airbag diagnostic code 51 ford f150
A flashing airbag diagnostic code of 51 appears on a 1994 Ford F150, indicating a potential issue that began approximately one month ago. The problem may be related to a leaky windshield, which raises questions about its effect on the airbag module. The code indicates that the internal fuse within the airbag control module has blown, a precautionary measure activated when a short to ground occurs in one of the airbag circuits. This safety feature is designed to prevent injuries from accidental airbag deployment due to electrical faults; thus, the module intentionally blows the fuse to disable the system. The fuse is not serviceable, and a new airbag module must be installed after the short to ground has been identified and repaired. The airbag diagnostic monitor contains an internal thermal fuse that is also not serviceable. This thermal fuse is controlled by a computer within the airbag diagnostic monitor, which will blow the fuse whenever a short on the deployment circuits occurs. It is important to note that the thermal fuse does not blow due to excessive current. Jumpering the thermal fuse with a circuit breaker or any other type of fuse is inadvisable. A new airbag diagnostic monitor should not be installed until the short has been located and corrected. If the short to ground has not been addressed, it may be intermittent and not present at the time. Installing a new airbag diagnostic monitor with an intermittent short can lead to further damage and repeated repairs. The airbag diagnostic monitor measures voltages at the diagnostic monitor connector pins. When certain airbag deployment wires are shorted to ground, the system may risk unwanted airbag deployment. The airbag diagnostic monitor detects a short to ground on these circuits and prevents unwanted deployment by blowing the thermal fuse, which removes all power from the airbag deployment circuits. While the short to ground exists, the monitor will flash code 13. If the short is intermittent, the monitor will flash code 51. A flashing code 51 indicates that an intermittent short to ground exists in the supplemental airbag restraint system, and the monitor should only be replaced after repairs to the short have been completed. To locate an intermittent short, inspect wiring and harnesses in areas where they pass through or are near metal components. Additionally, after an airbag deploys, internal wiring of the driver-side airbag module may short to the module's metal housing. This internal short is detected as a short to ground in the deployment wiring, leading to a code 13 and blowing the internal thermal fuse. As the airbag cools, the internal short may resolve, causing the monitor to flash code 51. If a vehicle with a deployed airbag shows code 51, inspect and replace any damaged wiring or sensors. If no damage is found, it may be assumed that the deployed airbag caused the intermittent short, and the airbag diagnostic monitor should be replaced.
The airbag diagnostic system in the 1994 Ford F150 employs a sophisticated mechanism to ensure safety through intelligent fault detection. The airbag control module's internal thermal fuse serves as a critical component in this system, designed to protect against inadvertent airbag deployment due to electrical faults. When a short circuit occurs in the airbag deployment wiring, the diagnostic monitor's computer detects this anomaly and activates the thermal fuse, thereby interrupting power to the airbag circuits. This design prevents potential injuries that could arise from accidental deployments during fault conditions.
The flashing diagnostic codes serve as a communication tool to indicate specific issues within the system. Code 13 signifies an active short to ground, while code 51 indicates that an intermittent short has been detected. This distinction is crucial for technicians in diagnosing and repairing airbag system faults effectively. The identification of intermittent shorts requires careful inspection of wiring, especially in areas prone to wear or damage, such as those adjacent to metal components or subject to mechanical stress.
In practice, the troubleshooting process involves a systematic approach to locating the source of the short. Technicians should begin by examining the integrity of wiring harnesses and connections, particularly in high-stress areas, and testing for continuity and insulation resistance. Any signs of abrasion, corrosion, or physical damage should be addressed promptly to restore the system's reliability.
After resolving any identified shorts, the airbag diagnostic monitor can be replaced, ensuring that the system is fully operational and compliant with safety standards. It is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines during repairs to maintain the integrity of the airbag system and prevent future faults. In summary, understanding the diagnostic codes and the underlying mechanisms of the airbag system is vital for effective troubleshooting and ensuring the safety of vehicle occupants.An flashing airbag diagnostic code of 51 flashing on a 1994 Ford F150, and I need to understand what this could mean. The probem started about one month ago. I also had a leaky windsheild, so I am also wonder if that could affect the airbag module as well. The code you have indicates that the internal fuse in the airbag control module has been blown; this happens automatically when a short to ground
occurs in one of the airbag circuits in the vehicle. This is a safety feature designed to rprevent injuries due to accidental deployment of the airbag due to an electrical fault; the module blows the fuse intentionally to disable the system. the fuse is not serviceable; a new airbag module must be installed after the short to ground has been located and repaired.
The air bag diagnostic monitor contains an internal thermal fuse that is not serviceable. The thermal fuse is controlled by a computer inside the air bag diagnostic monitor. The computer will blow the thermal fuse whenever a short on the deployment circuits occurs. The thermal fuse does not blow because of excessive current flowing through it. Do not attempt to jumper out the thermal fuse with a circuit breaker or any other type of fuse. Do not install a new air bag diagnostic monitor until the short has been located and corrected. If a short to ground has not been located and corrected, then the short to ground is intermittent and is not present at this time. Installing a new air bag diagnostic monitor with an intermittent short in the system will result in blown air bag diagnostic monitors and repeat repairs.
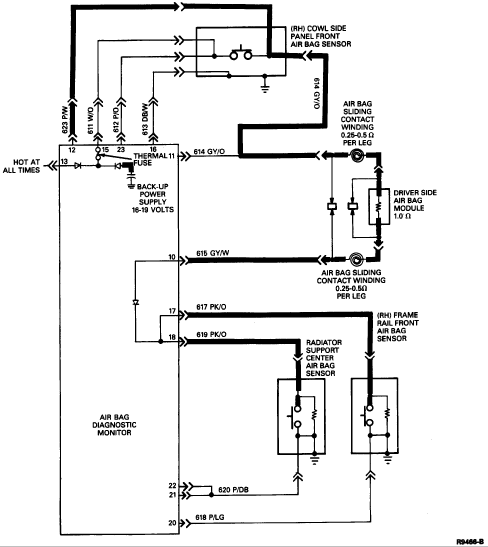
The air bag diagnostic monitor measures the voltages at the diagnostic monitor connector pins. When certain air bag deployment wires are shorted to ground (heavy lines illustrated in the schematic below), the system may become susceptible to unwanted deployment of the air bag(s). The air bag diagnostic monitor senses a short to ground on any of these circuits and helps prevent unwanted air bag deployment by blowing the diagnostic monitor thermal fuse.
Blowing this fuse removes all power (battery and backup power) from the air bag deployment circuits. While the short to ground exists, the air bag diagnostic monitor will flash code 13. If the short to ground is intermittent and temporarily corrects itself, the air bag diagnostic monitor will flash code 51. If the air bag indicator is flashing code 51 and a short to ground has not been serviced, this means that an intermittent short to ground exists in the supplemental air bag restraint system.
The air bag diagnostic monitor should be replaced only after repairs to the intermittent short have been completed. When trying to find an intermittent short to ground, inspect wiring and harnesses in areas where they pass through or are located next to metal components (i.
e. , engine compartment bulkhead, body sheet metal, component mounting brackets, etc). Occasionally, immediately after an air bag deploys, the internal wiring of the driver side air bag module may become shorted to the metal housings of the driver side air bag module. This internal short is detected by the air bag diagnostic monitor as short to ground in the air bag deployment wiring.
Since the air bag diagnostic monitor is still operating immediately after most deployments, the air bag diagnostic monitor will detect the shorted wiring and will flash code 13 and blow the internal thermal fuse. After the deployment, as the air bag cools off, the internal shorted wiring may correct itself, therefore the short to ground will no longer exist and the air bag diagnostic monitor will flash code 51.
If a vehicle with a deployed air bag is flashing code 51, inspect and replace all the damaged areas of the vehicle with crushed wiring, sensors, etc. If no damage is found assume that the deployed air bag was the cause for the intermittent short and replace the air bag diagnostic monitor when the new d
🔗 External reference
The airbag diagnostic system in the 1994 Ford F150 employs a sophisticated mechanism to ensure safety through intelligent fault detection. The airbag control module's internal thermal fuse serves as a critical component in this system, designed to protect against inadvertent airbag deployment due to electrical faults. When a short circuit occurs in the airbag deployment wiring, the diagnostic monitor's computer detects this anomaly and activates the thermal fuse, thereby interrupting power to the airbag circuits. This design prevents potential injuries that could arise from accidental deployments during fault conditions.
The flashing diagnostic codes serve as a communication tool to indicate specific issues within the system. Code 13 signifies an active short to ground, while code 51 indicates that an intermittent short has been detected. This distinction is crucial for technicians in diagnosing and repairing airbag system faults effectively. The identification of intermittent shorts requires careful inspection of wiring, especially in areas prone to wear or damage, such as those adjacent to metal components or subject to mechanical stress.
In practice, the troubleshooting process involves a systematic approach to locating the source of the short. Technicians should begin by examining the integrity of wiring harnesses and connections, particularly in high-stress areas, and testing for continuity and insulation resistance. Any signs of abrasion, corrosion, or physical damage should be addressed promptly to restore the system's reliability.
After resolving any identified shorts, the airbag diagnostic monitor can be replaced, ensuring that the system is fully operational and compliant with safety standards. It is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines during repairs to maintain the integrity of the airbag system and prevent future faults. In summary, understanding the diagnostic codes and the underlying mechanisms of the airbag system is vital for effective troubleshooting and ensuring the safety of vehicle occupants.An flashing airbag diagnostic code of 51 flashing on a 1994 Ford F150, and I need to understand what this could mean. The probem started about one month ago. I also had a leaky windsheild, so I am also wonder if that could affect the airbag module as well. The code you have indicates that the internal fuse in the airbag control module has been blown; this happens automatically when a short to ground
occurs in one of the airbag circuits in the vehicle. This is a safety feature designed to rprevent injuries due to accidental deployment of the airbag due to an electrical fault; the module blows the fuse intentionally to disable the system. the fuse is not serviceable; a new airbag module must be installed after the short to ground has been located and repaired.
The air bag diagnostic monitor contains an internal thermal fuse that is not serviceable. The thermal fuse is controlled by a computer inside the air bag diagnostic monitor. The computer will blow the thermal fuse whenever a short on the deployment circuits occurs. The thermal fuse does not blow because of excessive current flowing through it. Do not attempt to jumper out the thermal fuse with a circuit breaker or any other type of fuse. Do not install a new air bag diagnostic monitor until the short has been located and corrected. If a short to ground has not been located and corrected, then the short to ground is intermittent and is not present at this time. Installing a new air bag diagnostic monitor with an intermittent short in the system will result in blown air bag diagnostic monitors and repeat repairs.
The air bag diagnostic monitor measures the voltages at the diagnostic monitor connector pins. When certain air bag deployment wires are shorted to ground (heavy lines illustrated in the schematic below), the system may become susceptible to unwanted deployment of the air bag(s). The air bag diagnostic monitor senses a short to ground on any of these circuits and helps prevent unwanted air bag deployment by blowing the diagnostic monitor thermal fuse.
Blowing this fuse removes all power (battery and backup power) from the air bag deployment circuits. While the short to ground exists, the air bag diagnostic monitor will flash code 13. If the short to ground is intermittent and temporarily corrects itself, the air bag diagnostic monitor will flash code 51. If the air bag indicator is flashing code 51 and a short to ground has not been serviced, this means that an intermittent short to ground exists in the supplemental air bag restraint system.
The air bag diagnostic monitor should be replaced only after repairs to the intermittent short have been completed. When trying to find an intermittent short to ground, inspect wiring and harnesses in areas where they pass through or are located next to metal components (i.
e. , engine compartment bulkhead, body sheet metal, component mounting brackets, etc). Occasionally, immediately after an air bag deploys, the internal wiring of the driver side air bag module may become shorted to the metal housings of the driver side air bag module. This internal short is detected by the air bag diagnostic monitor as short to ground in the air bag deployment wiring.
Since the air bag diagnostic monitor is still operating immediately after most deployments, the air bag diagnostic monitor will detect the shorted wiring and will flash code 13 and blow the internal thermal fuse. After the deployment, as the air bag cools off, the internal shorted wiring may correct itself, therefore the short to ground will no longer exist and the air bag diagnostic monitor will flash code 51.
If a vehicle with a deployed air bag is flashing code 51, inspect and replace all the damaged areas of the vehicle with crushed wiring, sensors, etc. If no damage is found assume that the deployed air bag was the cause for the intermittent short and replace the air bag diagnostic monitor when the new d
🔗 External reference