A common car inverter circuit and principle
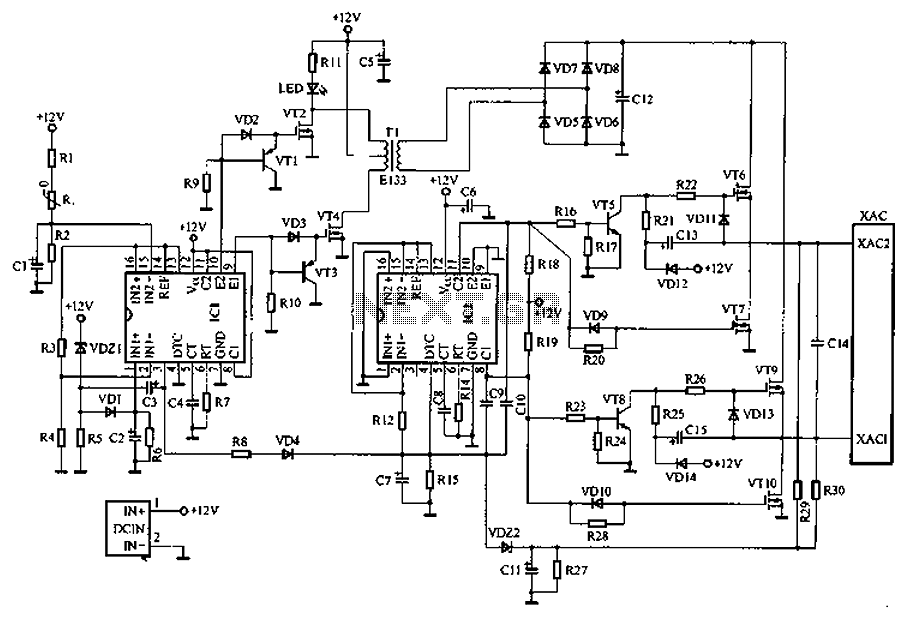
Car inverter specifications include an input voltage range of DC 10V to 14.5V, output voltage of AC 200V to 220V with a tolerance of 10%, output frequency of 50Hz with a tolerance of 5%, and an output power range of 70W to 150W. The conversion efficiency exceeds 85%, and the operating frequency of the inverter is between 30kHz and 50kHz. The most commonly sold car inverters in the market have output powers ranging from 70W to 150W. The inverter circuit typically utilizes TL494 or KA7500 chips in a pulse width modulation configuration. A schematic of a common car inverter circuit is illustrated in Figure 1.
The car inverter operates by converting direct current (DC) from the vehicle's electrical system into alternating current (AC) suitable for powering household appliances. The input voltage range of DC 10V to 14.5V corresponds to the typical voltage levels found in automotive batteries. An essential function of the inverter is to maintain a regulated output voltage of AC 200V to 220V, which is critical for the safe operation of devices designed for standard AC power.
The output frequency of 50Hz is standard for many regions, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of electrical devices. The inverter's output power, which can range from 70W to 150W, indicates its capacity to drive various loads, making it versatile for different applications. The conversion efficiency of over 85% signifies that the inverter effectively utilizes the input power, minimizing losses during the conversion process.
The operational frequency of the inverter, specified as 30kHz to 50kHz, is significant as it influences the size of the transformer and the overall efficiency of the inverter. Higher frequencies allow for smaller transformer designs, which can contribute to a more compact inverter design.
The use of TL494 or KA7500 integrated circuits is prevalent in these inverters as they provide robust pulse width modulation (PWM) control. PWM is a technique used to regulate the output voltage and frequency by varying the duty cycle of the output waveform. This method is efficient and allows for precise control over the inverter's performance.
The common car inverter circuit schematic serves as a guide for engineers and hobbyists looking to design or troubleshoot similar inverter systems. It typically includes components such as the input capacitor, transformer, output filter, and feedback mechanisms to ensure stable operation under varying load conditions. Car Inverter indicators: Input voltage: DC 10V ~ 14.5V; Output Voltage: AC 200V ~ 220V 10%; Output frequency: 50Hz 5%; Output power: 70W ~ 150W; conversion efficiency: more tha n 85%; the inverter operating frequency: 30kHz ~ 50kHz. Currently on the market sales of the largest, the most common car inverter output power of 70W-150W, the inverter circuit mainly uses TL494 or KA7500 chip-based pulse width modulation circuit. One of the most common car inverter circuit schematic shown in Figure 1.
The car inverter operates by converting direct current (DC) from the vehicle's electrical system into alternating current (AC) suitable for powering household appliances. The input voltage range of DC 10V to 14.5V corresponds to the typical voltage levels found in automotive batteries. An essential function of the inverter is to maintain a regulated output voltage of AC 200V to 220V, which is critical for the safe operation of devices designed for standard AC power.
The output frequency of 50Hz is standard for many regions, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of electrical devices. The inverter's output power, which can range from 70W to 150W, indicates its capacity to drive various loads, making it versatile for different applications. The conversion efficiency of over 85% signifies that the inverter effectively utilizes the input power, minimizing losses during the conversion process.
The operational frequency of the inverter, specified as 30kHz to 50kHz, is significant as it influences the size of the transformer and the overall efficiency of the inverter. Higher frequencies allow for smaller transformer designs, which can contribute to a more compact inverter design.
The use of TL494 or KA7500 integrated circuits is prevalent in these inverters as they provide robust pulse width modulation (PWM) control. PWM is a technique used to regulate the output voltage and frequency by varying the duty cycle of the output waveform. This method is efficient and allows for precise control over the inverter's performance.
The common car inverter circuit schematic serves as a guide for engineers and hobbyists looking to design or troubleshoot similar inverter systems. It typically includes components such as the input capacitor, transformer, output filter, and feedback mechanisms to ensure stable operation under varying load conditions. Car Inverter indicators: Input voltage: DC 10V ~ 14.5V; Output Voltage: AC 200V ~ 220V 10%; Output frequency: 50Hz 5%; Output power: 70W ~ 150W; conversion efficiency: more tha n 85%; the inverter operating frequency: 30kHz ~ 50kHz. Currently on the market sales of the largest, the most common car inverter output power of 70W-150W, the inverter circuit mainly uses TL494 or KA7500 chip-based pulse width modulation circuit. One of the most common car inverter circuit schematic shown in Figure 1.