A voice-activated lights control circuit
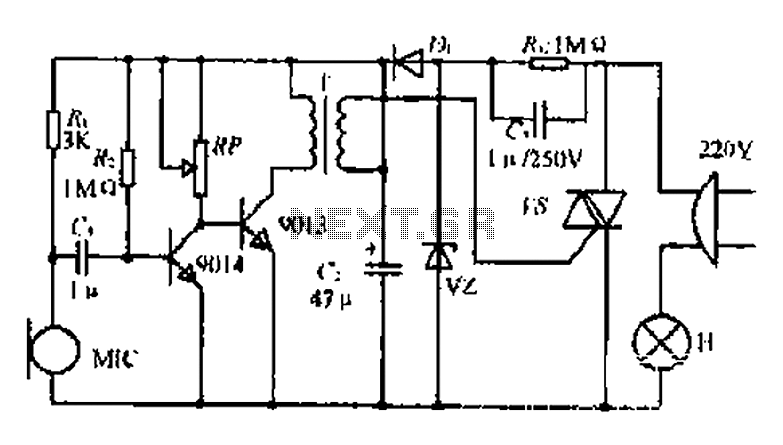
22W by Ct and R, RC Buck, rectified by n. c, filtering. vz 3V DC regulated output power, before U, V2 and MIC power supply. When the audio signal reaches the beam, the microphone MI converts acoustic energy into electrical energy. This is then processed through a general discharge tube T and after coupling, can be entrusted to a two-way silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) to dispatch a trigger voltage control. This setup uses audio signals to control thyristor conduction, resulting in the generation of light effects.
The circuit operates as a 22W power supply utilizing an RC buck converter topology, which efficiently steps down voltage while maintaining a regulated output. The rectification process is achieved through a normally closed (n.c.) configuration, followed by filtering to smooth out the rectified output, ensuring a stable 3V DC supply. This regulated output is essential for powering components labeled as U, V2, and the microphone (MIC).
The microphone (MI) plays a crucial role in the system by converting incoming acoustic signals into corresponding electrical signals. When an audio signal is detected, it triggers the discharge tube (T), which acts as a switch to control the flow of current. The output from the discharge tube is then coupled to a two-way silicon controlled rectifier (SCR), which is responsible for controlling the timing of the electrical pulses sent to the load.
The SCR is triggered by the audio signal, allowing it to conduct and control the discharge of energy to the connected load. This results in a visually appealing light effect, where the intensity and frequency of the light can vary based on the characteristics of the incoming audio signal. The entire system is designed to respond dynamically to sound, creating an interactive experience that links audio input with visual output.22W by Ct and R, RC Buck, rectified by n. c, filtering. vz 3V DC regulated output power, before U, V2 and MIC power supply. When the audio signal to the beam, the microphone MI C acoustic energy into electrical energy, and then the general discharge tube T and after coupling, can be entrusted to two-way silicon v dispatch a trigger voltage control, use audio to control thyristor conduction and cut u :, D generated so lights sparkle.
The circuit operates as a 22W power supply utilizing an RC buck converter topology, which efficiently steps down voltage while maintaining a regulated output. The rectification process is achieved through a normally closed (n.c.) configuration, followed by filtering to smooth out the rectified output, ensuring a stable 3V DC supply. This regulated output is essential for powering components labeled as U, V2, and the microphone (MIC).
The microphone (MI) plays a crucial role in the system by converting incoming acoustic signals into corresponding electrical signals. When an audio signal is detected, it triggers the discharge tube (T), which acts as a switch to control the flow of current. The output from the discharge tube is then coupled to a two-way silicon controlled rectifier (SCR), which is responsible for controlling the timing of the electrical pulses sent to the load.
The SCR is triggered by the audio signal, allowing it to conduct and control the discharge of energy to the connected load. This results in a visually appealing light effect, where the intensity and frequency of the light can vary based on the characteristics of the incoming audio signal. The entire system is designed to respond dynamically to sound, creating an interactive experience that links audio input with visual output.22W by Ct and R, RC Buck, rectified by n. c, filtering. vz 3V DC regulated output power, before U, V2 and MIC power supply. When the audio signal to the beam, the microphone MI C acoustic energy into electrical energy, and then the general discharge tube T and after coupling, can be entrusted to two-way silicon v dispatch a trigger voltage control, use audio to control thyristor conduction and cut u :, D generated so lights sparkle.