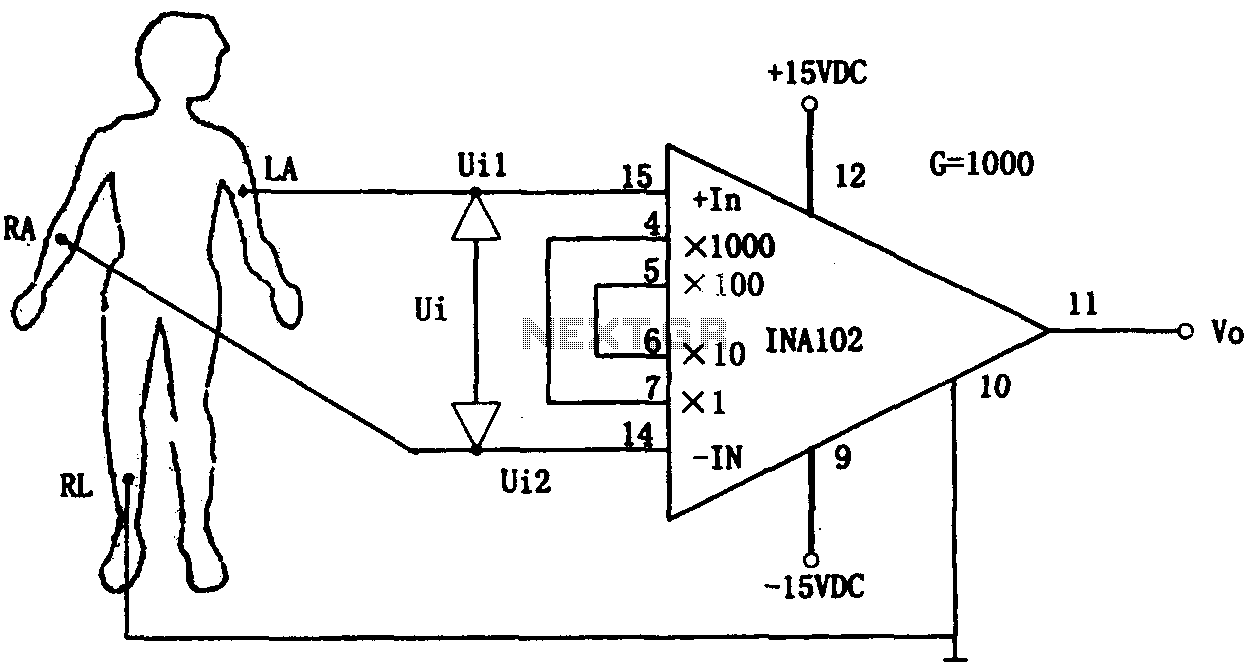
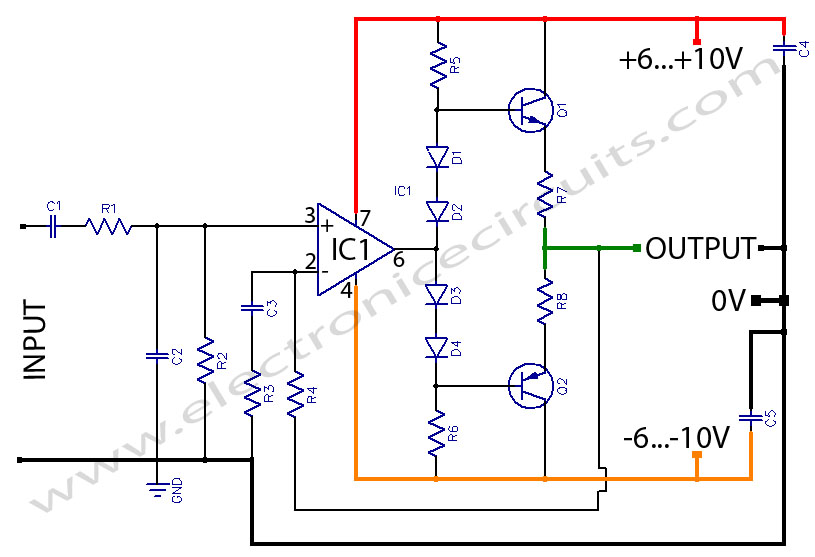
amp design

ESP - The Audio Pages. Amplifier design techniques, find out how amplifiers work, and how to design them.
Amplifiers are critical components in audio systems, serving to increase the amplitude of audio signals to drive speakers or other output devices. The design of an amplifier involves understanding various key parameters, including gain, bandwidth, and distortion characteristics.
Amplifier design techniques can be categorized into different classes, such as Class A, Class B, Class AB, and Class D, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages in terms of efficiency, linearity, and thermal performance. For instance, Class A amplifiers provide high linearity and low distortion but are less efficient, while Class D amplifiers are highly efficient and suitable for battery-powered applications.
To design an effective amplifier, one must consider the selection of active devices, such as bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or field-effect transistors (FETs), and passive components, including resistors and capacitors, which influence the frequency response and stability of the amplifier. Furthermore, feedback mechanisms are often employed to enhance performance and reduce distortion.
Practical design also involves simulating the circuit using software tools to predict performance before physical implementation. This allows for optimization of component values and circuit topology to achieve desired specifications.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of amplifier operation and design principles is essential for creating effective audio amplification solutions, whether for consumer electronics, professional audio equipment, or custom audio projects.ESP - The Audio Pages. Amplifier design techniques, find out how amplifiers work, and how to design them.. 🔗 External reference
Amplifiers are critical components in audio systems, serving to increase the amplitude of audio signals to drive speakers or other output devices. The design of an amplifier involves understanding various key parameters, including gain, bandwidth, and distortion characteristics.
Amplifier design techniques can be categorized into different classes, such as Class A, Class B, Class AB, and Class D, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages in terms of efficiency, linearity, and thermal performance. For instance, Class A amplifiers provide high linearity and low distortion but are less efficient, while Class D amplifiers are highly efficient and suitable for battery-powered applications.
To design an effective amplifier, one must consider the selection of active devices, such as bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or field-effect transistors (FETs), and passive components, including resistors and capacitors, which influence the frequency response and stability of the amplifier. Furthermore, feedback mechanisms are often employed to enhance performance and reduce distortion.
Practical design also involves simulating the circuit using software tools to predict performance before physical implementation. This allows for optimization of component values and circuit topology to achieve desired specifications.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of amplifier operation and design principles is essential for creating effective audio amplification solutions, whether for consumer electronics, professional audio equipment, or custom audio projects.ESP - The Audio Pages. Amplifier design techniques, find out how amplifiers work, and how to design them.. 🔗 External reference