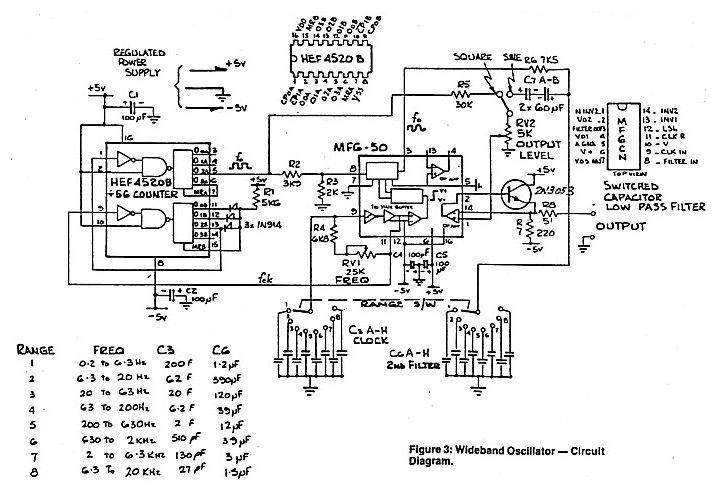
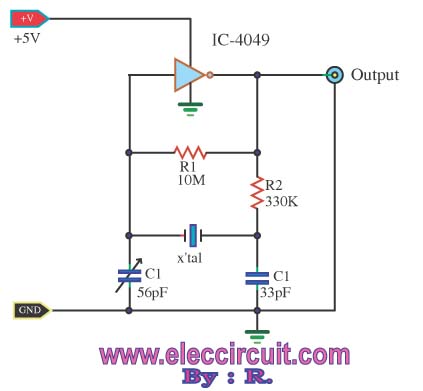
A crystal-controlled oscillator
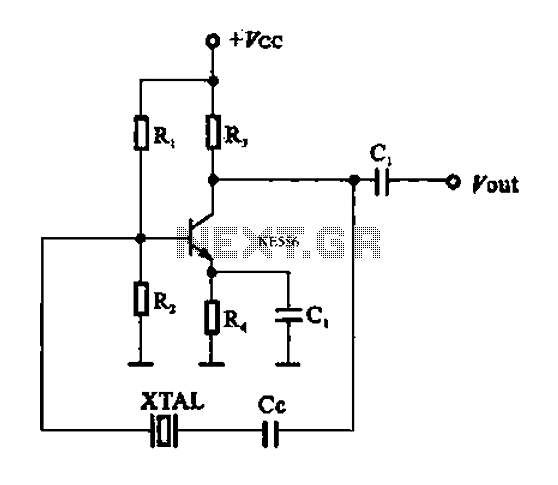
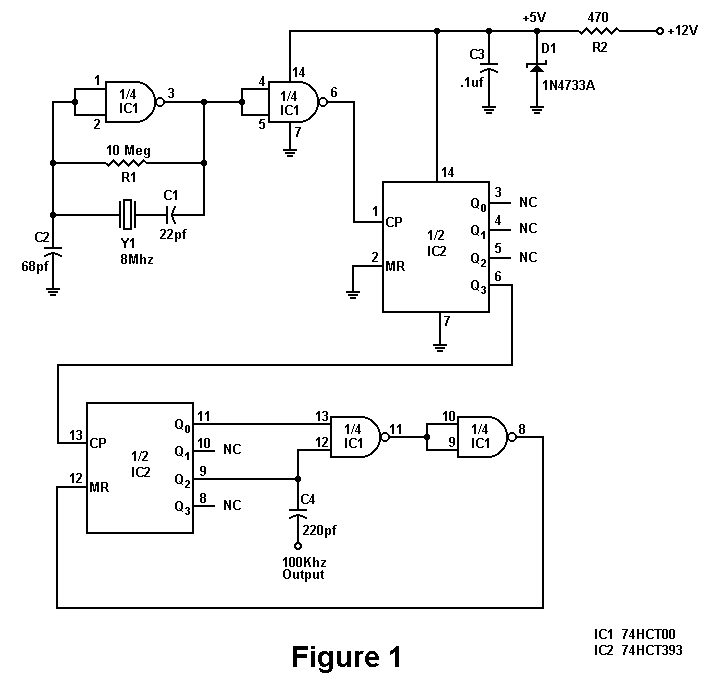
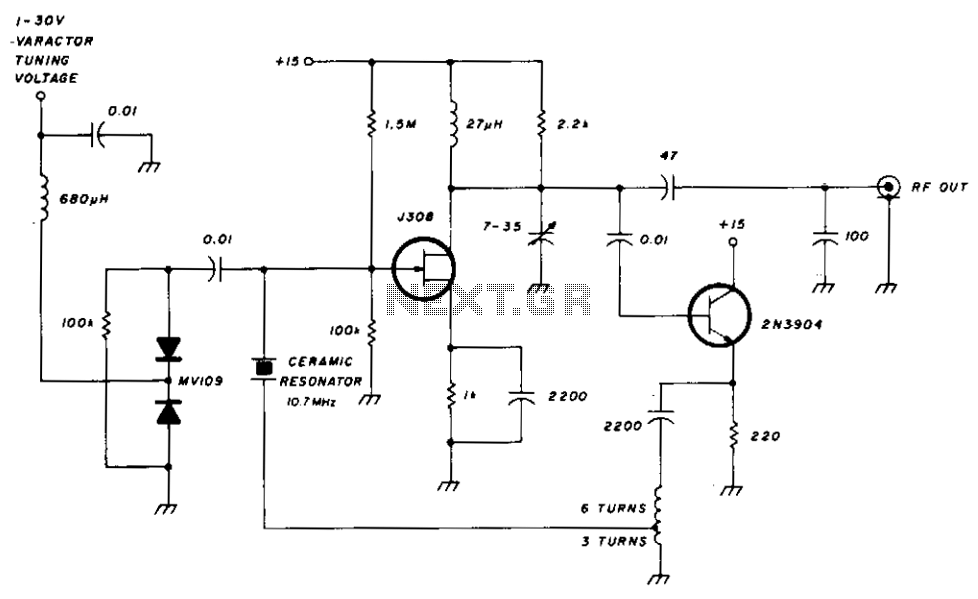
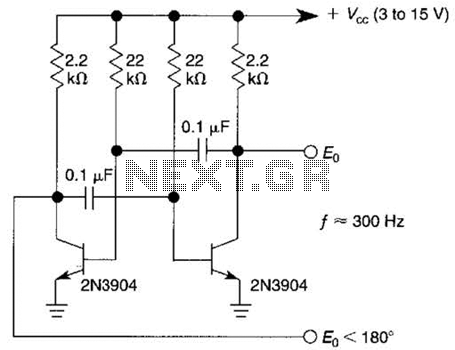
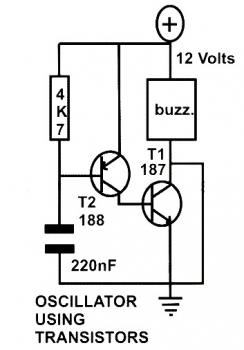
A series resonant circuit utilizing a crystal oscillator is illustrated. The crystal impedance reaches a minimum value at the series resonance frequency, resulting in a significant feedback amount. The crystal tuning capacitor (Cc) can slightly adjust the resonance frequency of the crystal, enabling fine-tuning of the oscillation frequency.
The series resonant circuit with a crystal oscillator is a fundamental electronic configuration used in various applications, including frequency stabilization and signal generation. In this setup, the crystal oscillator serves as a frequency-selective element, exhibiting a sharp resonance peak at its fundamental frequency. At this resonance frequency, the impedance of the crystal drops to a minimum, allowing maximum current flow and enhancing feedback within the circuit.
The circuit typically includes a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and the crystal itself, connected in series. The inductor and the crystal together form a resonant circuit, where the inductive reactance and the capacitive reactance of the crystal cancel each other out at the resonance frequency. This results in a high quality factor (Q), which is indicative of the circuit's ability to maintain oscillations with minimal energy loss.
The crystal tuning capacitor (Cc) is an essential component that allows for slight adjustments to the resonant frequency of the crystal. By changing the capacitance value of Cc, the resonant frequency can be fine-tuned either upwards or downwards, enabling the circuit to achieve precise frequency control. This micro-tuning capability is crucial in applications such as radio transmitters and receivers, where exact frequency alignment is necessary for optimal performance.
Overall, the series resonant circuit with a crystal oscillator and a tuning capacitor is a highly effective method for generating stable oscillations at a desired frequency, making it an integral part of many electronic devices. As shown in the series resonant circuit using a crystal oscillator. Crystal impedance has a minimum value in the series resonance frequency, thus providing a large feedback amo unt Sheng. Crystal tuning capacitor Cc may be the resonance frequency of the crystal slightly pull on or pull down to micro- tune the oscillation frequency.
The series resonant circuit with a crystal oscillator is a fundamental electronic configuration used in various applications, including frequency stabilization and signal generation. In this setup, the crystal oscillator serves as a frequency-selective element, exhibiting a sharp resonance peak at its fundamental frequency. At this resonance frequency, the impedance of the crystal drops to a minimum, allowing maximum current flow and enhancing feedback within the circuit.
The circuit typically includes a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and the crystal itself, connected in series. The inductor and the crystal together form a resonant circuit, where the inductive reactance and the capacitive reactance of the crystal cancel each other out at the resonance frequency. This results in a high quality factor (Q), which is indicative of the circuit's ability to maintain oscillations with minimal energy loss.
The crystal tuning capacitor (Cc) is an essential component that allows for slight adjustments to the resonant frequency of the crystal. By changing the capacitance value of Cc, the resonant frequency can be fine-tuned either upwards or downwards, enabling the circuit to achieve precise frequency control. This micro-tuning capability is crucial in applications such as radio transmitters and receivers, where exact frequency alignment is necessary for optimal performance.
Overall, the series resonant circuit with a crystal oscillator and a tuning capacitor is a highly effective method for generating stable oscillations at a desired frequency, making it an integral part of many electronic devices. As shown in the series resonant circuit using a crystal oscillator. Crystal impedance has a minimum value in the series resonance frequency, thus providing a large feedback amo unt Sheng. Crystal tuning capacitor Cc may be the resonance frequency of the crystal slightly pull on or pull down to micro- tune the oscillation frequency.