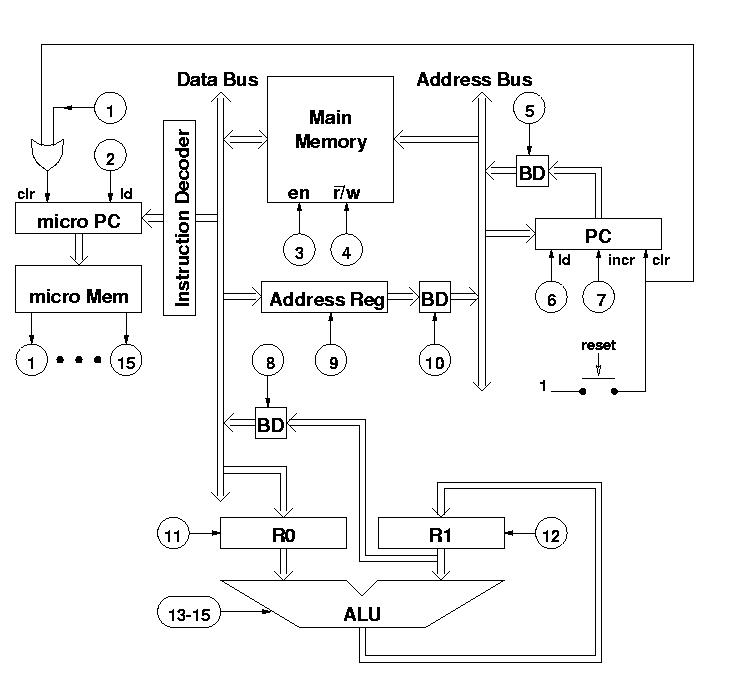
836MHz low-noise amplification circuit diagram RF2347
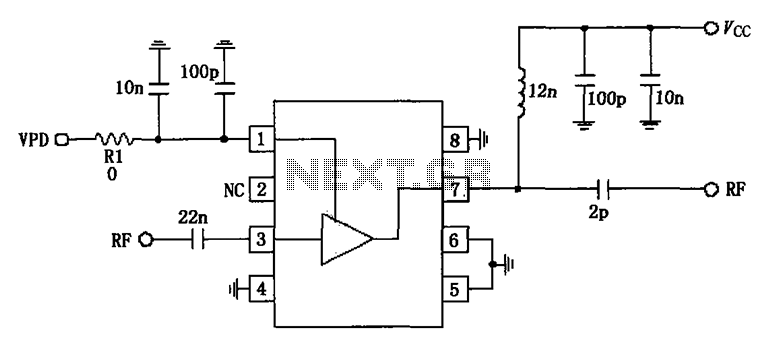
836MHz RF2347 low noise amplifier circuit diagram.
The RF2347 is a low noise amplifier (LNA) designed for operation at a frequency of 836 MHz. It is typically used in RF applications where signal amplification is critical, such as in communication systems, RF front-end modules, and various wireless devices. The circuit diagram for the RF2347 LNA includes several key components that contribute to its performance.
The main component of the circuit is the RF2347 IC, which integrates a low noise amplifier with a high gain and excellent linearity. The input stage of the amplifier is designed to minimize noise figure while maximizing gain, making it suitable for receiving weak signals. The circuit also employs impedance matching networks at both the input and output to ensure optimal power transfer and to reduce reflections that can degrade performance.
Additional passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, are used to set biasing conditions and stabilize the amplifier's operation. These components are crucial for ensuring that the amplifier operates within its specified parameters. Bypass capacitors are often included to filter out power supply noise, enhancing the overall performance of the amplifier in a noisy environment.
The power supply voltage for the RF2347 is typically in the range of 3V to 5V, with careful consideration given to the current consumption to maintain efficiency. The output of the LNA can be connected to subsequent stages in the RF chain, such as mixers or additional amplification stages, ensuring that the signal integrity is preserved throughout the system.
In summary, the RF2347 low noise amplifier circuit diagram represents a well-engineered solution for RF signal amplification at 836 MHz, featuring an integrated approach that combines high performance with ease of integration into various applications.836MHz RF2347 low noise amplifier constituting a circuit diagram:
The RF2347 is a low noise amplifier (LNA) designed for operation at a frequency of 836 MHz. It is typically used in RF applications where signal amplification is critical, such as in communication systems, RF front-end modules, and various wireless devices. The circuit diagram for the RF2347 LNA includes several key components that contribute to its performance.
The main component of the circuit is the RF2347 IC, which integrates a low noise amplifier with a high gain and excellent linearity. The input stage of the amplifier is designed to minimize noise figure while maximizing gain, making it suitable for receiving weak signals. The circuit also employs impedance matching networks at both the input and output to ensure optimal power transfer and to reduce reflections that can degrade performance.
Additional passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, are used to set biasing conditions and stabilize the amplifier's operation. These components are crucial for ensuring that the amplifier operates within its specified parameters. Bypass capacitors are often included to filter out power supply noise, enhancing the overall performance of the amplifier in a noisy environment.
The power supply voltage for the RF2347 is typically in the range of 3V to 5V, with careful consideration given to the current consumption to maintain efficiency. The output of the LNA can be connected to subsequent stages in the RF chain, such as mixers or additional amplification stages, ensuring that the signal integrity is preserved throughout the system.
In summary, the RF2347 low noise amplifier circuit diagram represents a well-engineered solution for RF signal amplification at 836 MHz, featuring an integrated approach that combines high performance with ease of integration into various applications.836MHz RF2347 low noise amplifier constituting a circuit diagram: