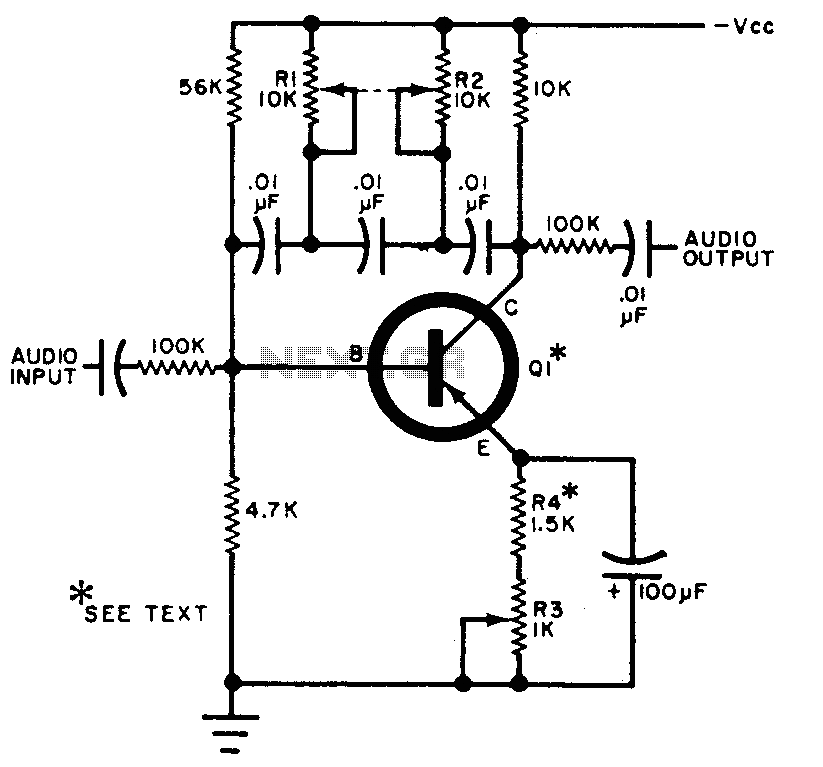
A Simple Audio Oscillator
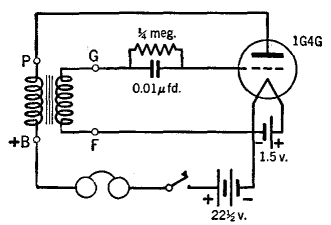
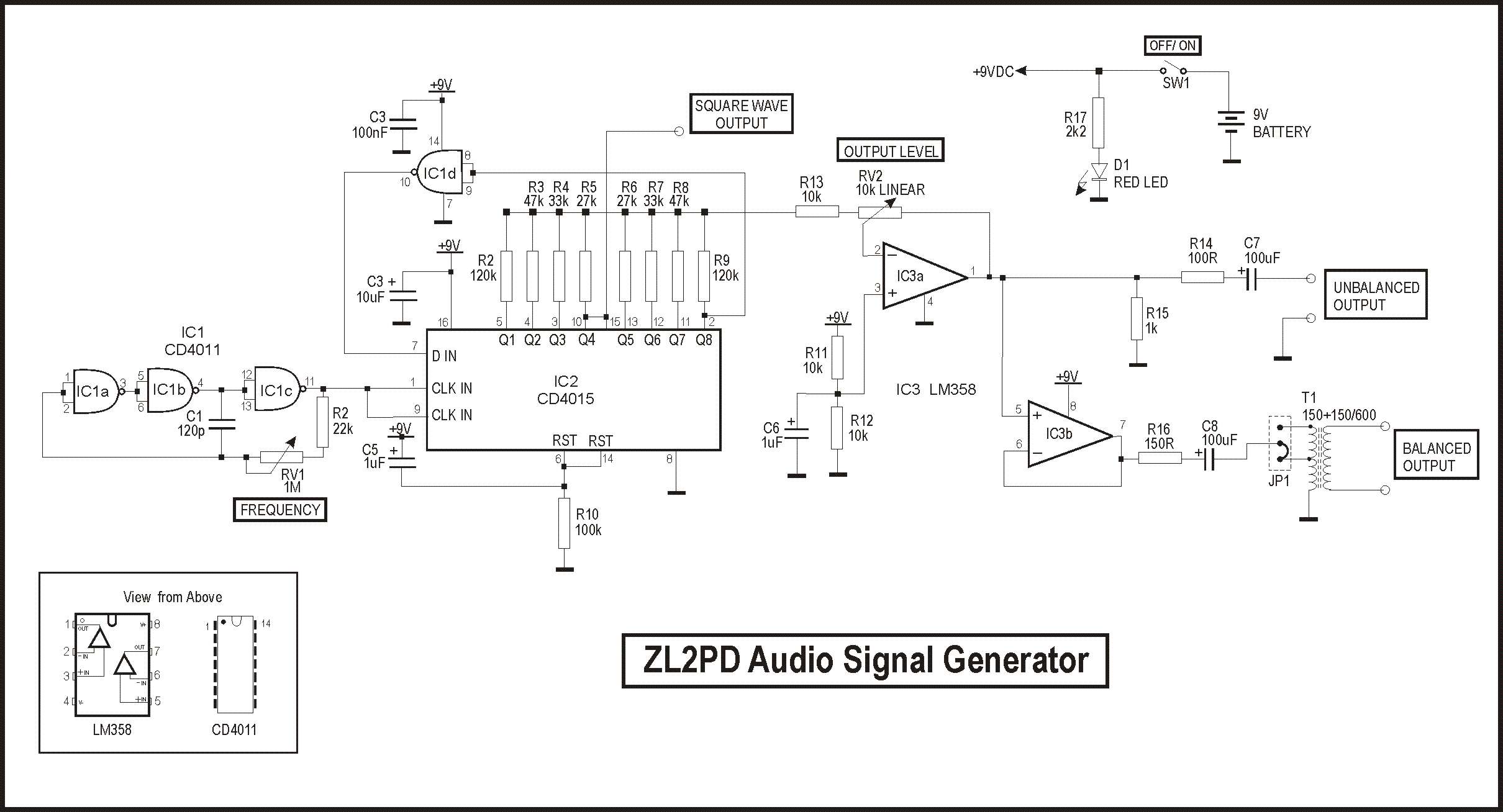
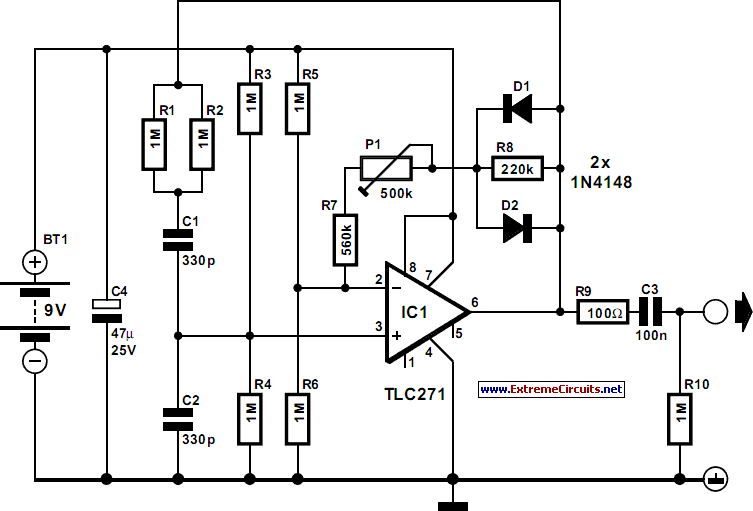
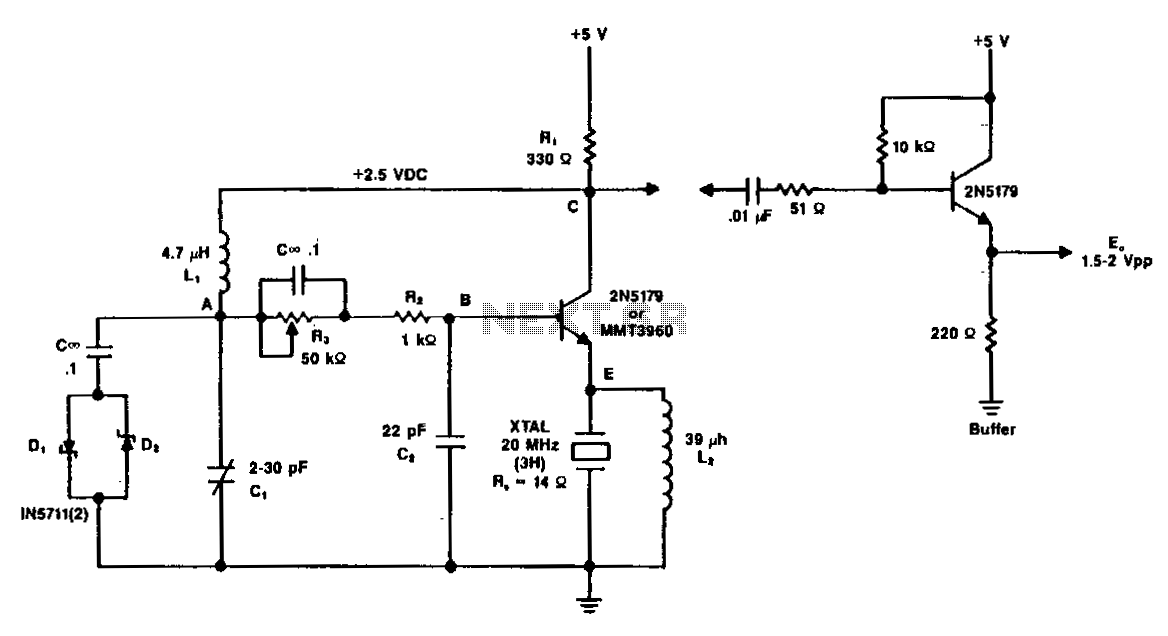
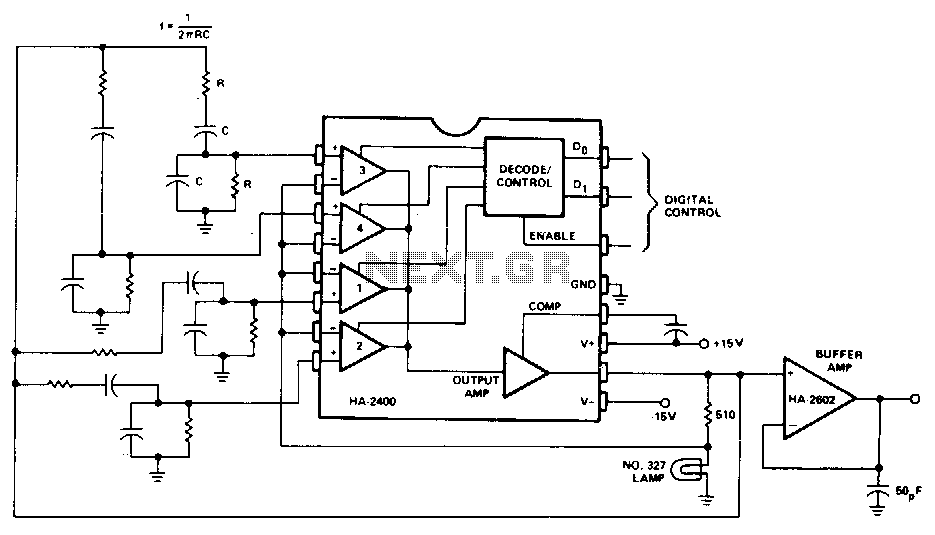
A simple oscillator that can be utilized for code practice. To achieve adequate inductance for generating an audio frequency, an iron core transformer, similar to those employed in audio transformer-coupled amplifiers, is connected as illustrated.
The circuit comprises a basic oscillator configuration designed to generate audio frequency signals suitable for code practice, particularly in Morse code training. The core component of this oscillator is an iron core transformer, which is critical for achieving the necessary inductance. The transformer enhances the circuit's ability to produce lower frequency oscillations, which are essential for generating clear and audible tones.
The oscillator circuit typically includes a feedback mechanism that allows the output signal to be fed back into the input, sustaining oscillations. Commonly, this is achieved using a transistor or a similar active component that can amplify the signal. The transformer is connected in such a way that it not only serves as an inductive element but also provides the necessary coupling between the different parts of the oscillator.
To ensure stable operation, passive components such as resistors and capacitors are incorporated into the circuit. These components help to set the frequency of oscillation and stabilize the output waveform. The selection of these components is crucial, as they determine the oscillation frequency and the quality of the audio output.
In practical applications, this oscillator can be used in conjunction with a speaker or headphones to provide an audible signal. The sound generated can be adjusted by modifying the values of the resistors and capacitors, allowing for a range of frequencies to be produced, which is particularly useful in code practice scenarios. Overall, this simple oscillator circuit serves as an effective tool for training and practice in various audio frequency applications.A simple oscillator which may be used for code practice. In order to have sufficient inductance to produce an audio frequency, an iron core transformer such as used in audio transformer-coupled amplifiers is hooked up as shown. 🔗 External reference
The circuit comprises a basic oscillator configuration designed to generate audio frequency signals suitable for code practice, particularly in Morse code training. The core component of this oscillator is an iron core transformer, which is critical for achieving the necessary inductance. The transformer enhances the circuit's ability to produce lower frequency oscillations, which are essential for generating clear and audible tones.
The oscillator circuit typically includes a feedback mechanism that allows the output signal to be fed back into the input, sustaining oscillations. Commonly, this is achieved using a transistor or a similar active component that can amplify the signal. The transformer is connected in such a way that it not only serves as an inductive element but also provides the necessary coupling between the different parts of the oscillator.
To ensure stable operation, passive components such as resistors and capacitors are incorporated into the circuit. These components help to set the frequency of oscillation and stabilize the output waveform. The selection of these components is crucial, as they determine the oscillation frequency and the quality of the audio output.
In practical applications, this oscillator can be used in conjunction with a speaker or headphones to provide an audible signal. The sound generated can be adjusted by modifying the values of the resistors and capacitors, allowing for a range of frequencies to be produced, which is particularly useful in code practice scenarios. Overall, this simple oscillator circuit serves as an effective tool for training and practice in various audio frequency applications.A simple oscillator which may be used for code practice. In order to have sufficient inductance to produce an audio frequency, an iron core transformer such as used in audio transformer-coupled amplifiers is hooked up as shown. 🔗 External reference