Arduino UNO
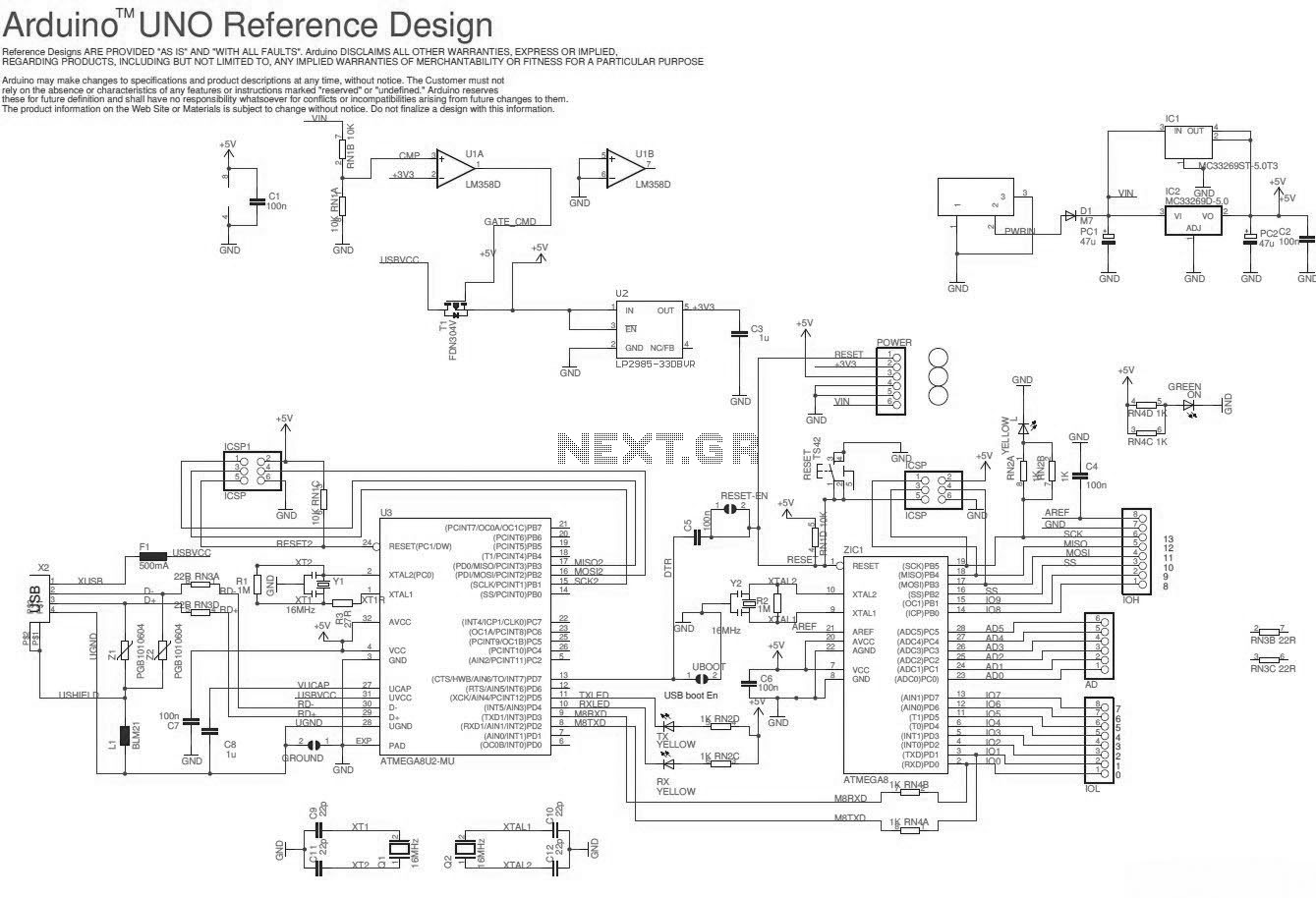
The Arduino Uno schematic diagram is available for viewing. The Arduino Uno is a microcontroller board that utilizes the ATmega328 chip. It features 14 digital input/output pins, of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs, and 6 analog input pins.
The Arduino Uno is an essential platform for electronics prototyping and development. The ATmega328 microcontroller at its core operates at a clock speed of 16 MHz and provides a robust environment for executing various programs. The board is equipped with 14 digital I/O pins, allowing for versatile interfacing with other electronic components. Among these, 6 pins are capable of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), which is particularly useful for applications requiring variable signal outputs, such as controlling the brightness of LEDs or the speed of motors.
Additionally, the Arduino Uno contains 6 analog input pins that can read varying voltage levels from sensors, enabling the board to interpret real-world signals. The board is powered via a USB connection or an external power supply, which can provide voltages between 7 to 12 volts. The onboard voltage regulator ensures that the microcontroller and connected components receive a stable 5V supply.
The schematic diagram of the Arduino Uno includes details about the power supply, pin configurations, and connections to critical components such as the crystal oscillator, reset button, and the USB interface. Understanding the schematic is crucial for anyone looking to modify the board or integrate it into larger systems, as it provides insight into the electrical pathways and component interactions. The simplicity and versatility of the Arduino Uno make it a favored choice among hobbyists and professionals alike for developing and testing electronic projects.Here the Arduino UNO schematic diagram (click to enlarge): About Arduino UNO: The Arduino Uno is really a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328. It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 may be employed as PWM outputs), 6 analo.. 🔗 External reference
The Arduino Uno is an essential platform for electronics prototyping and development. The ATmega328 microcontroller at its core operates at a clock speed of 16 MHz and provides a robust environment for executing various programs. The board is equipped with 14 digital I/O pins, allowing for versatile interfacing with other electronic components. Among these, 6 pins are capable of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), which is particularly useful for applications requiring variable signal outputs, such as controlling the brightness of LEDs or the speed of motors.
Additionally, the Arduino Uno contains 6 analog input pins that can read varying voltage levels from sensors, enabling the board to interpret real-world signals. The board is powered via a USB connection or an external power supply, which can provide voltages between 7 to 12 volts. The onboard voltage regulator ensures that the microcontroller and connected components receive a stable 5V supply.
The schematic diagram of the Arduino Uno includes details about the power supply, pin configurations, and connections to critical components such as the crystal oscillator, reset button, and the USB interface. Understanding the schematic is crucial for anyone looking to modify the board or integrate it into larger systems, as it provides insight into the electrical pathways and component interactions. The simplicity and versatility of the Arduino Uno make it a favored choice among hobbyists and professionals alike for developing and testing electronic projects.Here the Arduino UNO schematic diagram (click to enlarge): About Arduino UNO: The Arduino Uno is really a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328. It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 may be employed as PWM outputs), 6 analo.. 🔗 External reference