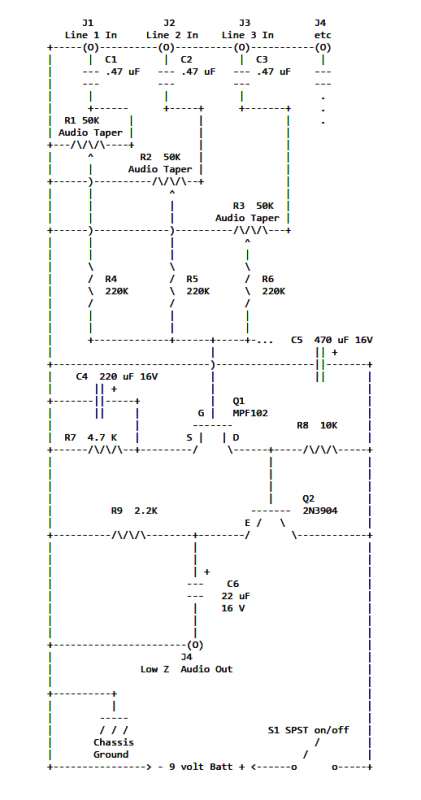
Audio Auto Fade circuit
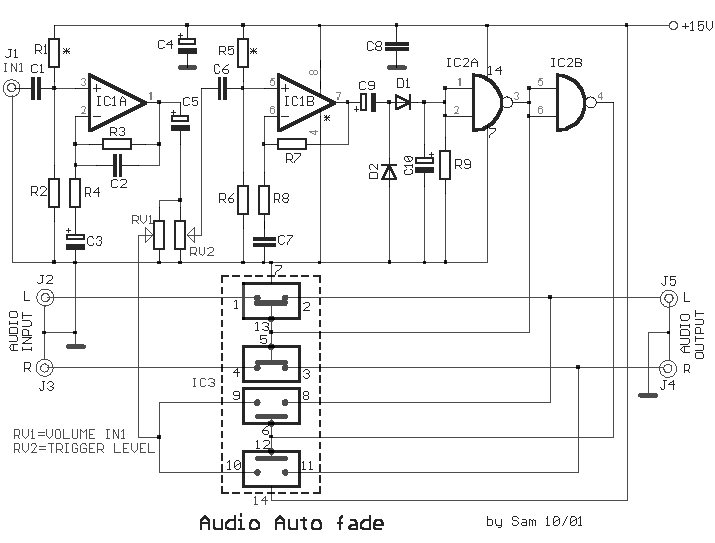
This circuit is designed to allow voice clarity over music playback. It is particularly useful for DJs, small radio stations, announcements over music in shops, and similar applications. Additionally, it can be utilized in scenarios where voice control is required for various devices. The circuit is compatible with stereo music and monophonic microphones, but it can be modified and adapted to meet specific needs or applications.
The circuit is primarily based on a voice-activated mixing system that integrates a microphone input with a music source. The core component of this design is a mixer circuit that allows for the adjustment of audio levels between the voice and the music. Typically, an operational amplifier (op-amp) is employed to amplify the microphone signal while simultaneously allowing the music signal to pass through with minimal attenuation.
The circuit may include a low-pass filter to ensure that the music does not interfere with the clarity of the voice. This filter helps to eliminate high-frequency noise that could mask the vocal signal. Furthermore, a compressor may be integrated into the design to dynamically adjust the voice level, ensuring that it remains prominent even when the music volume fluctuates.
For practical implementation, the circuit can be powered by a standard DC power supply, and it may feature a user-friendly interface consisting of volume knobs for both the microphone and the music source. Additionally, LED indicators can be included to provide visual feedback of the circuit's operation.
In applications where voice control is necessary, the circuit can be modified to include a relay or a microcontroller that responds to specific voice commands, allowing the user to control external devices or systems seamlessly. This flexibility makes the circuit suitable for a variety of environments, from entertainment venues to retail spaces, enhancing the overall audio experience.This circuit is design, in order to is heard the voice above the music. Useful for DJ, for small radio stations, for statements above the music, in shops etc. Also we can him use in applications that we want to handle some unit with our voice. As it has the circuit has become forecast for stereo music and monophonic microphone, but can be modified and be adapted in the needs or in the use that we want, him we use.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is primarily based on a voice-activated mixing system that integrates a microphone input with a music source. The core component of this design is a mixer circuit that allows for the adjustment of audio levels between the voice and the music. Typically, an operational amplifier (op-amp) is employed to amplify the microphone signal while simultaneously allowing the music signal to pass through with minimal attenuation.
The circuit may include a low-pass filter to ensure that the music does not interfere with the clarity of the voice. This filter helps to eliminate high-frequency noise that could mask the vocal signal. Furthermore, a compressor may be integrated into the design to dynamically adjust the voice level, ensuring that it remains prominent even when the music volume fluctuates.
For practical implementation, the circuit can be powered by a standard DC power supply, and it may feature a user-friendly interface consisting of volume knobs for both the microphone and the music source. Additionally, LED indicators can be included to provide visual feedback of the circuit's operation.
In applications where voice control is necessary, the circuit can be modified to include a relay or a microcontroller that responds to specific voice commands, allowing the user to control external devices or systems seamlessly. This flexibility makes the circuit suitable for a variety of environments, from entertainment venues to retail spaces, enhancing the overall audio experience.This circuit is design, in order to is heard the voice above the music. Useful for DJ, for small radio stations, for statements above the music, in shops etc. Also we can him use in applications that we want to handle some unit with our voice. As it has the circuit has become forecast for stereo music and monophonic microphone, but can be modified and be adapted in the needs or in the use that we want, him we use.. 🔗 External reference