs, the circuit can effectively distribute the load, thereby enhancing the overall output power while minimizing the thermal stress on individual devices.
The supply voltage range of 40 to 50 Vdc allows for flexibility in operation, enabling the designer to select an appropriate voltage based on the specific linearity requirements of the application. This voltage range is critical in ensuring that the FETs operate within their optimal performance envelope, thus achieving desired amplification characteristics without distortion.
A notable feature of this circuit design is the independently adjustable bias for each FET. This adjustability allows for fine-tuning of the operating point of each transistor, facilitating optimal performance across various operating conditions. The ability to set the bias independently negates the necessity for matching the gate threshold voltages among the FETs, simplifying the design process. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in applications where variations in device characteristics might otherwise lead to performance inconsistencies.
In summary, this push-pull parallel circuit configuration, leveraging the capabilities of the MRF150 RF power FETs, presents a robust solution for high-power RF applications, with adjustable biasing that enhances performance and simplifies circuit design.A unique push-pull parallel circuit. It uses four MRF150 RF power FETs paralleled at relatively high power levels. Supply voltages of 40 to 50 Vdc can be used, depending on linearity requirements The bias for each device is independently adjustable; therefore, no matching is required for the gate threshold voltages.