Audio Gambar Skema Condenser Microphone Amplifier
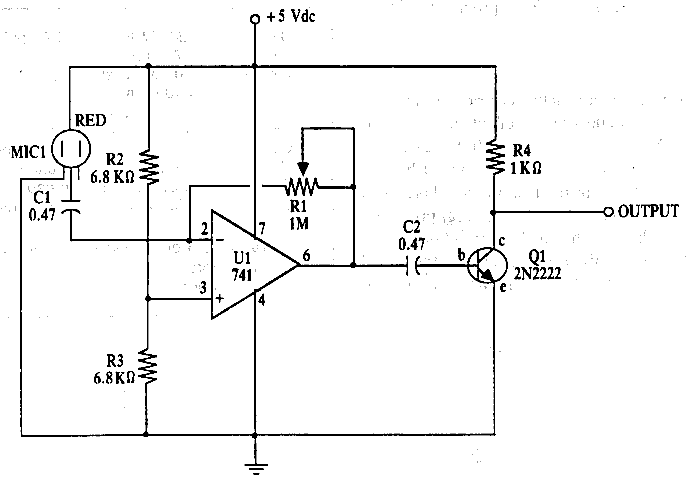
The amplifier features an adjustable gain, facilitated by R1, a 1 Mega Ohm variable resistor. This resistor regulates the feedback of the 741 operational amplifier (op-amp), which subsequently drives a 2N2222 output transistor. The circuit receives an audio signal from a condenser microphone and amplifies it, enabling the microphone to serve as an input to devices that typically do not accept microphone-level signals, which are inherently low.
The described circuit employs a 741 operational amplifier due to its favorable characteristics for audio applications, including low noise and high input impedance. The variable resistor R1 allows for fine-tuning of the gain, making it possible to adapt the amplification level according to the requirements of the connected device. By adjusting R1, the feedback loop of the op-amp can be modified, which directly influences the overall gain of the amplifier.
The output stage of the circuit utilizes a 2N2222 transistor, a widely used NPN transistor known for its reliability and efficiency in switching and amplification applications. The transistor amplifies the output from the op-amp, providing sufficient current to drive devices that require higher signal levels than the microphone can provide.
The circuit is designed to interface with a condenser microphone, which typically outputs a very low-level audio signal. By amplifying this signal, the circuit allows the microphone to be connected to devices such as mixers, amplifiers, or recording equipment that may not be capable of processing such low-level signals. Careful consideration should be given to the power supply requirements of the op-amp and transistor to ensure stable operation, as well as the overall impedance matching to avoid signal loss. Proper bypass capacitors may also be included in the design to filter out noise and ensure clean signal transmission.The amplifier has an adjustable gain, which is performed by. R1 (a 1 Mega Ohm variable resistor). It controls the feedback of the 741 opamp, which in turn drive a 2N2222 output transistor. The circuit takes the audio signal rom the condenser microphone & amplifier it, so you are able to use the microphone as the input to some device which wouldn`t normally accept microphone level signals (which are very low). 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a 741 operational amplifier due to its favorable characteristics for audio applications, including low noise and high input impedance. The variable resistor R1 allows for fine-tuning of the gain, making it possible to adapt the amplification level according to the requirements of the connected device. By adjusting R1, the feedback loop of the op-amp can be modified, which directly influences the overall gain of the amplifier.
The output stage of the circuit utilizes a 2N2222 transistor, a widely used NPN transistor known for its reliability and efficiency in switching and amplification applications. The transistor amplifies the output from the op-amp, providing sufficient current to drive devices that require higher signal levels than the microphone can provide.
The circuit is designed to interface with a condenser microphone, which typically outputs a very low-level audio signal. By amplifying this signal, the circuit allows the microphone to be connected to devices such as mixers, amplifiers, or recording equipment that may not be capable of processing such low-level signals. Careful consideration should be given to the power supply requirements of the op-amp and transistor to ensure stable operation, as well as the overall impedance matching to avoid signal loss. Proper bypass capacitors may also be included in the design to filter out noise and ensure clean signal transmission.The amplifier has an adjustable gain, which is performed by. R1 (a 1 Mega Ohm variable resistor). It controls the feedback of the 741 opamp, which in turn drive a 2N2222 output transistor. The circuit takes the audio signal rom the condenser microphone & amplifier it, so you are able to use the microphone as the input to some device which wouldn`t normally accept microphone level signals (which are very low). 🔗 External reference