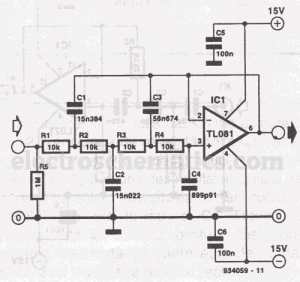
Active bandpass filter
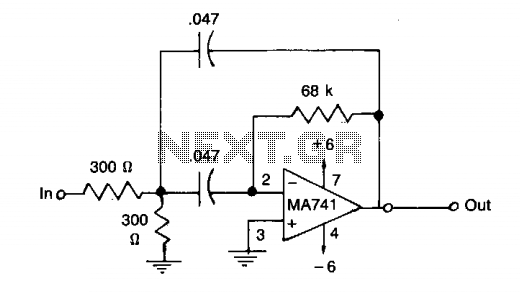
This filter features a bandpass characteristic centered around 1 kHz, suitable for applications such as bridge amplifiers and null detectors. The circuit employs a µ741 integrated circuit (IC) along with standard components that have a tolerance of 5%.
The described bandpass filter circuit is designed to allow frequencies around 1 kHz to pass while attenuating frequencies outside this range. This characteristic makes it particularly useful in signal processing applications where specific frequency selection is critical.
The µ741 operational amplifier serves as the core component of this filter design. It is a general-purpose op-amp that provides good performance for low-frequency applications, making it suitable for the 1 kHz center frequency. The filter can be configured using a combination of resistors and capacitors to establish the desired bandwidth and gain characteristics.
In a typical implementation, the circuit may consist of a combination of both passive and active components. The passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, are chosen based on their values to set the cutoff frequencies of the bandpass filter. The gain of the filter can be adjusted by varying the feedback resistor in the op-amp configuration.
The choice of standard 5% tolerance components ensures that the circuit is cost-effective while still providing reasonable accuracy for many practical applications. However, for applications requiring higher precision, components with tighter tolerances may be considered.
Overall, this bandpass filter design is a reliable solution for applications that require the isolation of a specific frequency range, such as in bridge amplifiers and null detectors, where accurate signal processing is essential.This filter has a bandpass centered around 1kHz, for applications such as bridge amplifiers, null detectors, etc. The circuit uses a µ741 IC and standard 5% tolerance components.
The described bandpass filter circuit is designed to allow frequencies around 1 kHz to pass while attenuating frequencies outside this range. This characteristic makes it particularly useful in signal processing applications where specific frequency selection is critical.
The µ741 operational amplifier serves as the core component of this filter design. It is a general-purpose op-amp that provides good performance for low-frequency applications, making it suitable for the 1 kHz center frequency. The filter can be configured using a combination of resistors and capacitors to establish the desired bandwidth and gain characteristics.
In a typical implementation, the circuit may consist of a combination of both passive and active components. The passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, are chosen based on their values to set the cutoff frequencies of the bandpass filter. The gain of the filter can be adjusted by varying the feedback resistor in the op-amp configuration.
The choice of standard 5% tolerance components ensures that the circuit is cost-effective while still providing reasonable accuracy for many practical applications. However, for applications requiring higher precision, components with tighter tolerances may be considered.
Overall, this bandpass filter design is a reliable solution for applications that require the isolation of a specific frequency range, such as in bridge amplifiers and null detectors, where accurate signal processing is essential.This filter has a bandpass centered around 1kHz, for applications such as bridge amplifiers, null detectors, etc. The circuit uses a µ741 IC and standard 5% tolerance components.