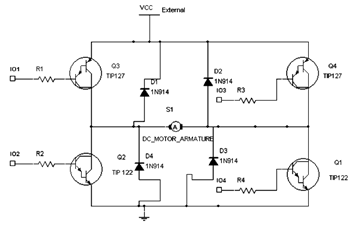
9V to 13.5kV Inverter Circuit Schematic Diagram
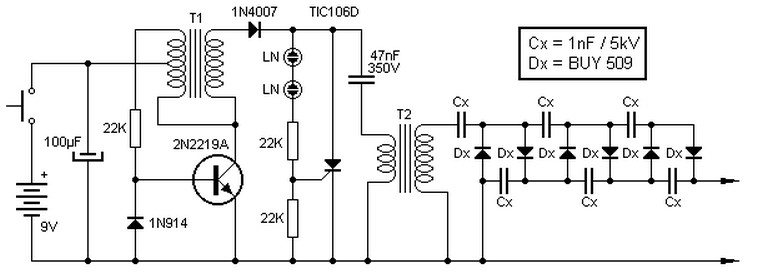
This high voltage source consists of an inverter built around a transistor that generates pulses of 150V. These pulses are supplied to an inverter made of a thyristor and a capacitor, which is connected in series with transformer T2. The output pulse of 4.5kV is then multiplied with the network to achieve a final output voltage of 13.5kV. Neon lamps (designated LN) are used to trigger the thyristor. Transformer T1 has a turns ratio of 3000:500 and is of the type typically used in audio output transistors. Transformer T2 serves as a flash lamp trigger with a secondary voltage of 6kV. This inverter circuit requires a 9V DC power supply with a current rating of 0.01A.
The circuit operates as a high-voltage inverter, utilizing a combination of transistors, thyristors, capacitors, and transformers to step up voltage levels significantly. The initial stage involves the transistor inverter, which generates 150V pulses. These pulses are crucial for driving the thyristor, which, in conjunction with a capacitor, forms a resonant circuit that can deliver high-voltage outputs.
Transformer T1, with its specified turns ratio of 3000:500, is designed to efficiently convert the low voltage pulses into a higher voltage suitable for further amplification. The transformer’s design is akin to those used in audio applications, ensuring that it can handle the necessary frequency response and power requirements.
The thyristor, triggered by the neon lamps, plays a critical role in controlling the timing and delivery of the high-voltage pulses. The use of neon lamps allows for reliable triggering of the thyristor, ensuring that the circuit operates at the desired frequency and voltage levels.
Following the thyristor stage, transformer T2 is employed to achieve a secondary voltage output of 6kV, which is then combined with the initial 4.5kV pulse output. This configuration effectively multiplies the voltage, resulting in a final output of 13.5kV. Such high-voltage outputs are essential for applications requiring significant electrical energy, such as in certain types of discharge lamps or other high-voltage devices.
The entire inverter circuit is powered by a 9V DC supply, which is relatively low, making the circuit efficient and manageable. The current requirement of 0.01A indicates that the circuit is designed to operate with minimal power consumption while still achieving high output voltages. This combination of components and design considerations ensures the circuit's effectiveness in generating the desired high-voltage outputs.This high voltage source is formed by an inverter, around the transistor, which provides pulses of 150V to the inverter formed by the thyristor and capacitor in series with the transformer 2. This pulse output of 4. 5kV to be multiplied with the network so as to achieve the output voltage of 13. 5kV. Neon lamps (marked LN) form the thyristor trigger ing pulses. The transformer T1 has a ratio 3000:500 © of the type used in audio output transistor. T2 is a transformer flash lamp trigger a secondary 6kV. This inverter circuit requires a 9VDC power supply with current 0. 01A You are reading the Circuits of 9V to 13. 5kV Inverter Circuit And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates as a high-voltage inverter, utilizing a combination of transistors, thyristors, capacitors, and transformers to step up voltage levels significantly. The initial stage involves the transistor inverter, which generates 150V pulses. These pulses are crucial for driving the thyristor, which, in conjunction with a capacitor, forms a resonant circuit that can deliver high-voltage outputs.
Transformer T1, with its specified turns ratio of 3000:500, is designed to efficiently convert the low voltage pulses into a higher voltage suitable for further amplification. The transformer’s design is akin to those used in audio applications, ensuring that it can handle the necessary frequency response and power requirements.
The thyristor, triggered by the neon lamps, plays a critical role in controlling the timing and delivery of the high-voltage pulses. The use of neon lamps allows for reliable triggering of the thyristor, ensuring that the circuit operates at the desired frequency and voltage levels.
Following the thyristor stage, transformer T2 is employed to achieve a secondary voltage output of 6kV, which is then combined with the initial 4.5kV pulse output. This configuration effectively multiplies the voltage, resulting in a final output of 13.5kV. Such high-voltage outputs are essential for applications requiring significant electrical energy, such as in certain types of discharge lamps or other high-voltage devices.
The entire inverter circuit is powered by a 9V DC supply, which is relatively low, making the circuit efficient and manageable. The current requirement of 0.01A indicates that the circuit is designed to operate with minimal power consumption while still achieving high output voltages. This combination of components and design considerations ensures the circuit's effectiveness in generating the desired high-voltage outputs.This high voltage source is formed by an inverter, around the transistor, which provides pulses of 150V to the inverter formed by the thyristor and capacitor in series with the transformer 2. This pulse output of 4. 5kV to be multiplied with the network so as to achieve the output voltage of 13. 5kV. Neon lamps (marked LN) form the thyristor trigger ing pulses. The transformer T1 has a ratio 3000:500 © of the type used in audio output transistor. T2 is a transformer flash lamp trigger a secondary 6kV. This inverter circuit requires a 9VDC power supply with current 0. 01A You are reading the Circuits of 9V to 13. 5kV Inverter Circuit And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference